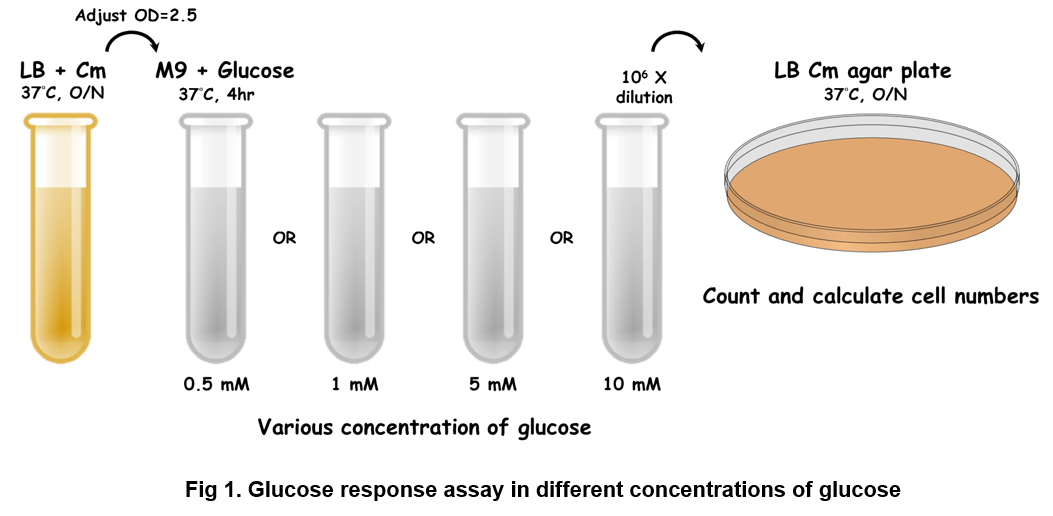Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K2230017"
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
Suicide genes of lysis was driven under the PhlF-repressed promoter (Pr). And the expression of the repressor (PhlF) would be induced upon glucose by a glucose responsive promoter (Pcar). That is, the bacteria can be killed by the suicide genes in the absence of (or running out of) glucose. | Suicide genes of lysis was driven under the PhlF-repressed promoter (Pr). And the expression of the repressor (PhlF) would be induced upon glucose by a glucose responsive promoter (Pcar). That is, the bacteria can be killed by the suicide genes in the absence of (or running out of) glucose. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Functional assay for glucose responsive suicide circuit === | ||
| + | [[File:Mingdaophil1025-14.png|500px|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The bacteria carrying the indicated vector were cultured in LB media supplemented with 34 g/ml of chloramphenicol (Cm) at 37°C overnight. The next day, OD600 was measured and adjusted to 2.5 in M9 minimal media with various concentrations of glucose. The bacteria then were incubated for 4 hours at 37°C. 100 l of the bacterial culture was put into one well of a black-walled, clear-bottom 96-well microplates (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.). OD600 was measured using BioTek Synergy H1 Hybrid Multi-Mode Reader System. Further, the culture media were taken out and diluted 106 times following by spreading onto LB Cm agar plate at 37°C overnight. The third day, the numbers of colonies were counted and bacterial viability was calculated. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Mingdaophil1025-16.png|500px|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | As you can see in Fig 2., the OD value in response to the decreasing concentration of glucose was gradually reduced to 1.89 much less than average 2.71 in control group without suicide gene expression, implying that the suicide proteins killed the cells in the loss of glucose in the environment. Moreover, when the