Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K2796028"
(→Modeling) |
|||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
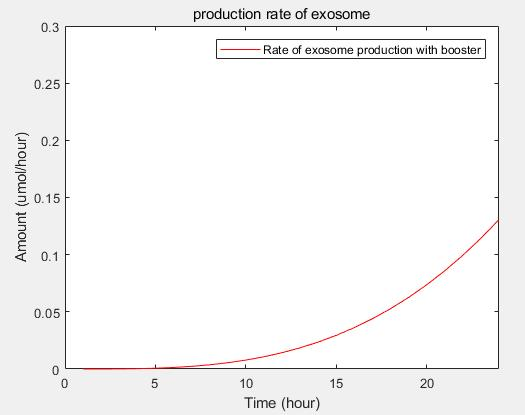
<b>c.production rate of exosomes in cell:</b> | <b>c.production rate of exosomes in cell:</b> | ||
[[File:2018 LZU-CHINA model6.png|300px|thumb|center|]] | [[File:2018 LZU-CHINA model6.png|300px|thumb|center|]] | ||
| − | |||
This model predicts the production rate of exosome over time in cells. | This model predicts the production rate of exosome over time in cells. | ||
| + | ===Experimental results=== | ||
| + | <li><b>Exosome booster</b> can enhance the ability of cells to secrete exosomes and it was expressed in <b> HEK293T by lentiviral vector </b>to verify its function. The experiments includes three parts: the transfection effect of exosome booster was detected by an inverted fluorescence microscope. The presence of exosome was detected by electron microscopy and the effect of exosome booster on the exosome secretion of HEK293T was detected by NTA analysis. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br><b>Exosome-booster stable cell line construction</b><br/> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [[File:2018 LZU-CHINA experimental result1.png|600px|thumb|center|]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
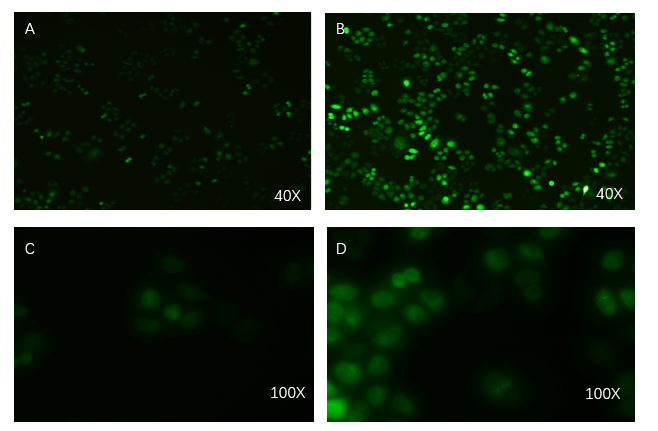
