Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K2541209"
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<h5> | <h5> | ||
<P style="text-indent:2em;"> | <P style="text-indent:2em;"> | ||
| − | A RNA-based thermosensor that can be used for temperature sensitive | + | A RNA-based thermosensor that can be used for temperature sensitive translational regulation which is based on the change of RNA sencondary structure. The cold-repressible RNA-based thermosensors can repress translation of downstream genes at low temperatures. |
</p> | </p> | ||
</h5> | </h5> | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<P style="text-indent:2em;"> | <P style="text-indent:2em;"> | ||
| − | Here, we designed short, cold-repressible RNA thermosensors, which will form a stem-loop upstream of the | + | Here, we designed short, cold-repressible RNA thermosensors, which will form a stem-loop upstream of the SD sequence. These thermosensor sequences contain a double-strand RNA cleavage site for RNase III, an enzyme native to ''Escherichia coli'' and many other organisms. At low temperatures, the mRNA stem-loop is stable to expose the RNase III cleavage site and the transcript will be degraded. At elevated temperatures, the stem-loop will unfold and translation will occur unhindered. |
</p> | </p> | ||
<P style="text-indent:2em;"> | <P style="text-indent:2em;"> | ||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
} | } | ||
| − | + | .cold-repressive .a, .b, .c, .f { | |
fill: none; | fill: none; | ||
stroke-width: 11px; | stroke-width: 11px; | ||
| Line 125: | Line 125: | ||
stroke-linecap:round; | stroke-linecap:round; | ||
fill:none; | fill:none; | ||
| − | opacity:0; | + | opacity:1; |
| + | transition: all 0.3s ease-out 3s; | ||
} | } | ||
.cold-repressive .i { | .cold-repressive .i { | ||
| − | opacity:0; | + | opacity:0.35; |
fill: #ed1c24; | fill: #ed1c24; | ||
stroke: #ed1c24; | stroke: #ed1c24; | ||
stroke-width: 4.39px; | stroke-width: 4.39px; | ||
| − | transition: all 0.3s ease-out | + | transition: all 0.3s ease-out 3s; |
} | } | ||
.cold-repressive.svg_checked .hydrogen-bond{ | .cold-repressive.svg_checked .hydrogen-bond{ | ||
| − | opacity:0 | + | opacity:0; |
| − | transition: all 0.3s linear | + | transition: all 0.3s linear 0s; |
} | } | ||
.cold-repressive.svg_checked .i{ | .cold-repressive.svg_checked .i{ | ||
| − | opacity:0 | + | opacity:0; |
| − | transition: all 0.3s ease-out | + | transition: all 0.3s ease-out 0s; |
} | } | ||
.cold-repressive.svg_checked .j{ | .cold-repressive.svg_checked .j{ | ||
| − | opacity: | + | opacity:0; |
| − | transition: all 0.3s ease-out | + | transition: all 0.3s ease-out 0s; |
} | } | ||
.cold-repressive.svg_checked #RNAse_3{ | .cold-repressive.svg_checked #RNAse_3{ | ||
| − | transform: translateX( | + | transform: translateX(60px); |
| − | opacity: | + | opacity:0; |
| − | transition: all | + | transition: all 0.5s ease-out 0s; |
} | } | ||
.cold-repressive.svg_checked #ribosome_text{ | .cold-repressive.svg_checked #ribosome_text{ | ||
| − | opacity: | + | opacity:0; |
| − | transition: all 0. | + | transition: all 0.5s linear 0s; |
} | } | ||
.cold-repressive.svg_checked #loop{ | .cold-repressive.svg_checked #loop{ | ||
| − | transform: translateY( | + | transform: translateY(130px); |
