Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3136004"
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
Our new part is used to detect the presence of Listeria monocytogenes, which is easily survival in low temperature like refrigerator environment,and then cause Listeriosis illness, like fever, muscle ache, and so on. | Our new part is used to detect the presence of Listeria monocytogenes, which is easily survival in low temperature like refrigerator environment,and then cause Listeriosis illness, like fever, muscle ache, and so on. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Engineering Success=== | ===Engineering Success=== | ||
Revision as of 21:00, 27 October 2020
FnCas12a-typeIIS
It is a conding sequence of CRISPR-Cas12a from Francisella novicida U112. The sequence is coden optimized.
Improvement by SHSID 2020
Sequence Analysis We blast the sequences of our new part BBa_K3521001 and the existing part BBa_K3136004. As shown in the figure, there is 2852bp inconsistent good, 1058bp inconsistent bad from the old one part.
Different Function First of all, we aim to detect different organisms for different illnesses. The old part is used to detect the African Swine fever virus (ASFV). Our new part is used to detect the presence of Listeria monocytogenes, which is easily survival in low temperature like refrigerator environment, and then cause Listeriosis illness, like fever, muscle ache, and so on.
Furthermore, the old part only designed a crRNA that just targeting a site of ASFV, which may have less wide application. In contrast, we design six different crRNAs that can guide our improved Cas12a (FnCpf1) protein targeting six different genomic sites of Listeria monocytogenes, so that our new part can detect more extensive Listeria monocytogenes.
Biology and Contribution
Our new part is used to detect the presence of Listeria monocytogenes, which is easily survival in low temperature like refrigerator environment,and then cause Listeriosis illness, like fever, muscle ache, and so on.
Engineering Success
The FnCpf1 (BBa_K3521001) was designed to function as the core part in constructing a reaction system consisting of recombinant FnCpf1, crRNA, and ssDNA, aiming at detecting Listeria monocytogenes.
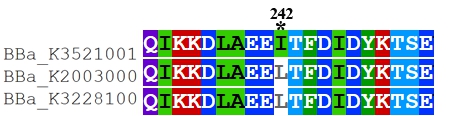
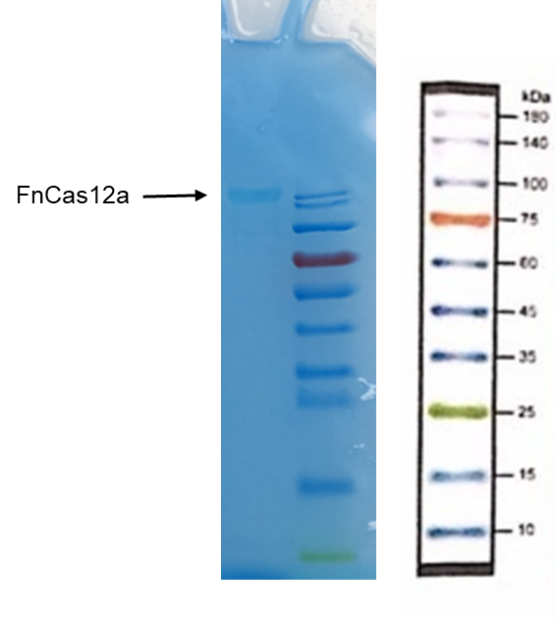
Recombinant FnCpf1 production, purification, and SDS-PAGE analysis. To date, two FnCpf1 related parts (BBa_K2003000 and BBa_K3228100) were registered in the part system. The nucleotide sequences of BBa_K3521001 is different from that of BBa_K2003000 and BBa_K3228100 (Figure 1). The amino acid sequences of the three FnCpf1 are almost identical except for a single amino acid variant at residue 242 (isoleucine in BBa_K3521001 and leucine in BBa_K2003000 and BBa_K3228100) (Figure 2).
In combination with T7 promoter, single RNA-guided endonuclease FnCpf1, and polyhistidine tag, the FnCpf1 BBa_K3521001 was used to construct a composite part BBa_K3521005 to detect Listeria monocytogenes. The N-terminal His tag was used to Ni-affinity purification of FnCpf1.