| + | <li>PCDH plasmid with exosome booster and <b>CopGFP reporting system</b> was transfected into HEK293T cells stably, and fluorescence before and after transfection was detected by inverted fluorescence microscopy. <b>Figure A is the HEK293T cells of the untransformed plasmid, while figure B is the HEK293T cells of the transformed exosome booster</b>. It can be observed that transfected cells can be stimulated to produce intense fluorescence. Figure. C and D were the fluorescence images of the control group at 100 times (figure. C) and the experimental group (figure. D).</li> | ||
| + | <br><b>Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) detection</b><br/> | ||
| + | [[File:2018 LZU-CHINA experimental result2.png|600px|thumb|center|]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
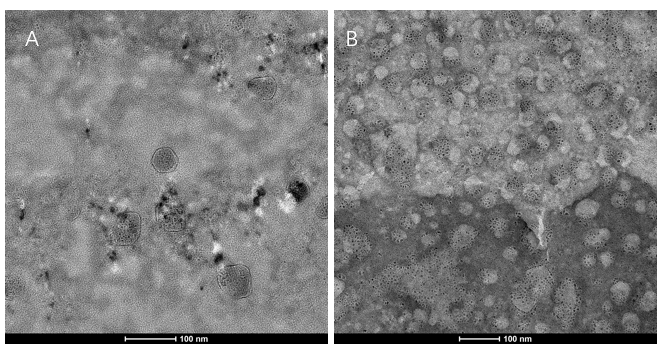
| + | <li>We extracted exosomes from HEK293T cell and negatively stained it with phosphotungstic acid. Subsequently, <b>we use TEM to detect it in 100nm</b> . The experimental results demonstrated that HEK293T expressed exosome booster genes (figure B) could dramatically increase its exosome secretion compare with control cell (figure A) </li> | ||
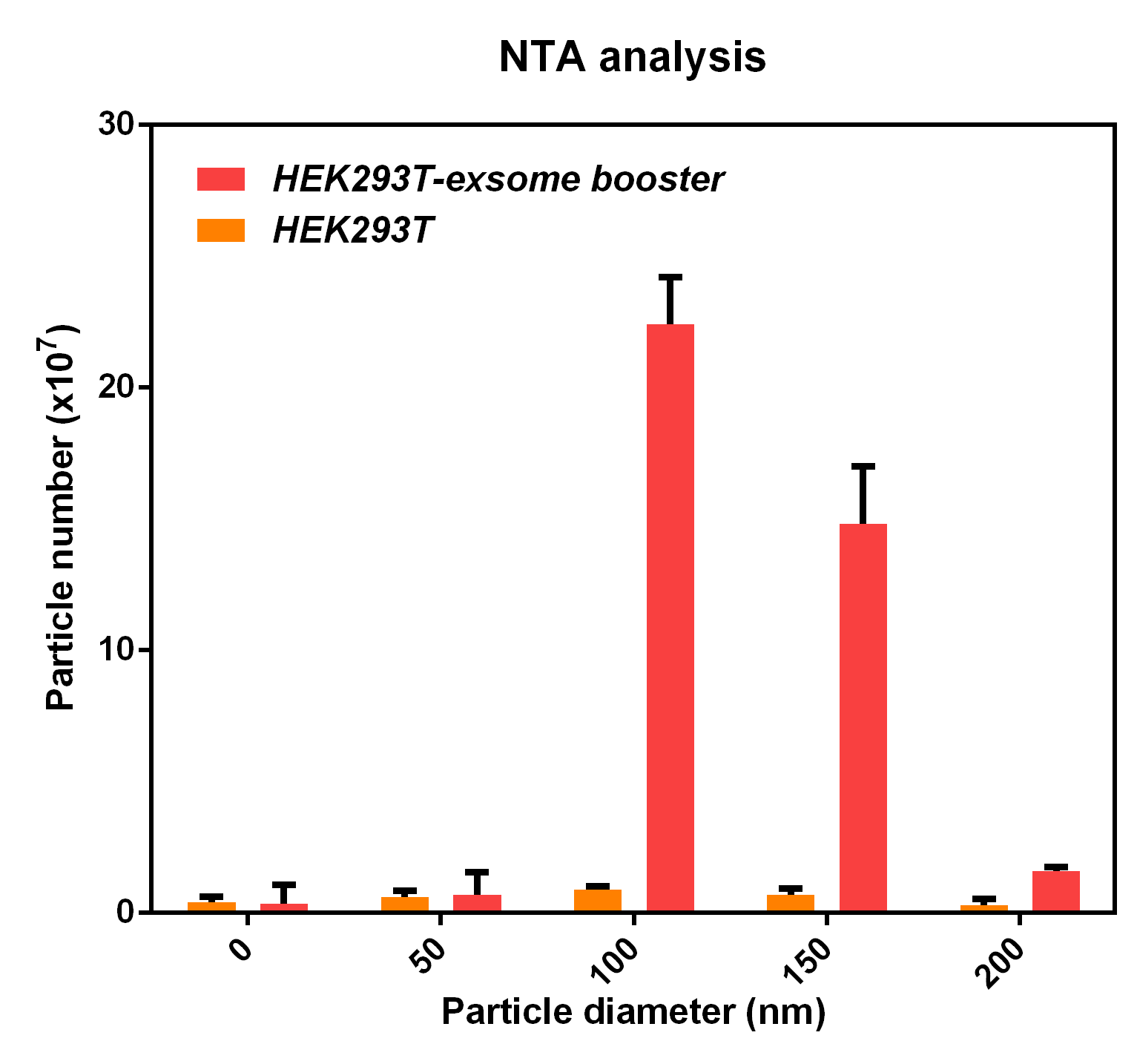
| + | <br><b>NTA analysis</b><br/> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [[File:2018 LZU-CHINA experimental result3.png|400px|thumb|center|]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <li>The NTA analysis refers to the nanoparticle tracking analysis. <b>The experimental results showed that HEK293T cell overexpressing exosome booster had significantly higher granules numbers at 100nm and 250nm</b> than the control cell (about 23 times as much as the control cell). This indicates that exosome booster can increase the number of exosomes secreted by 293T cell. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