} | } | ||
.cold-repressive #left,#right{ | .cold-repressive #left,#right{ | ||
| Line 164: | Line 165: | ||
} | } | ||
.cold-repressive.svg_checked #left{ | .cold-repressive.svg_checked #left{ | ||
| − | stroke-dashoffset: | + | stroke-dashoffset:-135; |
} | } | ||
.cold-repressive.svg_checked #right{ | .cold-repressive.svg_checked #right{ | ||
| − | stroke-dashoffset:- | + | stroke-dashoffset:-142; |
} | } | ||
| Line 177: | Line 178: | ||
} | } | ||
.cold-repressive.svg_checked #left_s{ | .cold-repressive.svg_checked #left_s{ | ||
| − | stroke-dashoffset:- | + | stroke-dashoffset:-265; |
} | } | ||
.cold-repressive.svg_checked #right_s{ | .cold-repressive.svg_checked #right_s{ | ||
| − | stroke-dashoffset:- | + | stroke-dashoffset:-82; |
} | } | ||
.cold-repressive .hydrogen-bond{ | .cold-repressive .hydrogen-bond{ | ||
| − | opacity:0; | + | opacity:0.3; |
| − | transition: all 0.3s linear | + | transition: all 0.3s linear 1s; |
} | } | ||
.cold-repressive #RNAse_3{ | .cold-repressive #RNAse_3{ | ||
| − | transform: translateX( | + | transform: translateX(0px); |
| − | opacity: | + | opacity:1; |
| − | transition: all | + | transition: all 1s ease-out 2s; |
} | } | ||
.cold-repressive #ribosome_text{ | .cold-repressive #ribosome_text{ | ||
| Line 197: | Line 198: | ||
} | } | ||
.cold-repressive #loop{ | .cold-repressive #loop{ | ||
| − | transform: translateY( | + | transform: translateY(0px); |
transition: all 2s ease-out; | transition: all 2s ease-out; | ||
} | } | ||
.cold-repressive #left{ | .cold-repressive #left{ | ||
| − | stroke-dashoffset: | + | stroke-dashoffset:0; |
stroke:red; | stroke:red; | ||
} | } | ||
.cold-repressive #right{ | .cold-repressive #right{ | ||
| − | stroke-dashoffset:- | + | stroke-dashoffset:-277; |
| − | stroke: | + | stroke:red; |
} | } | ||
.cold-repressive #left_s,#right_s{ | .cold-repressive #left_s,#right_s{ | ||
| Line 213: | Line 214: | ||
} | } | ||
.cold-repressive #left_s{ | .cold-repressive #left_s{ | ||
| − | stroke-dashoffset:- | + | stroke-dashoffset:-130; |
} | } | ||
.cold-repressive #right_s{ | .cold-repressive #right_s{ | ||
| − | stroke-dashoffset:- | + | stroke-dashoffset:-217; |
} | } | ||
</style> | </style> | ||
| + | |||
</defs> | </defs> | ||
<title>Stroke Version_1</title> | <title>Stroke Version_1</title> | ||
| Line 232: | Line 234: | ||
</g> | </g> | ||
<g id="text"> | <g id="text"> | ||
| − | <text class="d" transform="translate(429.01 185.45)"> | + | <text class="d" transform="translate(429.01 185.45)"></text> |
| − | <text class="e" transform="translate(123.8 185.45)"> | + | <text class="e" transform="translate(123.8 185.45)"></text> |
</g> | </g> | ||
| Line 283: | Line 285: | ||
</h5> | </h5> | ||
[[File:K2541209 f2.png|center|K2541209 f2]] | [[File:K2541209 f2.png|center|K2541209 f2]] | ||
| − | Figure 2. Design of | + | Figure 2. Design of K2541209. The RNA secondary structure, Tm and minimum free energy are predicted by mFOLD. |
<h1>'''3.Characterization'''</h1> | <h1>'''3.Characterization'''</h1> | ||
| + | <h3>3.1 Measurement device</h3> | ||
<h5> | <h5> | ||
<P style="text-indent:2em;"> | <P style="text-indent:2em;"> | ||
