Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K592009:Experience"
(→User Reviews) |
|||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
|}; | |}; | ||
<!-- End of the user review template --> | <!-- End of the user review template --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- DON'T DELETE --><partinfo>BBa_K1155003 StartReviews</partinfo> | ||
| + | <!-- Template for a user review | ||
| + | {|width='80%' style='border:1px solid gray' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |width='10%'| | ||
| + | <partinfo>BBa_K1155003 AddReview number</partinfo> | ||
| + | <I>Team</I> | ||
| + | |width='60%' valign='top'| | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |}; | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
<partinfo>BBa_K1155003 EndReviews</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K1155003 EndReviews</partinfo> | ||
| Line 34: | Line 52: | ||
<!-- DON'T DELETE --><partinfo>BBa_K1155003 EndReviews</partinfo> | <!-- DON'T DELETE --><partinfo>BBa_K1155003 EndReviews</partinfo> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {|width='80%' style='border:1px solid gray' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |width='10%'| | ||
| + | <partinfo>BBa_K592009 AddReview 5</partinfo> | ||
| + | <I>iGEM Sydney Australia</I> | ||
| + | |width='60%' valign='top'| | ||
| + | [[Image:https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/2/21/T--Sydney_Australia--amilCPmutants.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Sydney_ Australia 2016 team improved this part via error prone PCR for inclusion in our ethylene biosensor. We managed to produce three new colour strains, a purple, a pink, and a mint green. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File: Sydney_australia_amilcp_mutants.png |620px|center]] | ||
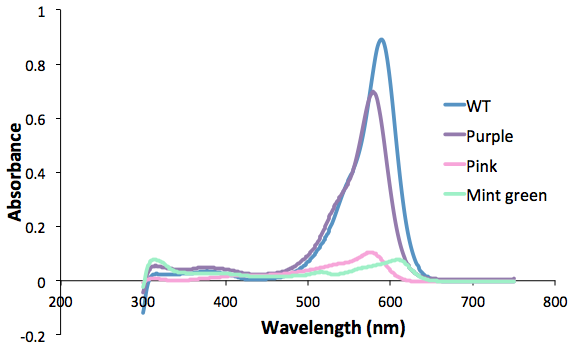
| + | <b>Figure 1. Purple, pink and green mutants compared to the wild type.<br> | ||
| + | Protein was extracted from 50mL of culture and resuspended in 0.5mL TE buffer.</b><br> | ||
| + | [[File:Sydney_australia_amilcp_spectrum.png|620px|center]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
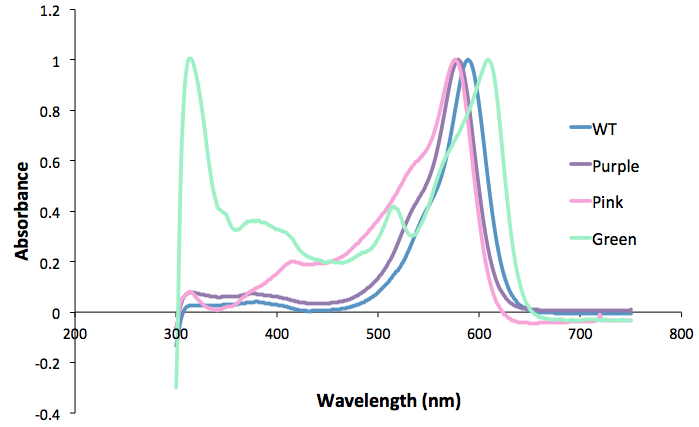
| + | <b>Figure 2. Spectrum scan of the extracted protein from the different coloured amilCP mutants. Protein concentration is equal between all samples.</b><br> | ||
| + | [[Image:Sydney_australia_amilcp_spectrum4.png |620px|center]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <b>Figure 3. Spectrum scan of the extracted protein from the different coloured amilCP mutants, with the spectrums all adjusted to the same levels to show peaks.</b> | ||
| + | |}; | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
{|width='80%' style='border:1px solid gray' | {|width='80%' style='border:1px solid gray' | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 17:42, 28 October 2016
This experience page is provided so that any user may enter their experience using this part.
Please enter
how you used this part and how it worked out.
