Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3036005"
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
This arabinose-induced suicide switch consists of pBAD (BBa_K206000) and mazF (BBa_K302033), aiming to enable users of this microbe to terminate engineered bacteria inside their intestines with L-arabinose whenever needed. This suicide switch does no harm to human and can be used by direct in-taking of inducer. PBAD (BBa_K206000) is applied for heterologous gene expression due to its advantages, including moderately high expression levels, induction by a low-cost and non-toxic monosaccharide L-arabinose and tight regulation of transcription, which is particularly significant to expressing toxins [1]. MazF is an endoribonuclease that cleaves RNAs at ACA sites and causes the death of microbe, mediates suicide of cells without causing lysis of bacterial cells[2]. | This arabinose-induced suicide switch consists of pBAD (BBa_K206000) and mazF (BBa_K302033), aiming to enable users of this microbe to terminate engineered bacteria inside their intestines with L-arabinose whenever needed. This suicide switch does no harm to human and can be used by direct in-taking of inducer. PBAD (BBa_K206000) is applied for heterologous gene expression due to its advantages, including moderately high expression levels, induction by a low-cost and non-toxic monosaccharide L-arabinose and tight regulation of transcription, which is particularly significant to expressing toxins [1]. MazF is an endoribonuclease that cleaves RNAs at ACA sites and causes the death of microbe, mediates suicide of cells without causing lysis of bacterial cells[2]. | ||
| − | Biology and Usage | + | <font size="4"><b>Biology and Usage</b></font> |
This arabinose-induced suicide switch consists of pBAD (BBa_K206000) and mazF (BBa_K302033), aiming to enable users of this microbe to terminate engineered bacteria inside their intestines with L-arabinose whenever needed. This suicide switch does no harm to human and can be used by direct in-taking of inducer. PBAD (BBa_K206000) is applied for heterologous gene expression due to its advantages, including moderately high expression levels, induction by a low-cost and non-toxic monosaccharide L-arabinose and tight regulation of transcription, which is particularly significant to expressing toxins [1]. MazF is an endoribonuclease that cleaves RNAs at ACA sites and causes the death of microbe, mediates suicide of cells without causing lysis of bacterial cells. [2] | This arabinose-induced suicide switch consists of pBAD (BBa_K206000) and mazF (BBa_K302033), aiming to enable users of this microbe to terminate engineered bacteria inside their intestines with L-arabinose whenever needed. This suicide switch does no harm to human and can be used by direct in-taking of inducer. PBAD (BBa_K206000) is applied for heterologous gene expression due to its advantages, including moderately high expression levels, induction by a low-cost and non-toxic monosaccharide L-arabinose and tight regulation of transcription, which is particularly significant to expressing toxins [1]. MazF is an endoribonuclease that cleaves RNAs at ACA sites and causes the death of microbe, mediates suicide of cells without causing lysis of bacterial cells. [2] | ||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K3036005 parameters</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K3036005 parameters</partinfo> | ||
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <font size="4"><b>Design and Properties</b></font> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Arabinose-induced suicide switch is characterized in a system where the mazF (BBa_K302033) gene encoding toxin is put under the control of L-arabinose induced promoter pBAD (BBa_K206000). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:2019_BNU-China_BBa_K206000_pic1.png| border | center | 400px]]<br> | ||