Following are the results of functional tests of our reaction system: The reaction system was incubated at 37℃ for 10 minutes then the value of fluorescence intensity was measured by microplate reader. The model number of our microplate reader is MD Spectra Max i3x with emission wavelength at 522nm and absorbing wavelength at 494nm.
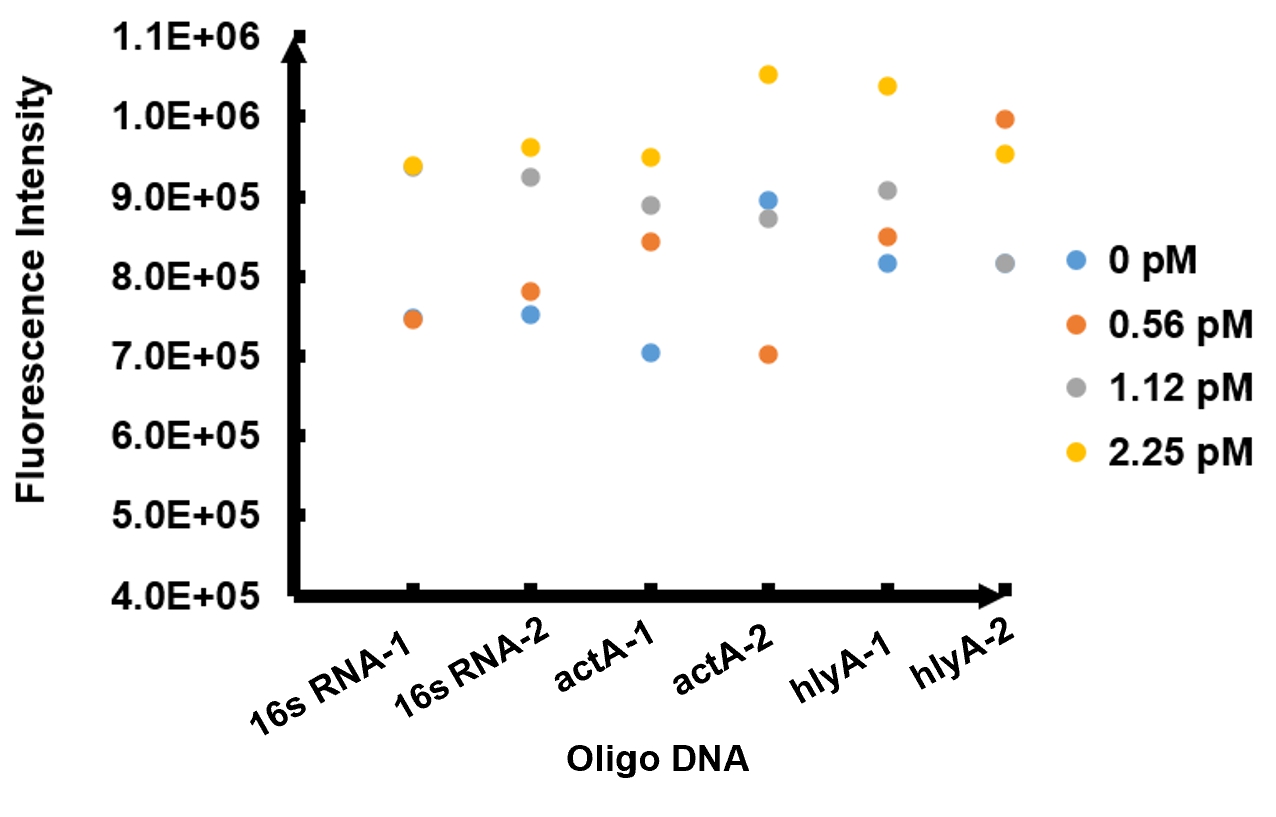
The results of fluorescence intensity for all the six oligo sequences which simulated Listeria monocytogenes. are shown in Figure 3. The oligo DNA 16s RNA-2, actA-1 and hylA-1 are the only ones show distinct fluorescence intensity at different concentrations. At the same time, they show a ubiquitous rising trend of fluorescence intensity with an increasing concentration, which is consistent with logic. Therefore, we choose to give a more detailed and specific analysis to these three groups. The results of our further analysis are presented in Figures 4 - 6.