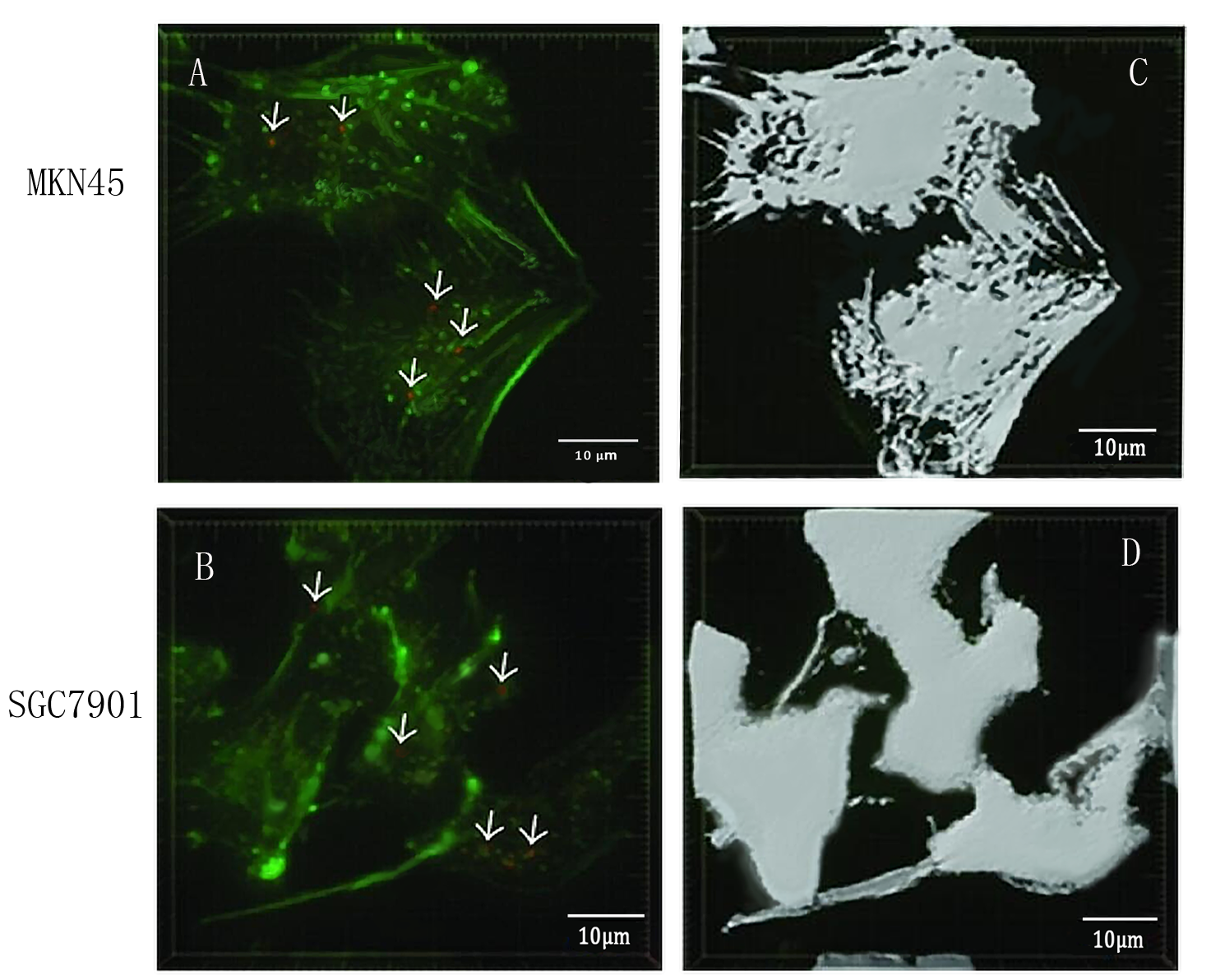
| + | <br><b>Exosome uptake experiments</b><br/></li> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [[File:2018 LZU-CHINA experimental result4.png|600px|thumb|center|]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <li>To detect whether exosomes whether could enter gastric cancer cells,<b>we used confocal microscopy to observe the uptake of gastric cancer cells MKN45 and SGC7901 with exosomes</b> . First, exosomes were extracted from 293T cells and stained with PKH26 exosomes (red fluorescent dye). The MKN45 and SGC7901 cells were stained with a FITC dye. Exosomes and gastric cancer cells were incubated together for 6 hours. Subsequently, the uptake of exosomes by gastric cancer cells was examined by fluorescence confocal microscopy. Figure. A and C indicate that gastric cancer cells MKN45 and SGC7901 can ingested exosomes. Figure. B and D showed the cytoskeletal structures of MKN45 and SGC7901 in gastric cancer cells detected by β-tubulin antibody. | ||
Revision as of 07:29, 16 October 2018
Exosome booster
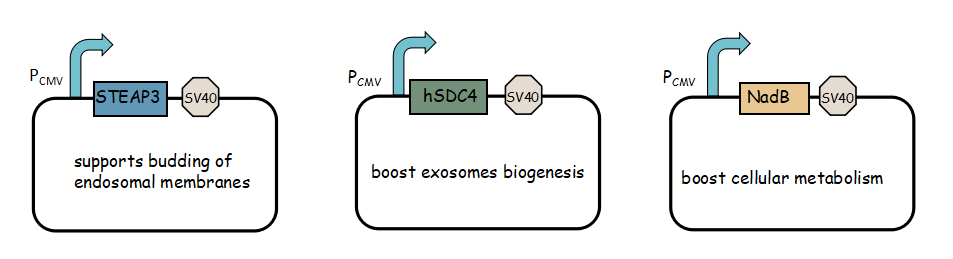
- Considering that TIL cells can't secret enough exosomes under normal condition, we fuse three genes to increase the number of exosomes (Alenquer, 2015), thus increasing the transfer efficiency of exosomes.
