Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3168004"
CMichielsen (Talk | contribs) |
CMichielsen (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
===dCas9-LargeBitNanoLuc=== | ===dCas9-LargeBitNanoLuc=== | ||
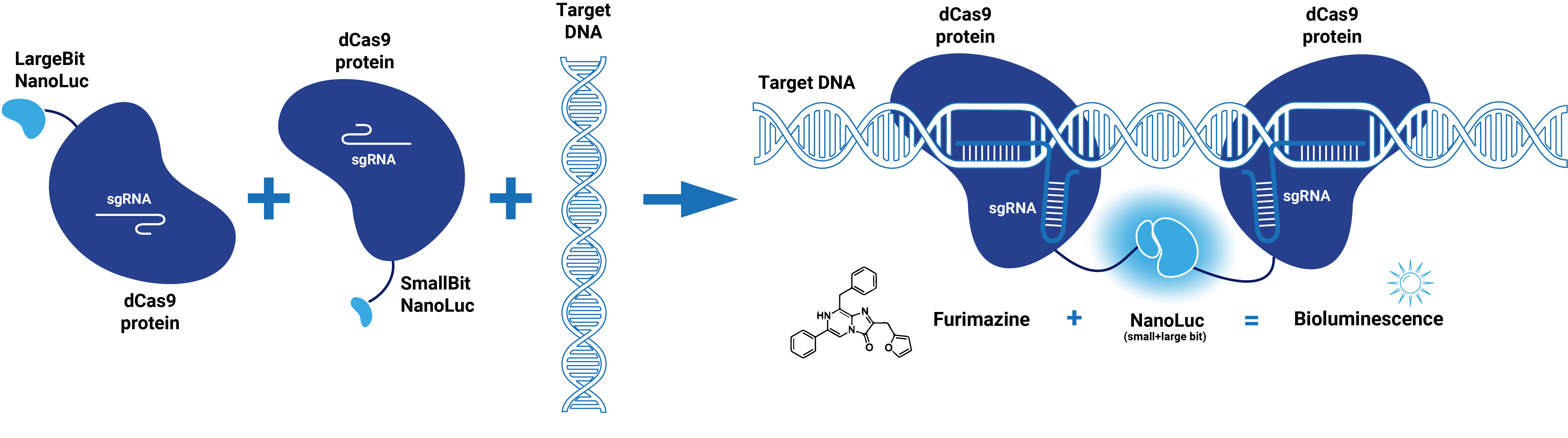
| − | This composite part is made up of two basic parts (figure 1). The first basic part [https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K3168000 (BBa_K3168000)] codes for a catalytically dead CRISPR associated protein 9 (dCas9). | + | This composite part is made up of two basic parts (figure 1). The first basic part [https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K3168000 (BBa_K3168000)] codes for a catalytically dead CRISPR associated protein 9 (dCas9). dCas9 binds to a specific double-stranded DNA sequence which is determined by the guide RNA. The second basic part [https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K3168002 (BBa_K3168002)], which is fused to dCas9, consists of a (GGS)<sub>5</sub> linker and the large bit of NanoLuc. When the large bit of Split-NanoLuc forms a complex with the small bit and the substrate Furimazine is present, blue light is emitted. dCas9-LargeBit itself is slightly bioluminescent when the substrate is added. However, the intensity is more bright when a complex is formed with the small bit. Thus this composite part is part of a Split-NanoLuc detection system, which targets a specific sequence on dsDNA and sends out a bioluminescent signal upon binding of this specific sequence (figure 2). |
[[File:T--TU_Eindhoven--dCas9-LargeBit.png|300px|]] | [[File:T--TU_Eindhoven--dCas9-LargeBit.png|300px|]] | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
===Usage and Biology=== | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
| − | dCas9 in combination with guide RNA forms a dsDNA recognition complex. A stronger bioluminescent signal is created when dCas9-LargBitNanoLuc and dCas9-SmallBitNanoLuc bind in close proximity. | + | dCas9 in combination with guide RNA forms a dsDNA recognition complex. A stronger bioluminescent signal is created when dCas9-LargBitNanoLuc and dCas9-SmallBitNanoLuc bind in close proximity. |
[[File:T--TU_Eindhoven--dCas9-SplitNL.png|900px|]] | [[File:T--TU_Eindhoven--dCas9-SplitNL.png|900px|]] | ||
Revision as of 12:06, 23 September 2019
dCas9-LargeBitNanoLuc
This composite part is made up of two basic parts (figure 1). The first basic part (BBa_K3168000) codes for a catalytically dead CRISPR associated protein 9 (dCas9). dCas9 binds to a specific double-stranded DNA sequence which is determined by the guide RNA. The second basic part (BBa_K3168002), which is fused to dCas9, consists of a (GGS)5 linker and the large bit of NanoLuc. When the large bit of Split-NanoLuc forms a complex with the small bit and the substrate Furimazine is present, blue light is emitted. dCas9-LargeBit itself is slightly bioluminescent when the substrate is added. However, the intensity is more bright when a complex is formed with the small bit. Thus this composite part is part of a Split-NanoLuc detection system, which targets a specific sequence on dsDNA and sends out a bioluminescent signal upon binding of this specific sequence (figure 2).
Figure 1. Schematic representation of dCas9-LargeBitNanoLuc.
Usage and Biology
dCas9 in combination with guide RNA forms a dsDNA recognition complex. A stronger bioluminescent signal is created when dCas9-LargBitNanoLuc and dCas9-SmallBitNanoLuc bind in close proximity.
Figure 2. Schematic representation of dCas9-Split-NanoLuc system.
References
Dixon, A. S., Schwinn, M. K., Hall, M. P., Zimmerman, K., Otto, P., Lubben, T. H., ... & Wood, M. G. (2015). NanoLuc complementation reporter optimized for accurate measurement of protein interactions in cells. ACS chemical biology, 11(2), 400-408.
Zhang, Y., Qian, L., Wei, W., Wang, Y., Wang, B., Lin, P., ... & Cheng, S. (2016). Paired design of dCas9 as a systematic platform for the detection of featured nucleic acid sequences in pathogenic strains. ACS synthetic biology, 6(2), 211-216.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 1099
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 3378
Illegal BamHI site found at 4630 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]