Applications of BBa_K592009
User Reviews
UNIQfb9d01e2b2265994-partinfo-00000000-QINU
UNIQfb9d01e2b2265994-partinfo-00000001-QINU
UNIQfb9d01e2b2265994-partinfo-00000002-QINU
|
•••••
iGEM Sydney Australia |
File:Https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/2/21/T--Sydney Australia--amilCPmutants.png The Sydney_ Australia 2016 team improved this part via error prone PCR for inclusion in our ethylene biosensor. We managed to produce three new colour strains, a purple, a pink, and a mint green.
Figure 1. Purple, pink and green mutants compared to the wild type.
|
|
•••••
iGEM Uppsala 2013 |
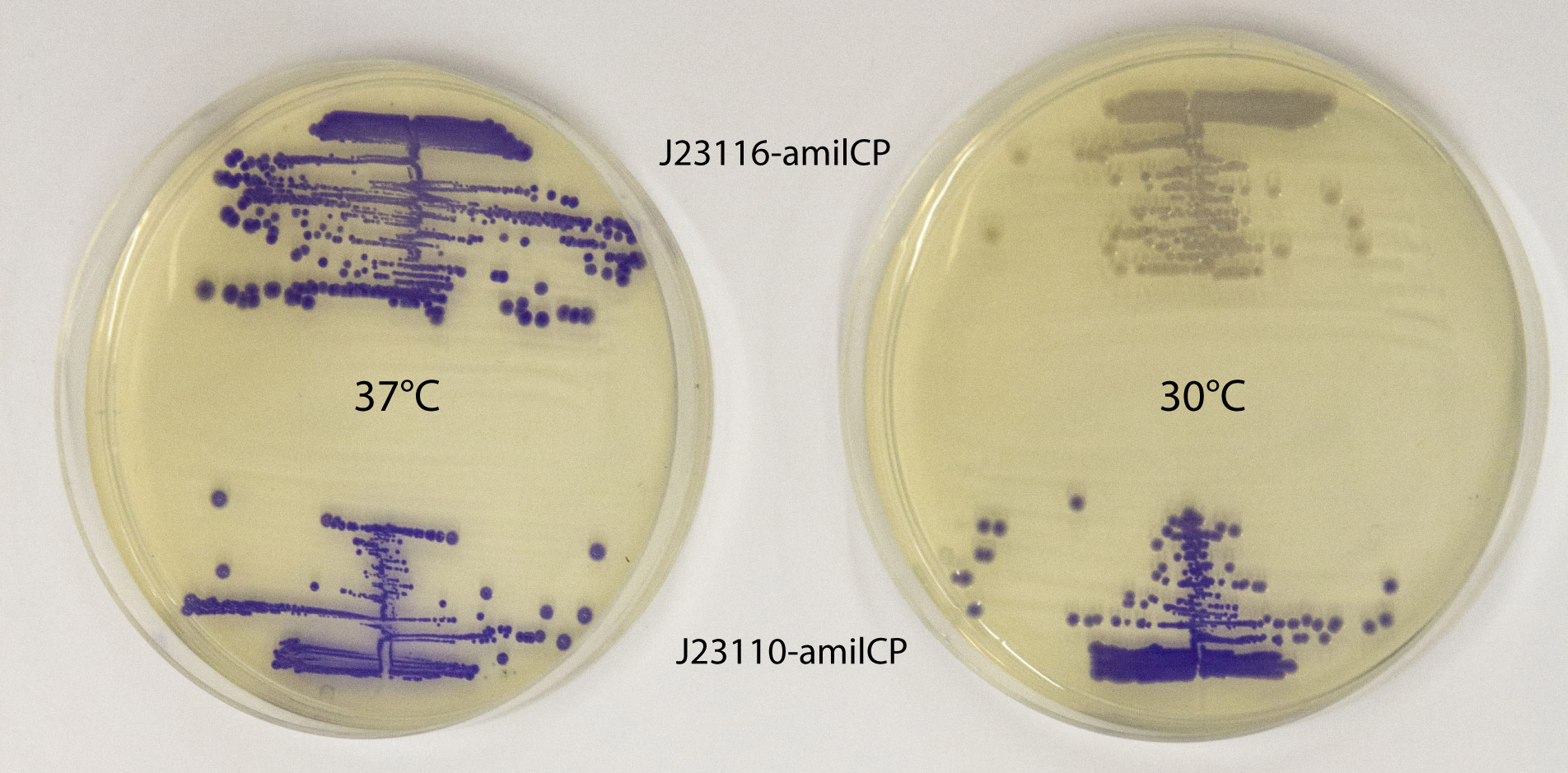
This part works well as a reporter. As expected, different levels of expression of amilCP in E. coli MG1655 generates different intensities in color. amilCP expressed from the high copy plasmid pSB1C3 by weak promoter J23116 (top part of plates) and strong promoter J23110 (bottom part of plates) at 37 °C (left plate) and 30 °C (right plate) respectively. After incubation at 30 °C a clear difference in color intensity can be seen between the expression from the two different promoters, while after incubation at 37 °C the difference in intensity is much less pronounced. This indicates that expression from the promoters are temperature dependent, and it shows that the quantifiable range of the chromoproteins is somewhat limited. Plates were incubated for 23 h at 37 °C or 30 °C followed by 20 h at 22 °C. |
UNIQfb9d01e2b2265994-partinfo-00000005-QINU
|
•••••
Paris_Saclay 2013 |
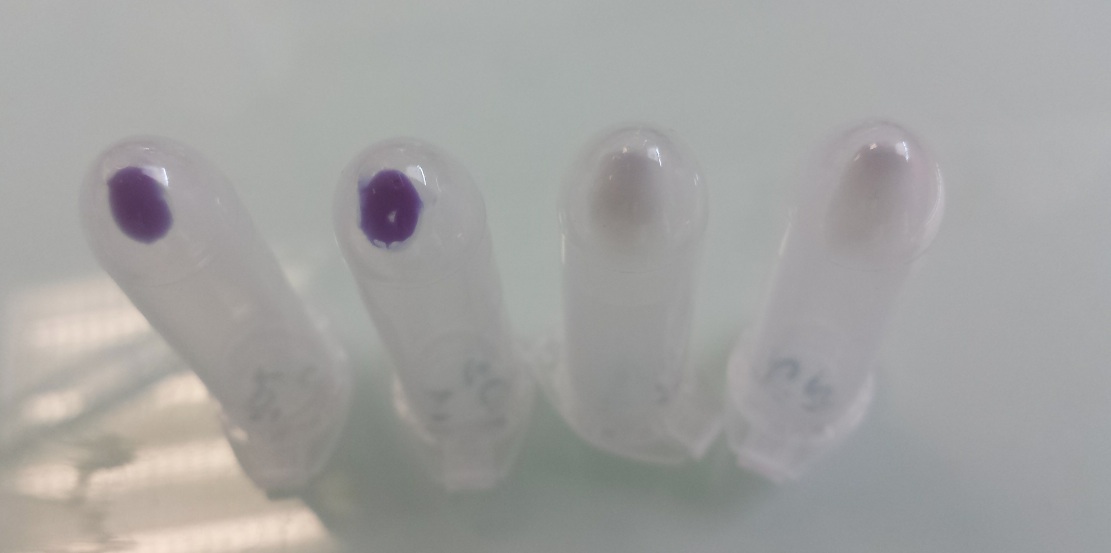
Our team improved the biobrick BBa_K592009 by assembly of biobricks B0034, BBa_K592009 and B0015 to construct a composite part including a ribosome binding site, full length of amilCP gene and double terminator. We used it as one of our reporter gene in Escherichia coli to controlled activator or repressor activity of our promotor under aerobic or anaerobic conditions (Pndh*, PnirB, PnarG, PnarK, PbphR1, PbphR2). Construction : Pndh* (repressor) + BBa_K1155003 :
