Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3521001"
(→Engineering Success) |
|||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
The fluorescence intensity all display an increasing trend when the concentration of oligo DNA increases in Figures 4 - 6. The system can detect the oligo sequence at a concentration as low as 0.56 pM. | The fluorescence intensity all display an increasing trend when the concentration of oligo DNA increases in Figures 4 - 6. The system can detect the oligo sequence at a concentration as low as 0.56 pM. | ||
[[File:T--SHSID-BBa_K3521005 Fig 3.jpg|400px|thumb|center|Figure 4 The fluorescence intensity corresponding to four different concentrations of 16s RNA-2 oligo DNA]] | [[File:T--SHSID-BBa_K3521005 Fig 3.jpg|400px|thumb|center|Figure 4 The fluorescence intensity corresponding to four different concentrations of 16s RNA-2 oligo DNA]] | ||
| + | As shown in Figure 5, when 16s RNA-2 is used as the oligo sequence, the fluorescence intensity is positively related to oligo concentrations. When the concentration of oligo DNA increases from 0.56 pM to 2.25 pM, the fluorescence intensity increases drastically from 7.82x105 to 9.61 x105. | ||
| + | [[File:T--SHSID-BBa_K3521005 Fig 3.jpg|400px|thumb|center|Figure 5. The fluorescence intensity corresponding to four different concentrations of actA-1 oligo DNA.]] | ||
| + | Figure 6 demonstrates the increasing trend of fluorescence intensity according to an increase in the concentration of actA-1. The trend follows a generally linear line with intensity being 8.90 x 105 at a concentration of 1.12 pM and 9.48 x 105 at 2.25 pM. | ||
Revision as of 09:16, 26 October 2020
FnCpf1
CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) systems are adaptive immune systems widely distributed across bacteria and archaea, designed to destroy DNA of invading mobile genetic elements. These immune systems, in which endonucleases are guided by single stranded RNA to find their target DNA, have been turned into powerful genome editing tools over the past few years FnCpf1 is one of class II family of CRISPR-Cas RNA programmable endonucleases with unique functions. In this project, FnCpf1 can mediate RNA-guided DNA cleavage and target single-stranded DNA to produce fluorescence.
Usage and Biology
Our new part is used to detect the presence of Listeria monocytogenes, which is easily survival in low temperature like refrigerator environment,and then cause Listeriosis illness, like fever, muscle ache, and so on.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 1717
Illegal NheI site found at 3437 - 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal XhoI site found at 3498
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Engineering Success
The FnCpf1 (BBa_K3521001) was designed to function as the core part in constructing a reaction system consisting of recombinant FnCpf1, crRNA, and ssDNA, aiming at detecting Listeria monocytogenes.
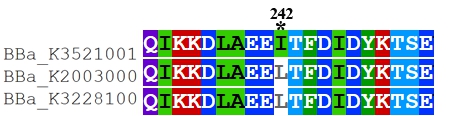
Recombinant FnCpf1 production, purification, and SDS-PAGE analysis. To date, two FnCpf1 related parts (BBa_K2003000 and BBa_K3228100) were registered in the part system. The nucleotide sequences of BBa_K3521001 is different from that of BBa_K2003000 and BBa_K3228100 (Figure 1). The amino acid sequences of the three FnCpf1 are almost identical except for a single amino acid variant at residue 242 (isoleucine in BBa_K3521001 and leucine in BBa_K2003000 and BBa_K3228100) (Figure 2).
In combination with T7 promoter, single RNA-guided endonuclease FnCpf1, and polyhistidine tag, the FnCpf1 BBa_K3521001 was used to construct a composite part BBa_K3521005 to detect Listeria monocytogenes. The N-terminal His tag was used to Ni-affinity purification of FnCpf1.