The fluorescence intensity all display an increasing trend when the concentration of oligo DNA increases in Figures 4 - 6. The system can detect the oligo sequence at a concentration as low as 0.56 pM.
As shown in Figure 4, when 16s RNA-2 is used as the oligo sequence, the fluorescence intensity is positively related to oligo concentrations. When the concentration of oligo DNA increases from 0.56 pM to 2.25 pM, the fluorescence intensity increases drastically from 7.82x105 to 9.61 x105.
Figure 5 demonstrates the increasing trend of fluorescence intensity according to an increase in the concentration of actA-1. The trend follows a generally linear line with intensity being 8.90 x 105 at a concentration of 1.12 pM and 9.48 x 105 at 2.25 pM.
In figure 6, the data points of the graph resemble a linear progression. The fluorescence intensity is 8.46 x 105 when the concentration of oligo DNA is 0.56 pM, the lowest concentration we tested. The fluorescence intensity is the highest corresponding to the lowest concentration of oligo DNA among all three samples. After this, the fluorescence intensity is 9.08 x 105 and1.04 x 106 when the concentration of hlyA-1 is 1.12 pM and 2.25 pM. At both low and high concentrations, its fluorescence intensity can be used to compare the concentrations of Listeria monocytogenes oligo DNA using the FnCpf1 system. The fluorescence intensity difference between different oligo DNAs demonstrates the highest efficiency for hylA-1 detection among all three samples.
The experiment results above provided us with the evidence that our detection system of Listeria monocytogenes functions as expected.
Usage and Biology
BBa_K3136004 FnCas12a-typeIIS
Methods:
1. Put the EP tube containing purified FnCas12a protein at 99℃ water for 15 minutes.
2. After heating, centrifuge the tubes for 5min.
3. Take and install the gel, add the electrophoresis buffer to the sample hole, and check if there is any leakage. Add marker, to the first and last sample holes, add FnCas12a to the other sample holes, respectively.
7. Connect the electrophoresis device to the power supply. Connect the positive electrode to the tank and the negative electrode to the slot for electrophoresis. The voltage is adjusted to 160V.
8. Turn off the power supply and disconnect the electrode until the bromophenol blue reaches the bottom of the release adhesive. Remove the glass sheet from the electrophoresis device and then remove the gel.
9. Soak the gel in Coomassie brilliant blue dye and dye it in a horizontal shaking bed for 15 min.
Observe the protein bands
Cas12a detection method:
Materials:
Water. 14.5 μL
Buffer. 2 μL
Enzyme (Cas12a). 0.5 μL
Template. 0.5 μL
(From solution we made after LAMP)
Detector. 2 μL
crRNA. 0.5 μL
(Note: the Deteror is sequence of ssDNA HEX-N12-BHQ1 or FAM-N12-BHQ1 or FITC-T14-Biotin)
Procedure:
1. Add all the materials together:
• Firstly, use pipette to straw 14.5 μL pure water from the pure water bottle to one tube.
• Secondly, use pipette to straw 2 μL buffer to the previous tube.
• Thirdly, use pipette to straw 0.5 μL enzyme to the previous tube.
• Next, use pipette to straw 0.5 μL template to the previous tube.
• Then, add 0.5 μL crRNA to the previous tube.
• Finally, use pipette to straw 2 μL detector to the previous tube.