Tubes 1 and 2 : cellular pallet of cultures grown in aerobic conditions Tubes 3 and 4 : cellular pallet of cultures grown in anaerobic conditions |
UNIQfb9d01e2b2265994-partinfo-00000007-QINU
UNIQfb9d01e2b2265994-partinfo-00000008-QINU
UNIQfb9d01e2b2265994-partinfo-00000009-QINU
|
•••••
iGEM Michigan 2013 |
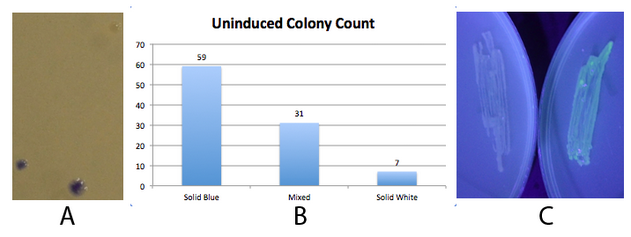
The 2013 Michigan igem team successfully used this part to produce amilCP. Fig 2. - An inducible fim transcriptor system changes states and produces protein output NEB 10-beta E. coli, which lack the native fim switch (fimS) and known fim recombinases, were co-transformed with K1077007(amilCP j23100 fim switch) or K1077003(GFP j23100 fim switch), and K1077002 (aTc inducible fimE, HSL inducible hbiF) and plated on to LB plates with or without inducer. A) Close up of 3 colonies on a plate containing K1077007 and K1077002 co transformants. Three distinct phenotypes were observed: Solid Blue colonies(bottom left), Mixed colonies that had distinct white and blue regions(bottom middle), and Solid White colonies(top right). Therefore, the uninduced fim transcriptor in the context of K1077002 is subject to leaky fimE and/or hbiF activity. B) Quantification of the phenotypes observed on the plate in A. C) When induced with 4.32µM aTc and grown overnight (left) , no GFP is produced as expected due to induced fimE turning the switch OFF. When induced with 1µM HSL and grown overnight (right), GFP is produced as expected due to induced hbiF turning the switch ON. |
|
•••••
Immudzen |
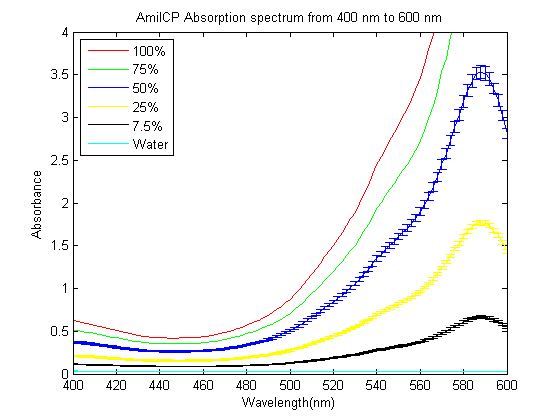
