Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1321348"
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
[[File:IC14-BSAbplot1.png|700px|left|]] | [[File:IC14-BSAbplot1.png|700px|left|]] | ||
| − | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 33: | Line 32: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | + | <br> | |
| + | <br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
==Contribution: WHU-China 2019== | ==Contribution: WHU-China 2019== | ||
<div> | <div> | ||
Revision as of 07:47, 18 October 2019
sfGFP fused to dCBD with linker in RFC 25
Super-folder GFP fused N-terminally to dCBD (a cellulose-binding domain), which contains an endogenous N-terminal linker sequence.
This construct is part of a library of Super-folder GFP fusions with cellulose binding domains, which we used to assay the CBD binding affinity. Please see our [http://2014.igem.org/Team:Imperial/Functionalisation project page] for more information. The collection of sfGFP-CBD fusion parts can be seen in the table below: 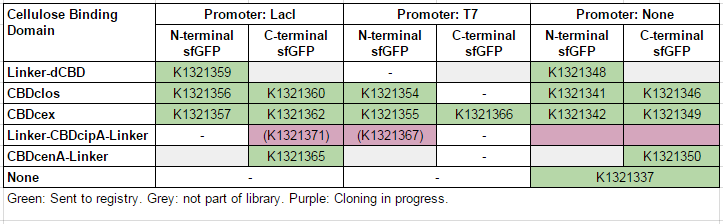