- Exosome booster refers to hSDC4-T2A-STEAP3-P2A-NadB.We identified STEAP3 (involved in exosomebiogenesis), syndecan-4(SDC4; supports budding of endosomal membranes to form multivesicular bodies), and a fragment of L-aspartate oxidase (NadB; possibly boosts cellular metabolism by tuning up the citric acid cycle) as potential synthetic exosome production boosters. Combined expression of these genes significantly increased exosome production.(Ryosuke Kojima et al. 2008)
-
They combine with each other to boost exosomal transfer efficiency:
-
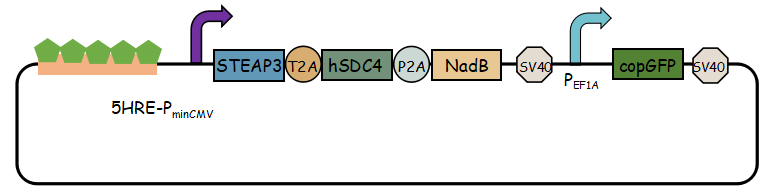
In previous article, it use IRES (internal ribosome entry site,IRES) to connect three genes, we change it into linkers T2A and P2A to ensure proper expression of three genes.Then we use use reporter gene copGFP to manifest the expression of exosome booster with the promoter of 5-HRE-PminCMV.
- Here is the final goal that we designed for this project.
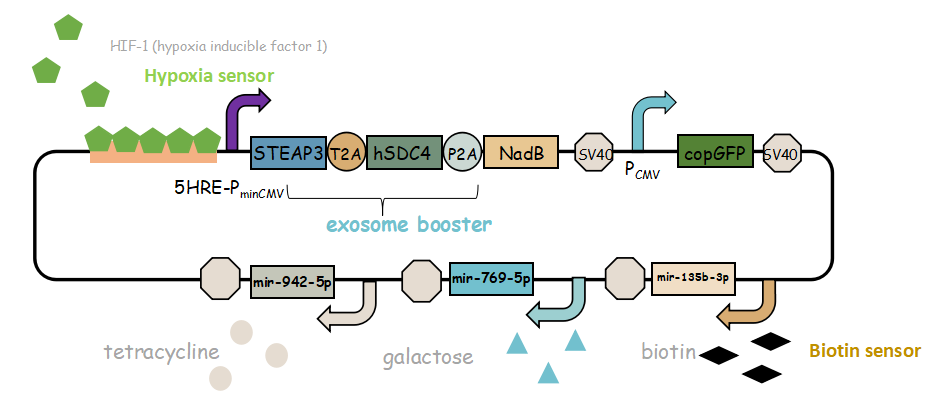
-
It combines with exosome booster and miR attacker (miR135b-3p, miR-942-5p,miR768-5p) under control of induced promoter (hypoxia,tetracycline, biotin and galactose induced system). By adding different inducers into the cell culture, we can prompt engineered 293T cells to express different concentrations of miRNA. There are six combinations; then we can find the optimum combination of miRNA to achieve our goal——kill tumor cells.
More design details and description you can obtain from our wiki!
- transcriptional rate simulation of three booster genes(left) and simulation of three booster genes transcriptional translation(right):
The interpretation of the parameters is shown in the following table
From the formula, we can obtain three model about exosome booster.