bacteria were grown in M9 media with 0.5mM glucose for 4 hours, the survival rate was decreased to 34% compared to 56% of bacteria without suicide genes (Fig. 3). And the cell numbers were reduced to 671 compared to 1120 of bacteria without suicide genes. Both data confirmed that this suicide device works well and indicated that killing process began when glucose in the media was running out. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Mingdaophil1025-17.png|800px|center]] | ||
Revision as of 08:38, 25 October 2017
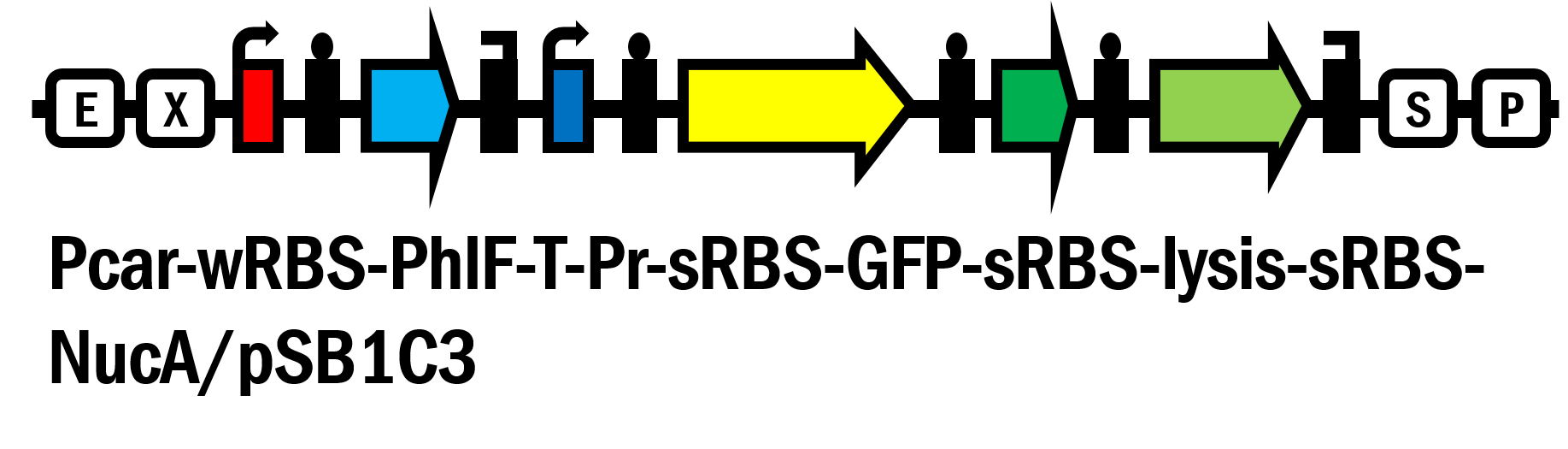
Pcar-wRBS-PhlF-T-Pr-sRBS-GFP-sRBS-lysis-sRBS-NucA/pSB1C3
Promoter Pcar [BBa_K861171] is a glucose responsive promoter created by WHU-China in 2012. Pcar promoter region was de novo designed with overlapping of CRP and RNA polymerase binding site. The initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase may be hindered by the binding of CRP, which occurs at the formation of cAMP-CRP complex in the low concentration of glucose. In other words, when the amount of glucose is high enough, Pcar would be turned on after the leaving of CPR due to the low concentration of cAMP, and vice versa.
PhlF repressor system contains the repressor PhlF [BBa_K1725041] and the PhlF repressible promoter [BBa_K1725001] created by Glasgow in 2015. PhlF could repress GFP fluorescence intensity by 83-fold according to the study of Glasgow’s work.
Lysis gene [BBa_K117000] created by NTU-Singapore in 2008 encodes Lysis protein which could not only lyse bacterial cell membrane but also activate the endonuclease of Colicin E7 (ColE7). The lysis-colicin is one class of bacteriocins which are produced to response to worsening environmental conditions and outcompete other bacteria1.
We’ve innovated this year a novel glucose responsive repressor system (Pcar-wRBS-PhlF-T-Pr-sRBS-GFP/pSB1C3 [BBa_K2230012]) by connecting these two system and extend the function of them. Furthermore, based on this new system, we assembled lysis and nuclease genes to the device and created the suicide circuit controlled by the presence of glucose (Pcar-wRBS-PhlF-T-Pr-sRBS-GFP-sRBS-lysis-sRBS-NucA/pSB1C3 [BBa_K2230017]).
