Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K2976005"
(→Characteration) |
|||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
<p>Plasmid (TLR2-P2A-TLR1-T2A-CD14) and plasmid (NF-κB induced promoter-hsa-let-7f pri-miRNA) were co-transfected into HEK293T cells. Then, we utilized Pam3Cys-Ser-(Lys)4, TLR1/TLR2 agonist to stimulate Toll like receptor (TLR) signaling pathway. In our project, the activation of NF-κB can eventually leads to the expression of hsa-let-7f pri-miRNAs, which are eventually cleaved by Drosha, DGCRB and Dicer to form mature miRNAs. The miRNAs are packaged into exosomes and secreted out of cells subsequently. Therefore, we determine the amount of hsa-let-7f in the exosomes by QPCR assay. </p> | <p>Plasmid (TLR2-P2A-TLR1-T2A-CD14) and plasmid (NF-κB induced promoter-hsa-let-7f pri-miRNA) were co-transfected into HEK293T cells. Then, we utilized Pam3Cys-Ser-(Lys)4, TLR1/TLR2 agonist to stimulate Toll like receptor (TLR) signaling pathway. In our project, the activation of NF-κB can eventually leads to the expression of hsa-let-7f pri-miRNAs, which are eventually cleaved by Drosha, DGCRB and Dicer to form mature miRNAs. The miRNAs are packaged into exosomes and secreted out of cells subsequently. Therefore, we determine the amount of hsa-let-7f in the exosomes by QPCR assay. </p> | ||
| − | + | [[File:T--CPU_CHINA--let7f.png|600px|thumb|center|'''Figure 1.'''QPCR assay of hsa-let-7f miRNA expression.]] | |
As shown in Figure 1, hsa-let-7f was successfully expressed in HEK293T cells and packaged into the exosomes. | As shown in Figure 1, hsa-let-7f was successfully expressed in HEK293T cells and packaged into the exosomes. | ||
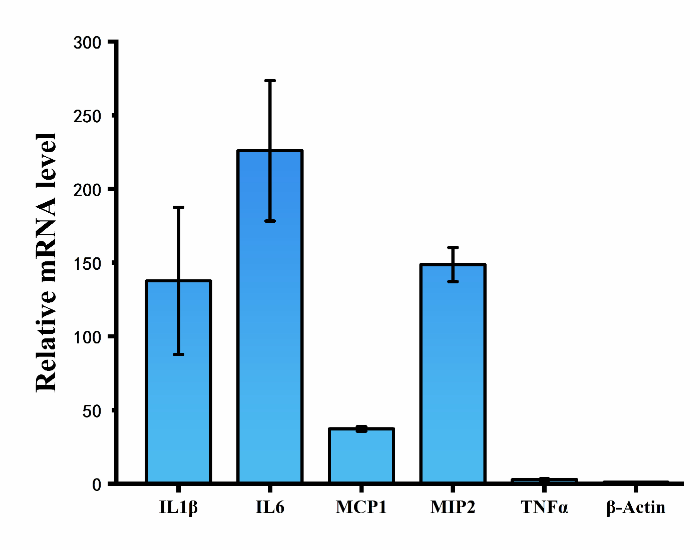
| − | + | [[File:T--CPU_CHINA--shiyan1-3.png|600px|thumb|center|'''Figure 2.'''Relative mRNA level of cytokines (IL-1β, IL6, TNF-α) and chemokines (MCP-1, MIP-2) in RAW264.7 cells.]] | |
<p>Exosomes with or without hsa-let-7f miRNAs were separately incubated with RAW264.7 cells for 48h, and then mRNA level of cytokines (IL-1β, IL6, TNF-α) and chemokines (MCP-1, MIP-2) in RAW264.7 cells were tested by using QPCR assay. The results show that mRNA level of both cytokines and chemokines in cells treated with exosomes containing hsa-let-7f miRNAs increased significantly compared to that of control group.</p> | <p>Exosomes with or without hsa-let-7f miRNAs were separately incubated with RAW264.7 cells for 48h, and then mRNA level of cytokines (IL-1β, IL6, TNF-α) and chemokines (MCP-1, MIP-2) in RAW264.7 cells were tested by using QPCR assay. The results show that mRNA level of both cytokines and chemokines in cells treated with exosomes containing hsa-let-7f miRNAs increased significantly compared to that of control group.</p> | ||
Revision as of 21:23, 21 October 2019
hsa-let-7f pri-miRNA
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a group of non-coding RNA molecules of 19-25 nt in length that regulates post-transcriptional gene expression [1]. The let-7 miRNA was one of the first miRNAs discovered in the Caenorhabditis elegans and its biological functions show a high level of evolutionary conservation from nematode to human [2].