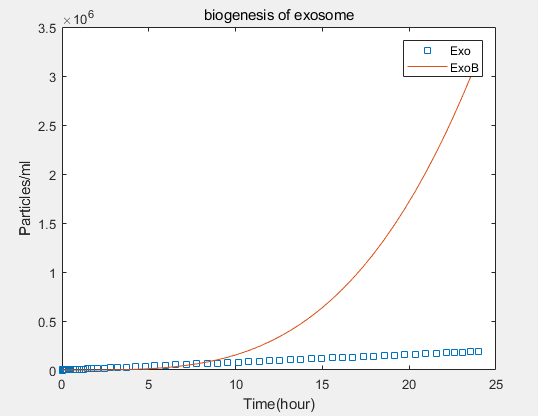
a.the promotional concentrations of the three promotional genes for the secretion of exosomes:Over time, the number of exosomes secreted by cells increased.
b.Comparison between the expression levels of three promoter genes and those of non-promoter exosomes:It demonstrates that exosome booster could dramatically increase exosome secrion.
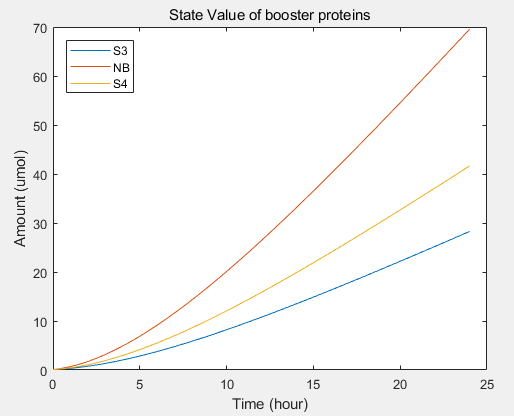
c.production rate of exosomes in cell:This model predicts the production rate of exosome over time in cells.
Experimental results
- Exosome booster can enhance the ability of cells to secrete exosomes and it was expressed in HEK293T by lentiviral vector to verify its function. The experiments includes three parts: the transfection effect of exosome booster was detected by an inverted fluorescence microscope. The presence of exosome was detected by electron microscopy and the effect of exosome booster on the exosome secretion of HEK293T was detected by NTA analysis.
Exosome-booster stable cell line construction
- PCDH plasmid with exosome booster and CopGFP reporting system was transfected into HEK293T cells stably, and fluorescence before and after transfection was detected by inverted fluorescence microscopy. Figure A is the HEK293T cells of the untransformed plasmid, while figure B is the HEK293T cells of the transformed exosome booster. It can be observed that transfected cells can be stimulated to produce intense fluorescence. Figure. C and D were the fluorescence images of the control group at 100 times (figure. C) and the experimental group (figure. D).
- We extracted exosomes from HEK293T cell and negatively stained it with phosphotungstic acid. Subsequently, we use TEM to detect it in 100nm . The experimental results demonstrated that HEK293T expressed exosome booster genes (figure B) could dramatically increase its exosome secretion compare with control cell (figure A)
- The NTA analysis refers to the nanoparticle tracking analysis. The experimental results showed that HEK293T cell overexpressing exosome booster had significantly higher granules numbers at 100nm and 250nm than the control cell (about 23 times as much as the control cell). This indicates that exosome booster can increase the number of exosomes secreted by 293T cell.
Exosome uptake experiments - To detect whether exosomes whether could enter gastric cancer cells,we used confocal microscopy to observe the uptake of gastric cancer cells MKN45 and SGC7901 with exosomes . First, exosomes were extracted from 293T cells and stained with PKH26 exosomes (red fluorescent dye). The MKN45 and SGC7901 cells were stained with a FITC dye. Exosomes and gastric cancer cells were incubated together for 6 hours. Subsequently, the uptake of exosomes by gastric cancer cells was examined by fluorescence confocal microscopy. Figure. A and C indicate that gastric cancer cells MKN45 and SGC7901 can ingested exosomes. Figure. B and D showed the cytoskeletal structures of MKN45 and SGC7901 in gastric cancer cells detected by β-tubulin antibody.
Sequence and Features
Assembly Compatibility:
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 192
Illegal BglII site found at 1777 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 2657
Illegal AgeI site found at 3277 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal SapI site found at 1367
- 10
Modeling
To increase the expression of exosomes, we added three enhanced genes to simulate the effect of increasing exosomes secretion through the model, providing guidance for our experiment. It includes three equations:
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) detection
NTA analysis