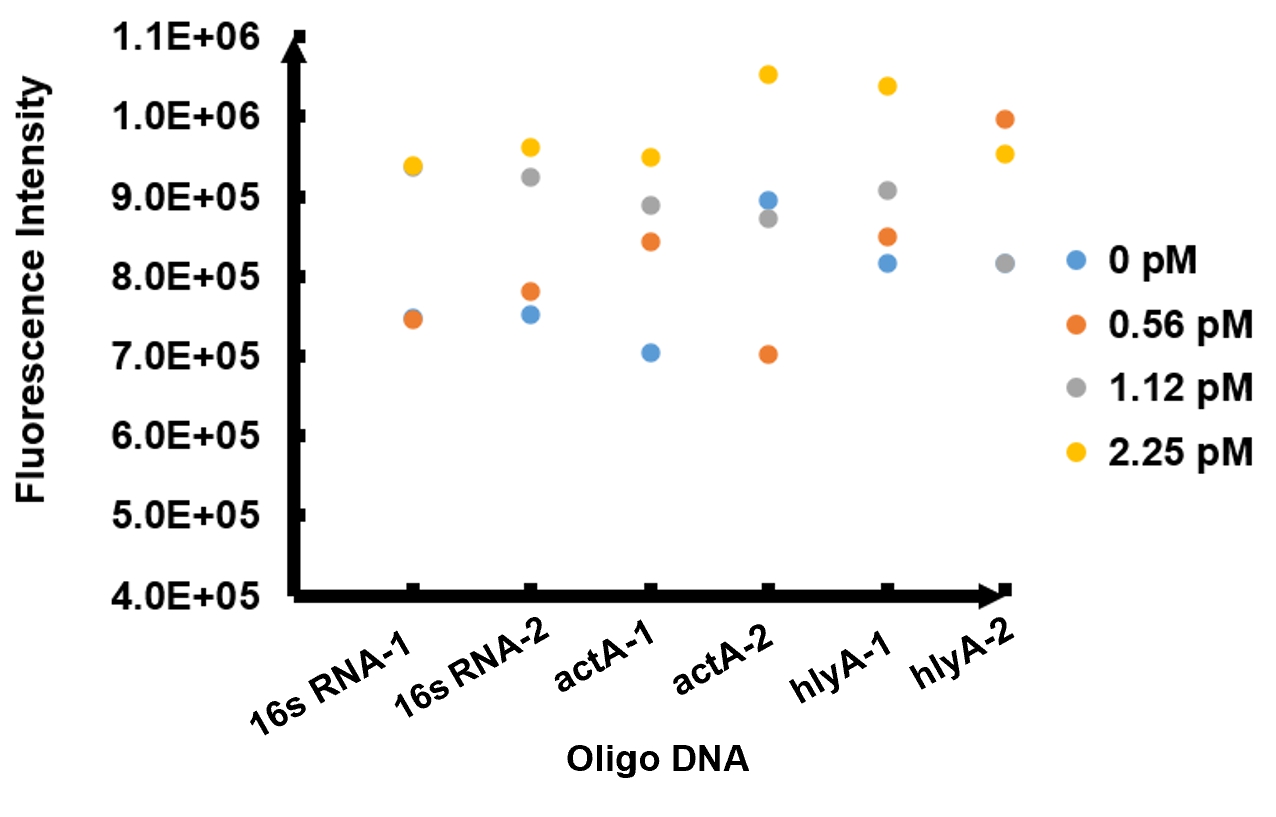
Following are the results of functional tests of our reaction system: The reaction system was incubated at 37℃ for 10 minutes then the value of fluorescence intensity was measured by microplate reader. The model number of our microplate reader is MD Spectra Max i3x with emission wavelength at 522nm and absorbing wavelength at 494nm.
The results of fluorescence intensity for all the six oligo sequences which simulated Listeria monocytogenes. are shown in Figure 3. The oligo DNA 16s RNA-2, actA-1 and hylA-1 are the only ones show distinct fluorescence intensity at different concentrations. At the same time, they show a ubiquitous rising trend of fluorescence intensity with an increasing concentration, which is consistent with logic. Therefore, we choose to give a more detailed and specific analysis to these three groups. The results of our further analysis are presented in Figures 4 - 6.
The fluorescence intensity all display an increasing trend when the concentration of oligo DNA increases in Figures 4 - 6. The system can detect the oligo sequence at a concentration as low as 0.56 pM.
As shown in Figure 5, when 16s RNA-2 is used as the oligo sequence, the fluorescence intensity is positively related to oligo concentrations. When the concentration of oligo DNA increases from 0.56 pM to 2.25 pM, the fluorescence intensity increases drastically from 7.82x105 to 9.61 x105.
Figure 6 demonstrates the increasing trend of fluorescence intensity according to an increase in the concentration of actA-1. The trend follows a generally linear line with intensity being 8.90 x 105 at a concentration of 1.12 pM and 9.48 x 105 at 2.25 pM.