Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3895003"
(→Modeling) |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K3895003 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K3895003 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | KerAVDZ50 is an extracellular serine thiol alkaline protease from ''Actinomadura viridilutea'' strain, which can be isolated from Algerian fishing port [1]. As a thermo-alkaline keratinases, it can function at a pH range of 7–12 and a temperature range of 35–80 °C. | + | KerAVDZ50 is an extracellular serine thiol alkaline protease from the ''Actinomadura viridilutea'' strain, which can be isolated from the Algerian fishing port [1]. As a thermo-alkaline keratinases, it can function at a pH range of 7–12 and a temperature range of 35–80 °C. |
| + | |||
| + | 6x His-tags were added to both sides of the sequence for purification. | ||
===Modeling=== | ===Modeling=== | ||
Revision as of 15:27, 10 October 2021
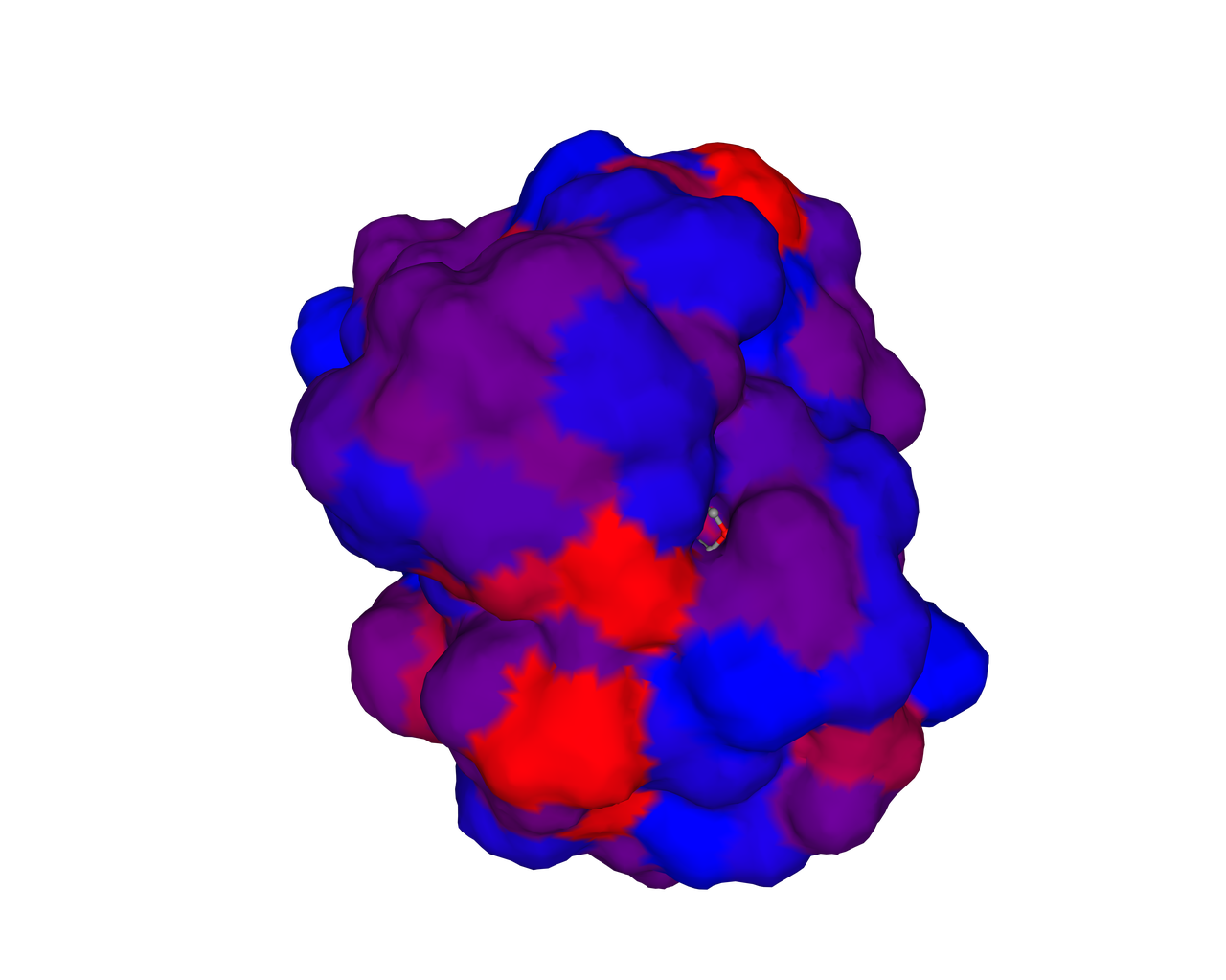
Keratinase kerAvDZ50
KerAVDZ50 is an extracellular serine thiol alkaline protease from the Actinomadura viridilutea strain, which can be isolated from the Algerian fishing port [1]. As a thermo-alkaline keratinases, it can function at a pH range of 7–12 and a temperature range of 35–80 °C.
6x His-tags were added to both sides of the sequence for purification.
Modeling
Sequence and Features
Assembly Compatibility:
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 577
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 382
Illegal AgeI site found at 1120 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 322
Reference
Biochemical and molecular characterization of new keratinoytic protease from Actinomadura viridilutea DZ50. (n.d.). International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 92, 299–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.07.009