Cloning
wRBS-lysis was amplified from Lysis gene (BBa_K117000) using a primer with weak RBS sequence (B0032) and assembled with Pcar-wRBS-PhlF-T-Pr-sRBS-GFP/pSB1C3 (BBa_K2230012)
Function
Suicide genes of lysis was driven under the PhlF-repressed promoter (Pr). And the expression of the repressor (PhlF) would be induced upon glucose by a glucose responsive promoter (Pcar). That is, the bacteria can be killed by the suicide genes in the absence of (or running out of) glucose.
Functional assay for glucose responsive suicide circuit
The bacteria carrying the indicated vector were cultured in LB media supplemented with 34 g/ml of chloramphenicol (Cm) at 37°C overnight. The next day, OD600 was measured and adjusted to 2.5 in M9 minimal media with various concentrations of glucose. The bacteria then were incubated for 4 hours at 37°C. 100 l of the bacterial culture was put into one well of a black-walled, clear-bottom 96-well microplates (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.). OD600 was measured using BioTek Synergy H1 Hybrid Multi-Mode Reader System. Further, the culture media were taken out and diluted 106 times following by spreading onto LB Cm agar plate at 37°C overnight. The third day, the numbers of colonies were counted and bacterial viability was calculated.
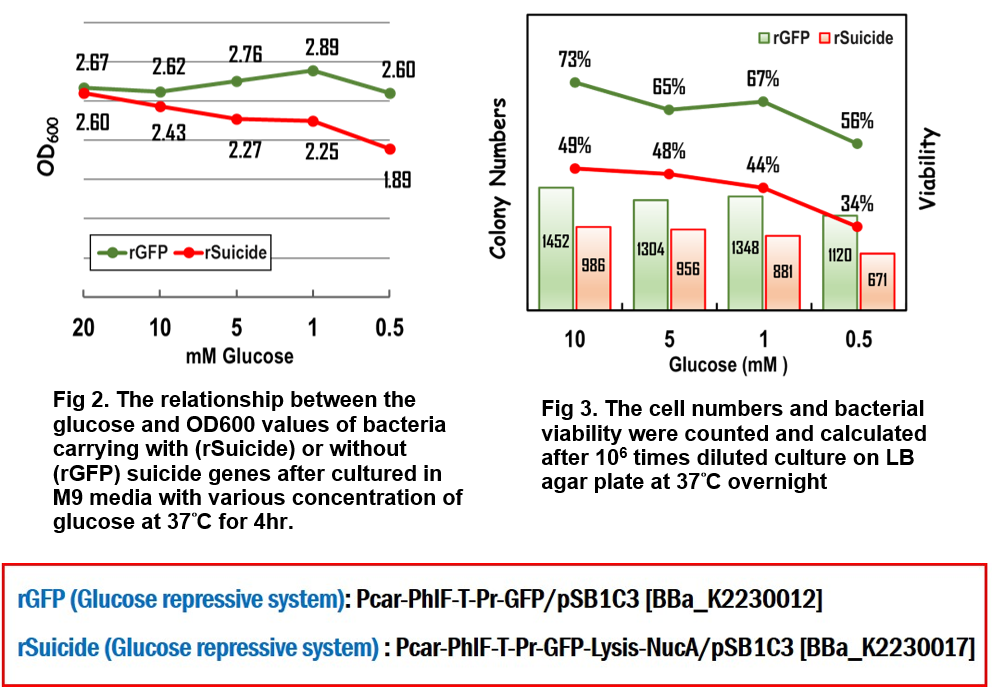
As you can see in Fig 2., the OD value in response to the decreasing concentration of glucose was gradually reduced to 1.89 much less than average 2.71 in control group without suicide gene expression, implying that the suicide proteins killed the cells in the loss of glucose in the environment. Moreover, when the bacteria were grown in M9 media with 0.5mM glucose for 4 hours, the survival rate was decreased to 34% compared to 56% of bacteria without suicide genes (Fig. 3). And the cell numbers were reduced to 671 compared to 1120 of bacteria without suicide genes. Both data confirmed that this suicide device works well and indicated that killing process began when glucose in the media was running out.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 7
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 1501