| + | |||
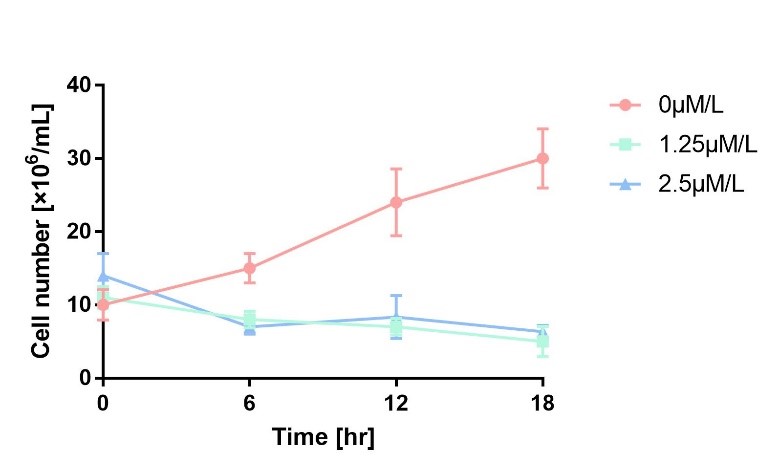
| + | As is shown in Fig.1, the cell number of experimental groups show a significant decrease upon induction, which indicates the arabinose-induced suicide switch works upon induction of 1.25μM/L and 2.5μM/L L-arabinose. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:2019_BNU-China_BBa_K206000_pic2.png| border | center | 400px]]<br> | ||
| + | <div class = "center">Figure 1 Cell number declines after induction.</div> | ||
| + | |||
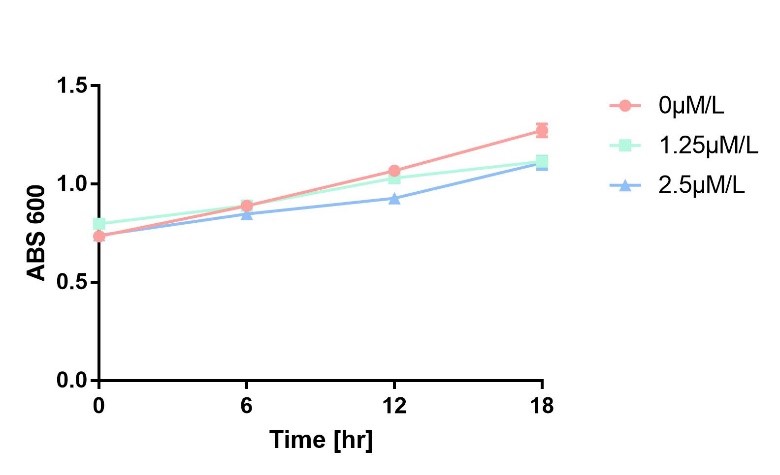
| + | Then, in order to prove that this arabinose-induced suicide switch kills the cell without lysing it, we measure OD600 of each sample to give an overall number of intact bacteria, dead and alive. As is shown in Fig.2, there is little difference between control and experimental groups, although it is validated that numbers of alive cells differ. Hence, we reach a conclusion that the switch mediates suicide of cells without causing lysis of bacterial cells, which is harmless to native microbe. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:2019_BNU-China_BBa_K302033_pic3.png| border | center | 400px]]<br> | ||
| + | <div class = "center">Figure 2 Absorbance at 600nm with time.</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <font size="4"><b>Experimental approach</b></font> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1.Transform the plasmids into E. coli DH5α competent cells.<br> | ||
| + | 2.The engineered bacteria are cultured in 200mL LB-ampicillin (50 ng/µl) medium overnight at 37℃, 200rpm;<br> | ||
| + | 3.Equally divide the culture into 90 centrifuge tubes, which is 1mL respectively. Centrifuge them at 4000rpm for 5 minutes. Discard the liquid.<br> | ||
| + | 4.Resuspend 30 tubes of collected bacteria with LB-ampicillin (50 ng/µl) containing 1.25μM/L and 2.5μM/L L-arabinose respectively as experimental groups. Resuspend 30 tubes of bacteria with pure LB-ampicillin (50 ng/µl) medium.<br> | ||
| + | 5.Collect 3 tubes of all groups every 6 hours, dilute all of the samples to 107 times and then spread them on solid LB-ampicillin (50 ng/µl) medium separately. At the same time, refresh the medium to maintain the concentration of L-arabinose.<br> | ||
| + | 6.Count the number of colonies in 5 cm2 per plate after cultured for 24 hours at 37℃<br> | ||
| + | 7.Three repicas are tested in each group.<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <font size="4"><b>Reference</b></font> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [1] Diana Széliová, Ján Krahulec, Martin Šafránek, et al. Modulation of heterologous expression from PBAD promoter in Escherichia coli production strains[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2016, 236:1-9.<br> | ||
| + | [2] Nigam A, Ziv T, Oron-Gottesman A, Engelberg-Kulka H2019. Stress-induced MazF-mediated proteins in Escherichia coli. mBio 10: e00340-19. doi:10.1128/mBio.00340-19. | ||
Revision as of 10:46, 12 October 2019
Arabinose-induced suicide switch
This arabinose-induced suicide switch consists of pBAD (BBa_K206000) and mazF (BBa_K302033), aiming to enable users of this microbe to terminate engineered bacteria inside their intestines with L-arabinose whenever needed. This suicide switch does no harm to human and can be used by direct in-taking of inducer. PBAD (BBa_K206000) is applied for heterologous gene expression due to its advantages, including moderately high expression levels, induction by a low-cost and non-toxic monosaccharide L-arabinose and tight regulation of transcription, which is particularly significant to expressing toxins [1]. MazF is an endoribonuclease that cleaves RNAs at ACA sites and causes the death of microbe, mediates suicide of cells without causing lysis of bacterial cells[2].