Note that the start and stop codon, plus 6 bp either side of the sequence, are included the RFC25 prefix and suffix which is not shown.
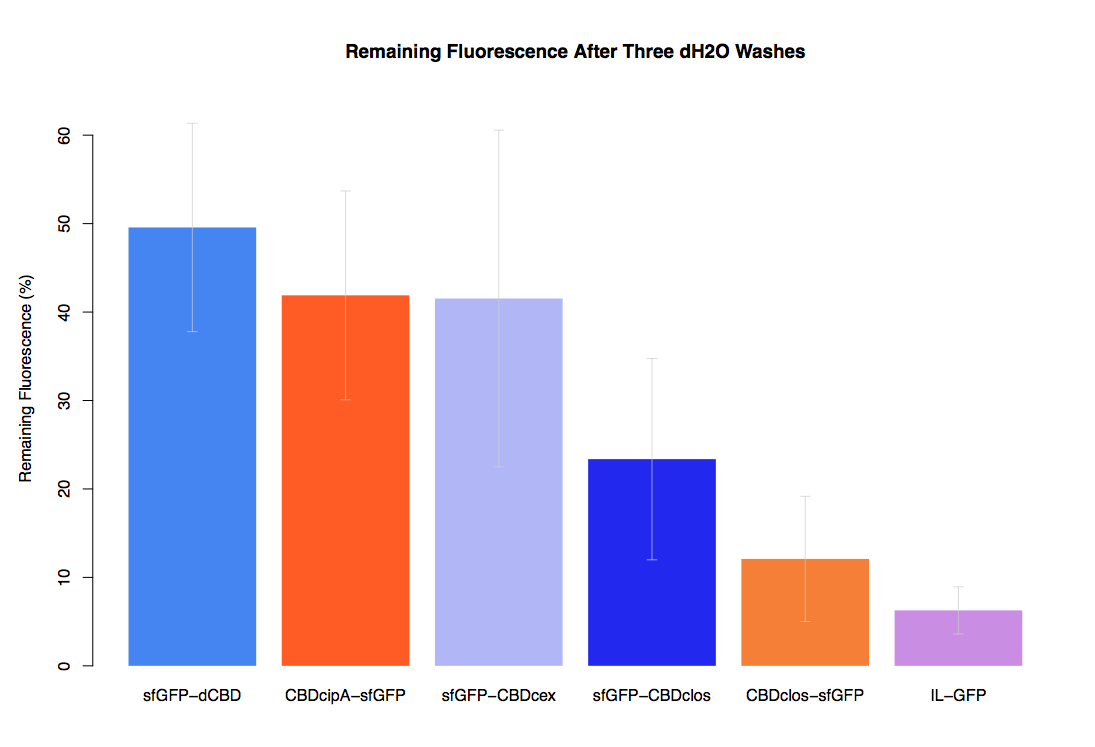
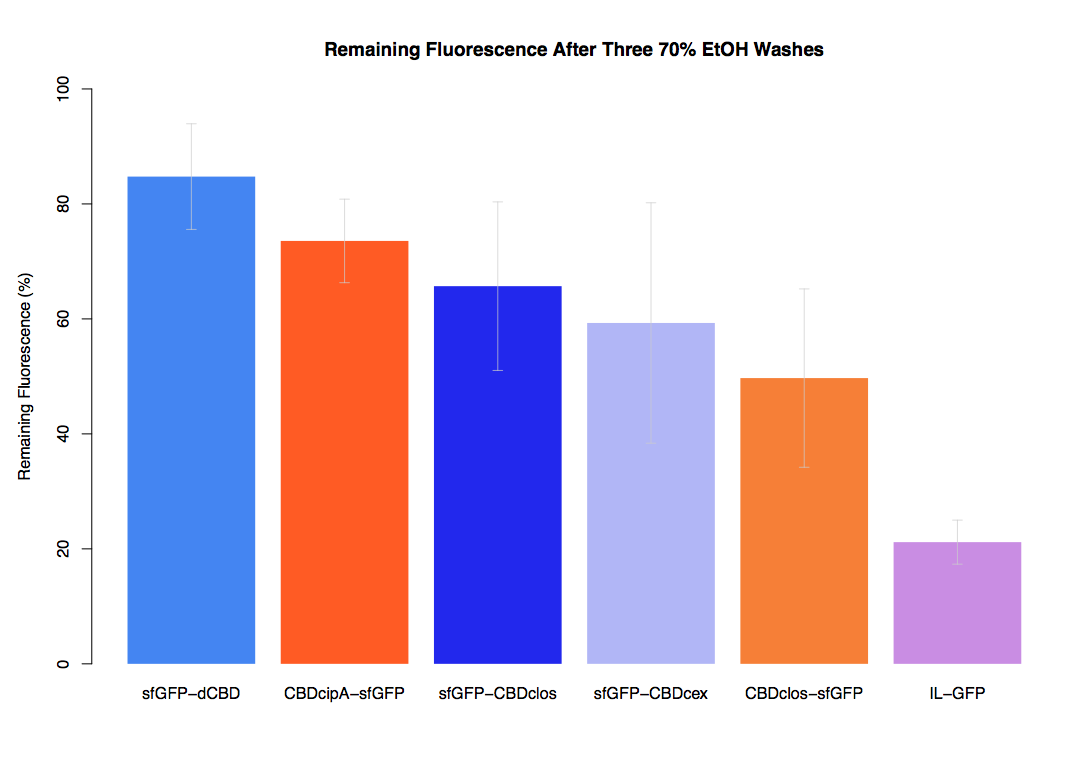
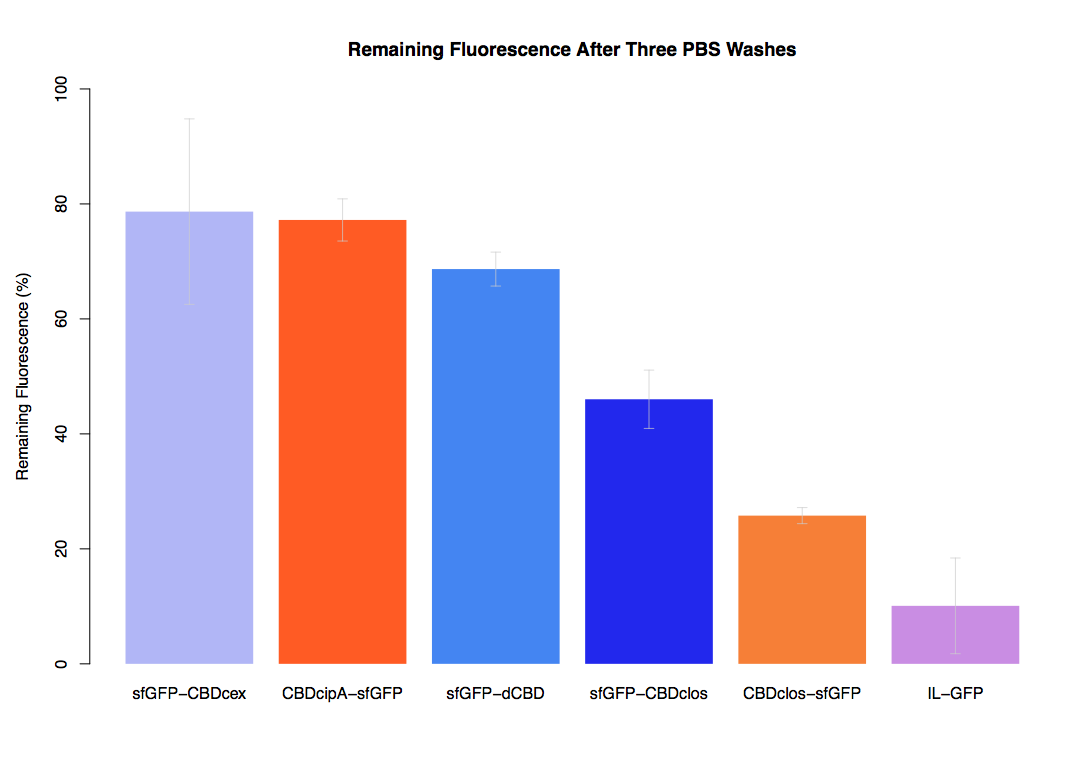
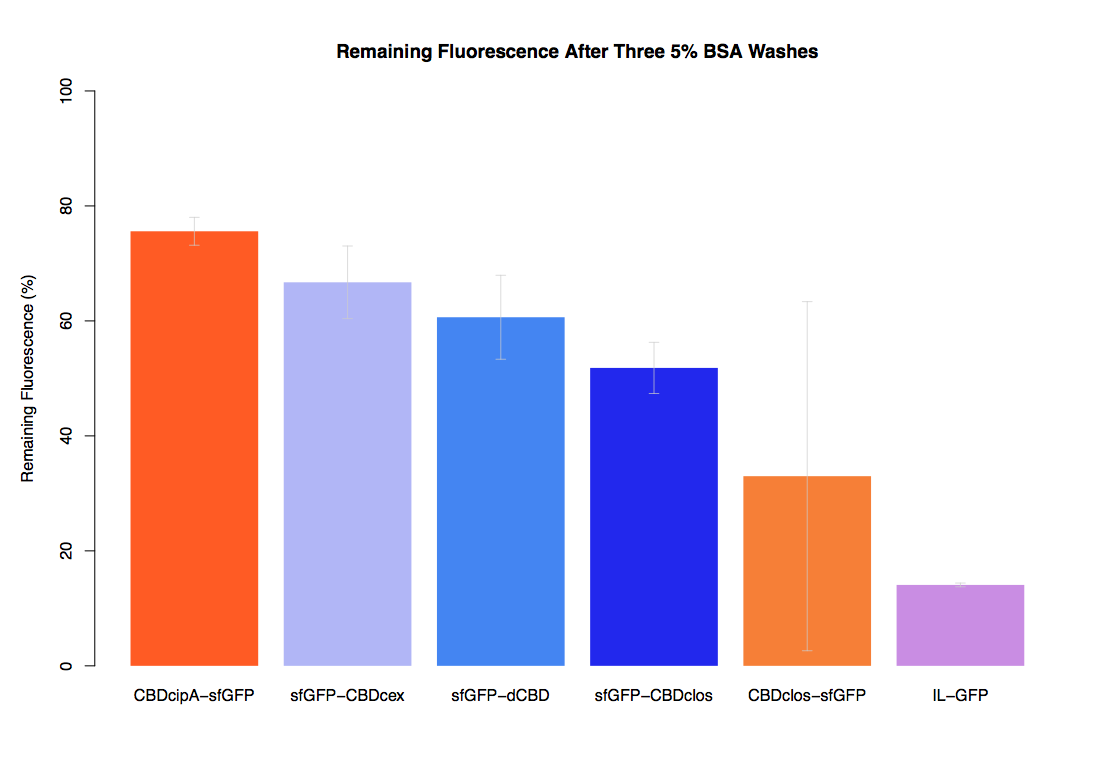
As part of our project we carried out an assay to determine the relative binding ability of CBD-sfGFP fusions to bacterial cellulose.
In our first assay performed to determine the relative strengths of various CBDs’ binding to bacterial cellulose – represented by the percentage fluorescence left from CBDs fused to (sfGFP (RFC25)) bound to bacterial cellulose discs, when subjected to various washes - it was determined that the fusion with dCBD had the greatest binding ability in comparison to four other CBDs fused to sfGFP after three washes with both dH2O and 70% EtOH.
In the same assay, results suggested that dCBD had on average the third greatest ability to bind bacterial cellulose, after three washes with both PBS and 5% BSA.
Contribution: WHU-China 2019
Group: WHU-China
Authors: Junfan chen
Summary: We confirmed the function of dCBD fused with sfGFP as a reporter by testing the combination strength between dCBD and bacteria cellulose.
Documentation:
1.Qualitative experiment
The experimental group we set is the mixture of dCBD sample with bacteria cellulose homogenate. We also set a negative control which mixed sfGFP with bacteria cellulose homogenate.

After a series of operations such as mixing, centrifugation and washing, the following conclusions were obtained:

When we used ddH2O (0.1% TWEEN 20) to wash the mixture and centrifugated it, we got that the residual amount of sfGFP on BC gel was lower than that of dCBD which were visible to naked eyes.
2.Quantitative experiment
We did the quantitative test of the fluorescence intensity by using a multifunctional microplate reader. We got the results as follows:

- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal SapI.rc site found at 10