Usage
In 2019 CPU_CHINA project, we deliver the hsa-let-7f miRNA into Mtb-infected macrophages to promote their bioactivities. External supplement of let-7f could alleviate the decrease of it caused by Mtb and increase the expression of a series of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, KC, MCP-1, MIP-2 and nitrite. Then the anti-TB activity of macrophages renews and the intracellular Mtb will be killed.
Biology
MicroRNA (miRNA) act as post-transcriptional gene suppressors by base-pairing with their target mRNAs and inducing either translational repression or mRNA destabilization. Their genes are transcribed as primary miRNAs (pri-miRNAs) by RNA polymerase II (Pol II) in the nucleus. The long pri-miRNAs are cleaved by Drosha and DiGeorge syndrome critical region 8 (DGCRB), to produce 60-70 nt precursor miRNAs (pre-miRNAs). The pre-miRNAs are then exported and further processed by Dicer to produce the mature miRNAs [3].
MicroRNA hsa-let-7f is reported to regulate human immune responses to Mtb via control of A20, an inhibitor of the NF-κB pathway. The Nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) family of transcription factor plays an essential role in regulating the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokine and chemokine genes, which is regarded as the central mediator of inflammatory process. However, Kumar et al. show that Mtb suppresses innate immune responses via inhibiting microRNA let-7f expression, which facilitates the survival of Mtb in macrophages [4]. It is tempting to speculate that targeted intervention of miRNA regulated processes could provide attractive host-directed therapies for management of mycobacterial diseases.
Characteration
Plasmid (TLR2-P2A-TLR1-T2A-CD14) and plasmid (NF-κB induced promoter-hsa-let-7f pri-miRNA) were co-transfected into HEK293T cells. Then, we utilized Pam3Cys-Ser-(Lys)4, TLR1/TLR2 agonist to stimulate Toll like receptor (TLR) signaling pathway. In our project, the activation of NF-κB can eventually leads to the expression of hsa-let-7f pri-miRNAs, which are eventually cleaved by Drosha, DGCRB and Dicer to form mature miRNAs. The miRNAs are packaged into exosomes and secreted out of cells subsequently. Therefore, we determine the amount of hsa-let-7f in the exosomes by QPCR assay.
As shown in Figure 1, hsa-let-7f was successfully expressed in HEK293T cells and packaged into the exosomes.
Exosomes with or without hsa-let-7f miRNAs were separately incubated with RAW264.7 cells for 48h, and then mRNA level of cytokines (IL-1β, IL6, TNF-α) and chemokines (MCP-1, MIP-2) in RAW264.7 cells were tested by using QPCR assay. The results show that mRNA level of both cytokines and chemokines in cells treated with exosomes containing hsa-let-7f miRNAs increased significantly compared to that of control group.
Reference
[1] Lu, T. X. , Rothenberg, M. E. (2018). MicroRNA. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 141(4):1202-1207.
[2] Lee, H. , Han, S. , Kwon, C. S. , Lee, D. (2016). Biogenesis and regulation of the let-7 miRNAs and their functional implications. Protein Cell, 7(2):100-13.
[3] Han, J. , Lee, Y. , Yeom, K. H. , Nam, J. W. , Heo, I. , & Rhee, J. K. , et al. (2006). Molecular basis for the recognition of primary micrornas by the drosha-dgcr8 complex. Cell, 125(5), 0-901.
[4] Kumar, M. , Sahu, S. K. , Kumar, R. , Subuddhi, A. , & Basu, J. . (2015). Microrna let-7 modulates the immune response to mycobacterium tuberculosis infection via control of a20, an inhibitor of the nf-κb pathway. Cell host & microbe, 17(3).
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]