2. Straw 1 μL of the mixed solution in the tubes to the 96-well Plate.
3. Detect the solution using fluorescent detector machine to check the fluorescence when they react 10min.
Results:
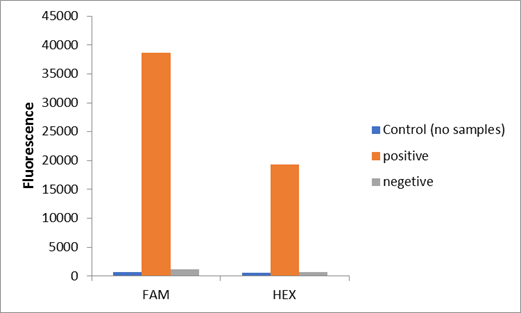
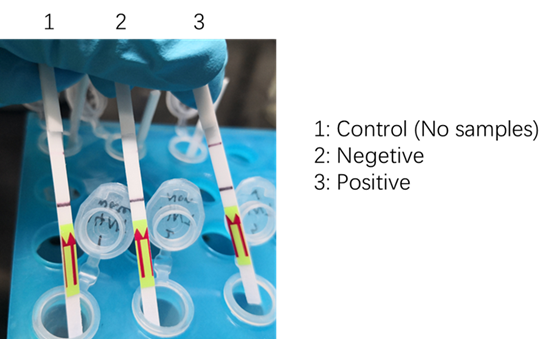
We used two types of fluorescent probe (FAM and HEX) to check the fluorescence of FnCas12a reaction system at 10min as shown in Fig1. Linked to the control and negative samples, the positive sample has a high fluorescence. It means that FnCas12a slices the fluorescent probe in the reaction system and the cracked fluorescent probe produce fluorescence. we also checked the fluorescence of FnCas12a reaction system at 10min by lateral flow using briDetect (Milenia Biotec GmbH) (Fig2).
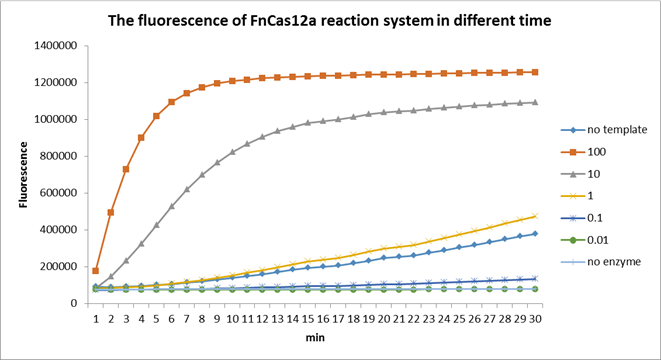
Using fluorescent detector machine, we can detect the fluorescence of FnCas12a reaction system at different time by setting up program properly in the machine. We detect the fluorescence under different concentration FnCas12a and different time(Fig3). With the time growth, the fluorescence gradually raised until a certain time. Higher concentration FnCas12a had higher fluorescence and the fluorescence increased quickly.
Reference
Li S Y, Cheng Q X, Liu J K, et al. CRISPR-Cas12a has both cis-and trans-cleavage activities on single-stranded DNA[J]. Cell research, 2018, 28(4): 491.
Sequence and Features
- 10INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]Illegal PstI site found at 310
Illegal PstI site found at 364
Illegal PstI site found at 1627
Illegal PstI site found at 2533
Illegal PstI site found at 3727 - 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal PstI site found at 310
Illegal PstI site found at 364
Illegal PstI site found at 1627
Illegal PstI site found at 2533
Illegal PstI site found at 3727 - 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 1253
Illegal BglII site found at 1586
Illegal BglII site found at 1706
Illegal BglII site found at 2000
Illegal BglII site found at 2444
Illegal BglII site found at 3335
Illegal BglII site found at 3425 - 23INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]Illegal PstI site found at 310
Illegal PstI site found at 364
Illegal PstI site found at 1627
Illegal PstI site found at 2533
Illegal PstI site found at 3727 - 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal PstI site found at 310
Illegal PstI site found at 364
Illegal PstI site found at 1627
Illegal PstI site found at 2533
Illegal PstI site found at 3727
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 2480
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 3319
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 3530 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]