Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1981202"
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
===Usage and Biology=== | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
| − | [[ | + | ==Activity Analysis of [https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K863005 ECOL]== |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Initial activity tests of purified fractions=== | ||
| + | |||
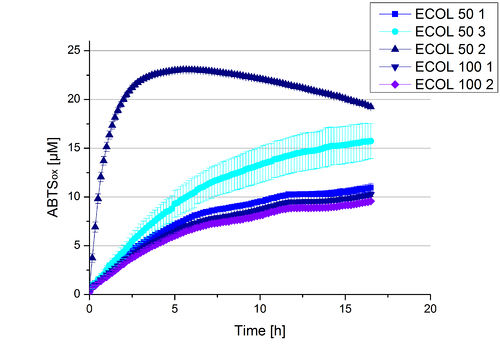
| + | A cultivation of ECOL has been done and the fractions of the purification were analyzed further on protein content and re-buffered subsequently into deionized H<sub>2</sub>O. To determine the protein content afterwards because of loss of proteins through re-buffering, another [http://2012.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Amsterdam/Labjournal#Tuesday_October_17th/ protein concentration measurement] has been done. The re-buffered fractions have been incubated with 0.4 mM CuCl<sub>2</sub> to gain higher activity of the laccases, because they are copper-dependent. Standard activity tests were done with all ECOL fractions with adjusted protein content for comparison. The experimental setup included the ECOL fractions, Britton-Robinson buffer (pH 5) and 0.1 mM ABTS. Measurements were done at 25 °C. Resulting, one fraction showed very high activity in comparison to the other fractions (see Fig. 10). This fraction, fraction 50% 2, oxidized up to 23 µM ABTS after 5 hours. The first number of the sample indicates the percentage of used elution buffer, whereas the second number stands for the fraction number of this elution. This fraction was set as containing 90 % ECOL laccase of the whole protein content. Therefore a ECOL concentration of 63,9 µg mL<sup>-1</sup> was gained. This fraction was analyzed further on pH optimum, temperature dependency and ABTS saturation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Bielefeld2012_new_ECOL_activity.jpg|500px|thumb|center|'''Figure 10:''' Activity assay of each purified fraction of the cultivation with ECOL. Samples were re-buffered into H<sub>2</sub>O and the protein amount in each fraction has been adjusted. The measurements were done using the [http://2012.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Analytics#General_setup_of_enzyme_activity_measurements/ standard activity assay protocol] over night. The first number indicates the percentage of used elution buffer, whereas the second number stands for the fraction number of this elution.]] | ||
===Characterization=== | ===Characterization=== | ||
Revision as of 15:24, 14 October 2016
Autoinducer-2 Response Device B
Device B long description
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 1996
Usage and Biology
Activity Analysis of ECOL
Initial activity tests of purified fractions
A cultivation of ECOL has been done and the fractions of the purification were analyzed further on protein content and re-buffered subsequently into deionized H2O. To determine the protein content afterwards because of loss of proteins through re-buffering, another [http://2012.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Amsterdam/Labjournal#Tuesday_October_17th/ protein concentration measurement] has been done. The re-buffered fractions have been incubated with 0.4 mM CuCl2 to gain higher activity of the laccases, because they are copper-dependent. Standard activity tests were done with all ECOL fractions with adjusted protein content for comparison. The experimental setup included the ECOL fractions, Britton-Robinson buffer (pH 5) and 0.1 mM ABTS. Measurements were done at 25 °C. Resulting, one fraction showed very high activity in comparison to the other fractions (see Fig. 10). This fraction, fraction 50% 2, oxidized up to 23 µM ABTS after 5 hours. The first number of the sample indicates the percentage of used elution buffer, whereas the second number stands for the fraction number of this elution. This fraction was set as containing 90 % ECOL laccase of the whole protein content. Therefore a ECOL concentration of 63,9 µg mL-1 was gained. This fraction was analyzed further on pH optimum, temperature dependency and ABTS saturation.