Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K2728001"
Bluepumpkin (Talk | contribs) (→Features) |
Bluepumpkin (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K2728001 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K2728001 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | + | <br /> | |
=== Basic Description === | === Basic Description === | ||
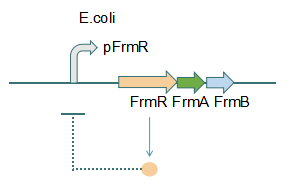
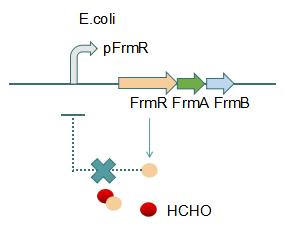
This promoter is an engineered formaldehyde-inducible promoter. Escherichia coli has a native formaldehyde-inducible promoter, pfrm, which is found upstream of the frmRAB formaldehyde detoxification operon. FrmR, the first product of the operon, is a member of the DUF156 family of DNA-binding transcriptional regulators. It binds the frmRAB promoter region and is negatively allosterically modulated by formaldehyde. FrmR is specific to formaldehyde, responding to acetaldehyde, methylglyoxal, and glyoxal to far lesser degrees and not at all to a range of other aldehydes and alcohols tested. The genes frmA and frmB encode a formaldehyde dehydrogenase and S-formylglutathione hydrolase, respectively, and are responsible for detoxifying formaldehyde to formic acid in a glutathione-dependent pathway. The negative-feedback regulation of the frmRAB operon is similar to that of many other prokaryotic operons, whereby the transcription factor represses its own transcription. | This promoter is an engineered formaldehyde-inducible promoter. Escherichia coli has a native formaldehyde-inducible promoter, pfrm, which is found upstream of the frmRAB formaldehyde detoxification operon. FrmR, the first product of the operon, is a member of the DUF156 family of DNA-binding transcriptional regulators. It binds the frmRAB promoter region and is negatively allosterically modulated by formaldehyde. FrmR is specific to formaldehyde, responding to acetaldehyde, methylglyoxal, and glyoxal to far lesser degrees and not at all to a range of other aldehydes and alcohols tested. The genes frmA and frmB encode a formaldehyde dehydrogenase and S-formylglutathione hydrolase, respectively, and are responsible for detoxifying formaldehyde to formic acid in a glutathione-dependent pathway. The negative-feedback regulation of the frmRAB operon is similar to that of many other prokaryotic operons, whereby the transcription factor represses its own transcription. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
===== Fig 2: With Formaldehyde ===== | ===== Fig 2: With Formaldehyde ===== | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | + | <br /> | |
=== Features === | === Features === | ||
# It’s a formaldehyde-inducible promoter from E.coli. | # It’s a formaldehyde-inducible promoter from E.coli. | ||
#It’s an engineered promoter. It retains formaldehyde responsiveness, with 2-fold higher GFP expression in response to 100 μM formaldehyde than the native pfrm. Application of this promoter with higher basal and induced expression levels before methanol assimilation genes achieves higher biomass titers than the native E. coli pfrm. | #It’s an engineered promoter. It retains formaldehyde responsiveness, with 2-fold higher GFP expression in response to 100 μM formaldehyde than the native pfrm. Application of this promoter with higher basal and induced expression levels before methanol assimilation genes achieves higher biomass titers than the native E. coli pfrm. | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | + | <br /> | |
=== Origins === | === Origins === | ||
Escherichia coli | Escherichia coli | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | + | <br /> | |
=== Experimental Characterization === | === Experimental Characterization === | ||
Revision as of 04:32, 14 October 2018
pfrmR - An Engineered Formaldehyde-Inducible Promoter
Basic Description
This promoter is an engineered formaldehyde-inducible promoter. Escherichia coli has a native formaldehyde-inducible promoter, pfrm, which is found upstream of the frmRAB formaldehyde detoxification operon. FrmR, the first product of the operon, is a member of the DUF156 family of DNA-binding transcriptional regulators. It binds the frmRAB promoter region and is negatively allosterically modulated by formaldehyde. FrmR is specific to formaldehyde, responding to acetaldehyde, methylglyoxal, and glyoxal to far lesser degrees and not at all to a range of other aldehydes and alcohols tested. The genes frmA and frmB encode a formaldehyde dehydrogenase and S-formylglutathione hydrolase, respectively, and are responsible for detoxifying formaldehyde to formic acid in a glutathione-dependent pathway. The negative-feedback regulation of the frmRAB operon is similar to that of many other prokaryotic operons, whereby the transcription factor represses its own transcription.
Fig 1: Without Formaldehyde
Fig 2: With Formaldehyde
Features
- It’s a formaldehyde-inducible promoter from E.coli.
- It’s an engineered promoter. It retains formaldehyde responsiveness, with 2-fold higher GFP expression in response to 100 μM formaldehyde than the native pfrm. Application of this promoter with higher basal and induced expression levels before methanol assimilation genes achieves higher biomass titers than the native E. coli pfrm.
Origins
Escherichia coli
Experimental Characterization
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]