Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K2440001"
Zhuchushu13 (Talk | contribs) (→Functional Test) |
Zhuchushu13 (Talk | contribs) (→PCR) |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
The result of the agarose electrophoresis was shown on the picture below. | The result of the agarose electrophoresis was shown on the picture below. | ||
| − | [[File:NUDT-part-lockerB.png| | + | [[File:NUDT-part-lockerB.png|300px|]] |
===Enzyme digestion test === | ===Enzyme digestion test === | ||
Latest revision as of 03:10, 2 November 2017
Locker B
Locker B is a miRNA locker with two different functional modules to target miR-214 and miR-654 at the same time.
Usage and Biology
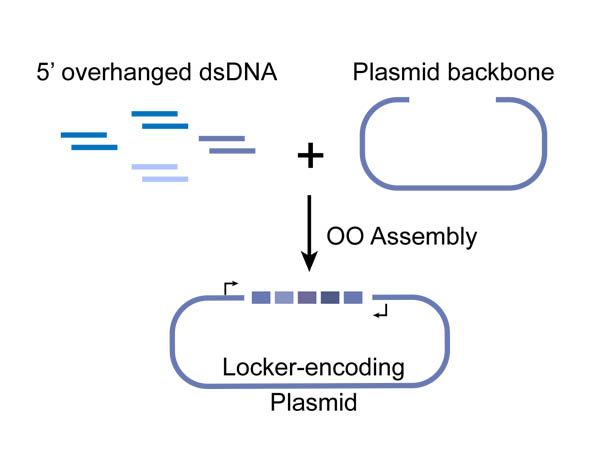
It is one of the experimental cases which were constructed to examine the scalability, reliability and efficiency of the Overlapped Oligo Assembly (OOA) method.
Overlapped Oligo Assembly method
In OOA method, modularized DNA parts is designed into the chemically synthesized DNA oligo, and overlapped 5’-overhangs are added for assembly. After that, dsDNAs can be obtained by annealing of two complementary single-strand oligonucleotides, then phosphorylated by T4 Polynucleotide Kinase to facilitate the following ligation reaction. T4 DNA ligase is use for their ligation onto pSB1C3 plasmid backbone. High-throughput one-step assemble of multiple short dsDNA nucleotides can therefore be achieved, and the correct assembling order is guaranteed by using identical overlap sequences among oligos, serving as zipcodes. The zipcodes are introduced as the intervals in a miRNA Locker. The dsDNA assembles are capable of being sub-cloned into plasmid backbones for amplification and long-term storage. In view of that, a prefix and a suffix is added to the dsDNA oligos forming the 5’ and 3’ terminus of the assembly, ensuring that the plasmids we constructed are compatible with BioBrick RFC[10].
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the Overlapped Oligo Assembly method
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Experimental Validation
This part is validated through four ways: enzyme cutting, PCR, Sequence, and functional testing
Sequencing
This part is sequenced as correct after construction.
PCR
Methods
The PCR is performed with Premix EX Taq by Takara.
F-Prime: 5’- GAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGAATGC-3’
R-Prime: 5’- GGACTAGTATTATTGTTTGTCTGCC-3’
The PCR protocol is selected based on the Users Manuel. The Electrophoresis was performed on a 1% Agarose glu. The result of the agarose electrophoresis was shown on the picture below.
Enzyme digestion test
Methods
After the assembly ,the plasmid was transferred into the Competent E. coli DH5α). After culturing overnight in LB,we minipreped the plasmid for cutting. The preparation of the plasmid was performed with TIANprep Mini Plasmid Kit from TIANGEN. The cutting procedure was performed with EcoRI and SpeI restriction endonuclease bought from TAKARA.
The plasmid was cutted in a 20μL system at 37 ℃ for 2 hours. The Electrophoresis was performed on a 1% Agarose glu.
The result of the agarose electrophoresis was shown on the picture above.
Functional Test
This part functions as the template for ssDNA. To validate the function of Locker B, asymmetric PCR was performed. MiRNA-Locker-coding region was digested from the plasmid backbone and then used as the template for asymmetric PCR. To optimize the PCR protocol, primers in ratios of 20/1, 50/1 and 1/0 were tested. The asymmetric PCR products were analyzed through 3% agarose gel electrophoresis. As showed in Figure 1, bands showing ssDNA products were observed when 20/1, 50/1 and 1/0 primer ratios were applied. Generally, 20/1 could be thought to be an optimal primer ratio for asymmetric PCR of Locker B. Single strand DNAs can be harvested and purified by PAGE purification assay.
Figure 2. Electrophoresis showing the production of four miRNA lockers by asymmetric PCR.