| − | The thermosensor sequence is constructed on the pSB1C3 vector by GoldenGate assembly. The measurement device is composed of Anderson promotor (BBa_J23106), thermosensor (BBa_K2541209), sfGFP_optimism (BBa_K2541400) and double terminator (BBa_B0010 and BBa_B0012). We select a constitutive Anderson promoter J23106 as an appropriate promoter by pre-experiment. The sfGFP_optimism has faster folding speed and higher fluorescence intensity. The double terminator can reduce | + | The thermosensor sequence is constructed on the pSB1C3 vector by GoldenGate assembly. The measurement device is composed of Anderson promotor (BBa_J23106), thermosensor (BBa_K2541209), sfGFP_optimism (BBa_K2541400) and double terminator (BBa_B0010 and BBa_B0012). We select a constitutive Anderson promoter J23106 as an appropriate promoter by pre-experiment. The sfGFP_optimism has faster folding speed and higher fluorescence intensity. The double terminator can reduce leakage (Figure 3). We characterized RNA-based thermosensors in ''E.coli'' DH5a. |
</p> | </p> | ||
</h5> | </h5> | ||
| Line 298: | Line 301: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | + | <h3>3.2 Measurement results</h3> | |
<h5> | <h5> | ||
<P style="text-indent:2em;"> | <P style="text-indent:2em;"> | ||
| Line 305: | Line 308: | ||
</h5> | </h5> | ||
[[File:K2541209 f4.png|center|K2541209 f4]] | [[File:K2541209 f4.png|center|K2541209 f4]] | ||
| − | Figure 4. Characteristics of | + | Figure 4. Characteristics of K2541209. Each set of five bars represents the activity level of a different thermosensor. The bar colors purple, green, yellow, orange and red represent the temperatures 15, 25, 29, 35 and 37°C, respectively. The height of the bars corresponds to the normalized fluorescence. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | [[File:RIII figure6.png|center|RIII figure6]] | + | <h1>'''4. Collection of cold-repressible RNA-based thermosensors '''</h1> |
| + | [[File:RIII figure6 新.png|center|RIII figure6 新]] | ||
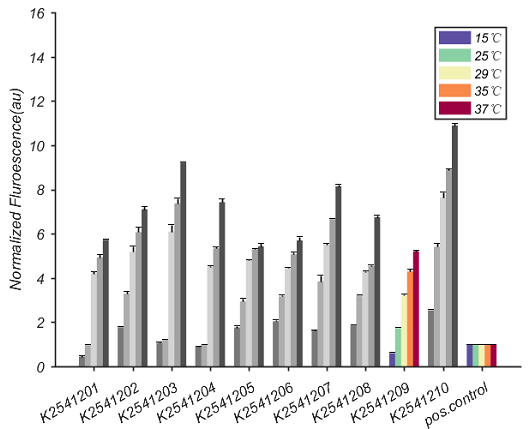
Figure 5. Experimental measurements of the collection of cold-repressible RNA-based thermosensors show a variety of responses. (A) Rows represent activity levels of different thermosensors. (B) Each set of five bars represents the activity level of a different thermosensor. The bar colors purple, green, yellow, orange and red represent the temperatures 15, 25, 29, 35 and 37°C, respectively. The height of the bars corresponds to the normalized fluorescence. | Figure 5. Experimental measurements of the collection of cold-repressible RNA-based thermosensors show a variety of responses. (A) Rows represent activity levels of different thermosensors. (B) Each set of five bars represents the activity level of a different thermosensor. The bar colors purple, green, yellow, orange and red represent the temperatures 15, 25, 29, 35 and 37°C, respectively. The height of the bars corresponds to the normalized fluorescence. | ||
| − | <h1>''' | + | <h1>'''5. Conclusion'''</h1> |
<h5> | <h5> | ||
<P style="text-indent:2em;"> | <P style="text-indent:2em;"> | ||
Revision as of 21:36, 14 October 2018
Cold-repressible RNA-based thermosensor-1
A RNA-based thermosensor that can be used for temperature sensitive translational regulation which is based on the change of RNA sencondary structure. The cold-repressible RNA-based thermosensors can repress translation of downstream genes at low temperatures.