Biology and Usage
This arabinose-induced suicide switch consists of pBAD (BBa_K206000) and mazF (BBa_K302033), aiming to enable users of this microbe to terminate engineered bacteria inside their intestines with L-arabinose whenever needed. This suicide switch does no harm to human and can be used by direct in-taking of inducer. PBAD (BBa_K206000) is applied for heterologous gene expression due to its advantages, including moderately high expression levels, induction by a low-cost and non-toxic monosaccharide L-arabinose and tight regulation of transcription, which is particularly significant to expressing toxins [1]. MazF is an endoribonuclease that cleaves RNAs at ACA sites and causes the death of microbe, mediates suicide of cells without causing lysis of bacterial cells. [2]
| Arabinose-induced suicide switch | |
| Function | Arabinose-induced suicide switch |
| Use in | Prokaryotes |
| RFC standard | RFC10 compatible |
| Backbone | pSB1C3 |
| Derived from | Escherichia. coli DH5alpha |
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 125
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 65
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Design and Properties
Arabinose-induced suicide switch is characterized in a system where the mazF (BBa_K302033) gene encoding toxin is put under the control of L-arabinose induced promoter pBAD (BBa_K206000).
As is shown in Fig.1, the cell number of experimental groups show a significant decrease upon induction, which indicates the arabinose-induced suicide switch works upon induction of 1.25μM/L and 2.5μM/L L-arabinose.
Then, in order to prove that this arabinose-induced suicide switch kills the cell without lysing it, we measure OD600 of each sample to give an overall number of intact bacteria, dead and alive. As is shown in Fig.2, there is little difference between control and experimental groups, although it is validated that numbers of alive cells differ. Hence, we reach a conclusion that the switch mediates suicide of cells without causing lysis of bacterial cells, which is harmless to native microbe.
Experimental approach
1.Transform the plasmids into E. coli DH5α competent cells.
2.The engineered bacteria are cultured in 200mL LB-ampicillin (50 ng/µl) medium overnight at 37℃, 200rpm;
3.Equally divide the culture into 90 centrifuge tubes, which is 1mL respectively. Centrifuge them at 4000rpm for 5 minutes. Discard the liquid.
4.Resuspend 30 tubes of collected bacteria with LB-ampicillin (50 ng/µl) containing 1.25μM/L and 2.5μM/L L-arabinose respectively as experimental groups. Resuspend 30 tubes of bacteria with pure LB-ampicillin (50 ng/µl) medium.
5.Collect 3 tubes of all groups every 6 hours, dilute all of the samples to 107 times and then spread them on solid LB-ampicillin (50 ng/µl) medium separately. At the same time, refresh the medium to maintain the concentration of L-arabinose.
6.Count the number of colonies in 5 cm2 per plate after cultured for 24 hours at 37℃
7.Three repicas are tested in each group.
Reference
[1] Diana Széliová, Ján Krahulec, Martin Šafránek, et al. Modulation of heterologous expression from PBAD promoter in Escherichia coli production strains[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2016, 236:1-9.
[2] Nigam A, Ziv T, Oron-Gottesman A, Engelberg-Kulka H2019. Stress-induced MazF-mediated proteins in Escherichia coli. mBio 10: e00340-19. doi:10.1128/mBio.00340-19.