As part of the 2013 CU Boulder project we worked on separating RFP from AmilCP and we measured the spectrum of AmilCP from 400 nm to 600 nm. We also found that when running on an agarose gel RFP will run down on the gel while AmilCP runs up on the gel. |
|
•••••
iGEM 2013 Hong_Kong_HKUST Trevor Y.H. HO |
Error creating thumbnail: Invalid thumbnail parameters This part was employed in testing our Gibson Assembly protocol. In the experiment design, the mRFP coding DNA sequence in J04450 was replaced with that of amilCP. The resulting plate from transformation of the post-reaction mixture is shown. The color of the blue chromoprotein was clearly distinguished from that of mRFP, which aided in my evaluation of the performance of Gibson Assembly. |
|
BBa_K592009 iGEM Groningen 2012 |
Our team has managed to couple this biobrick part with our promoters: alsT, fnr, and sboA. The cloning was done in BBa_K818000 (plasmid backbone for B. subtilis, engineered by team Groningen 2012), to allow color expression in B. subtilis. We utilized a strong RBS BBa_B0034 for pigment expression in E. coli and B. subtilis. The purple/blue colour was strongly visible in E.coli without any induction, while the expression in B. subtilis was more subtle (B. subtilis colony looks slightly blue on the plate agar). After induction of the promoter before AmilCP, B. subtilis also turned clearly purple/blue. Please have a look at the page of BBa_K818400 for more information. |
|
No review score entered. User:agynna |
iGEM Team Uppsala University 2012 We have observed that expression of amilCP confers a noticeable fitness cost in E coli. This is surprising, given that such behaviour is not seen in other homologous chromoproteins and fluorescent proteins. We thus recommend using the new aeBlue (BBa_K864401) chromoprotein for blue color expression, which also has a more clear blue color. |