1. Usage and Biology
RNA-based temperature sensing is common in bacteria that live in fluctuating environments. Most naturally occurring RNA-based thermosensors have long sequences and complicated sencondary structure and function by sequestering the Shine–Dalgarno (SD) sequence in a stem-loop structure at low temperatures.
Here, we designed short, cold-repressible RNA thermosensors, which will form a stem-loop upstream of the SD sequence. These thermosensor sequences contain a double-strand RNA cleavage site for RNase III, an enzyme native to Escherichia coli and many other organisms. At low temperatures, the mRNA stem-loop is stable to expose the RNase III cleavage site and the transcript will be degraded. At elevated temperatures, the stem-loop will unfold and translation will occur unhindered.
These short, modular cold-repressible RNA thermosensors can be exploited as convenient on/off switches of gene expression.
2. Design
The RNase III recognition site is distal box (db) sequence ad its cleavage site is proximal box (pb) sequence. We keep the db and pb sequence conserved which is necessary for RNase III to cleave. And we change their adjacent base pairs to increase or decrease the stem length to design cold-repressible RNA-based thermosensors with different melting temperatures, intensity and sensitivity. Moreover, changing adjacent base pairs may also influence RNase III catalytic efficiency.
Adding stem length can optimize cold-repressible RNA-based thermosensors to higher temperature, while decreasing stem length has the opposite effect. The stem length is 13 base parings in K2541209. After designing, the theromsensor sequence is predicted by computational methods mFOLD to get its Tm, minimum free energy and secondary structure (figure 2). The Tm is 30.9°C and minimum free energy is -6.6kcal/mol.
Figure 2. Design of K2541209. The RNA secondary structure, Tm and minimum free energy are predicted by mFOLD.
3.Characterization
3.1 Measurement device
The thermosensor sequence is constructed on the pSB1C3 vector by GoldenGate assembly. The measurement device is composed of Anderson promotor (BBa_J23106), thermosensor (BBa_K2541209), sfGFP_optimism (BBa_K2541400) and double terminator (BBa_B0010 and BBa_B0012). We select a constitutive Anderson promoter J23106 as an appropriate promoter by pre-experiment. The sfGFP_optimism has faster folding speed and higher fluorescence intensity. The double terminator can reduce leakage (Figure 3). We characterized RNA-based thermosensors in E.coli DH5a.
3.2 Measurement results
In figure 4, there are ten different cold-repressible RNA-based thermosensors. pos.control is positive control. The final normalized fluorescence was calculated as follows: normalized fluorescence = [(Fluorescence/Abs600)TS - (Fluorescence/Abs600)neg] / [(Fluorescence/Abs600)pos - (Fluorescence/Abs600)neg] ( TS = thermosensor, pos = positive control, and neg = BBa_J364007 ). As shown in figure 4, the fluorescence intensity of K2541209 reduces with decreased temperature.
Figure 4. Characteristics of K2541209. Each set of five bars represents the activity level of a different thermosensor. The bar colors purple, green, yellow, orange and red represent the temperatures 15, 25, 29, 35 and 37°C, respectively. The height of the bars corresponds to the normalized fluorescence.
4. Collection of cold-repressible RNA-based thermosensors
Figure 5. Experimental measurements of the collection of cold-repressible RNA-based thermosensors show a variety of responses. (A) Rows represent activity levels of different thermosensors. (B) Each set of five bars represents the activity level of a different thermosensor. The bar colors purple, green, yellow, orange and red represent the temperatures 15, 25, 29, 35 and 37°C, respectively. The height of the bars corresponds to the normalized fluorescence.
5. Conclusion
Our data show that efficient RNA-based thermosensors with different melting temperatures, intensity and sensitivity can be built from a single small RNA stem-loop structure, thus providing useful SynRT toolkit for the regulation of gene expression.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]