Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1824018"
(→Characterization) |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
===Characterization=== | ===Characterization=== | ||
| − | XJTLU-CHINA tested accumulation status of blue chromoprotein with two different fast digestion tag,lva and aav tag, under the regulation of T7 promter-lac operator in E.coil strain BL21 (DE 3). The construction | + | XJTLU-CHINA tested accumulation status of blue chromoprotein with two different fast digestion tag,lva and aav tag, under the regulation of T7 promter-lac operator in E.coil strain BL21 (DE 3). The construction is shown in Figure 1. |
<br>[[Image:Aeblue.png|400px]] | <br>[[Image:Aeblue.png|400px]] | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
<br>'''Figure 3:''' The color of non-tag, AAV tail and LVA tail after induced 720 minutes. | <br>'''Figure 3:''' The color of non-tag, AAV tail and LVA tail after induced 720 minutes. | ||
| − | <br>As shown in the Figure 2, both blue chromoprotein with LVA tail and AAV tail had less accumulation amount than the group of no-tail, which indicated both LVA tail and AAV tail raised the degradation rate. In addition, blue chromoprotein with LVA tail had an even lower accumulation in host cells compared to blue chromoprotein with AAV tail. It was speculated that the LVA tail provided a higher degradation rate. In conclusion, the tails can speed up the degradation of chromoprotein, and LVA tail is highly effective in protein degradation, whereas in our project the AAV tag was chosen to gain a balance between clear color performance and high speed of degradation. | + | <br>As shown in the Figure 2, both blue chromoprotein with LVA tail and AAV tail had less accumulation amount than the group of no-tail, which indicated both LVA tail and AAV tail raised the degradation rate. In addition, blue chromoprotein with LVA tail had an even lower accumulation in host cells compared to blue chromoprotein with AAV tail. It was speculated that the LVA tail provided a higher degradation rate. In conclusion, the tails can speed up the degradation of chromoprotein, and LVA tail is highly effective in protein degradation, whereas in our project the AAV tag was chosen to gain a balance between clear color performance and high speed of degradation. |
===References=== | ===References=== | ||
Latest revision as of 05:08, 18 September 2015
aeBlue Blue chormoprotein with lva tag
AeBlue chromoprotein could be expressed as a deep blue color in E.coli, which was added by Uppsala University in 2012. We add lva tag to before stop codon to increase the degradation of the Aeblue chromoprotein, which is necessary in our earth map for color changing.
Characterization
XJTLU-CHINA tested accumulation status of blue chromoprotein with two different fast digestion tag,lva and aav tag, under the regulation of T7 promter-lac operator in E.coil strain BL21 (DE 3). The construction is shown in Figure 1.
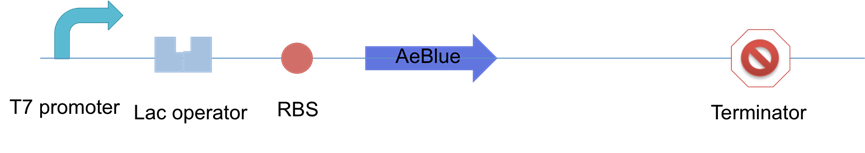
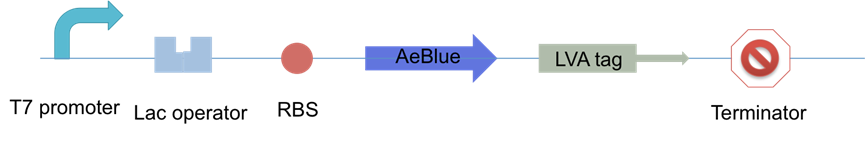
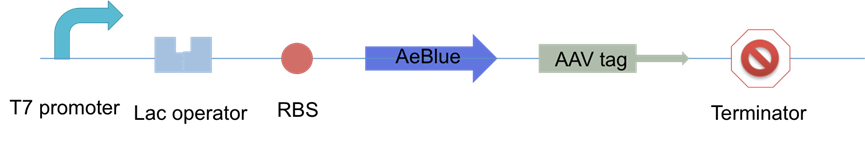
Figure 1: The constructions that XJTLU-CHINA made to perform chromoprotein accumulation test.
Three groups were used in experiments: AeBlue chromoprotein, AeBlue chromoprotein with AAV tag and AeBlue chromoprotein with LVA tag. Two mono-colonies were chosen from each group. 300ml LB was used to culture the 6 colonies at 37 degrees Celsius for 4 hours. Then 300ul IPTG was added to induce at 16 degrees Celsius for 12 hours. The data was collected from 5 hours to 12 hours, totally 13 points. For each point, 20ml colony liquid was obtained from the 300ml LB culture. 4ml of them was used for OD measurement at 600nm and the rest 16ml of them was used for protein extraction.
Firstly, 16ml bacteria were centrifuged at 6000 rpm for 5 minutes. Then the supernatant was discarded and 10ml PBS was added to resuspend the sediment. After using ultrasonic wave to break the cell, 4ml of mixture was centrifuged at 12000 rpm for 5 minutes. Finally, the absorbance of blue chromoprotein was measured at 597nm by spectrophotometer.
Results as shown in diagram below.
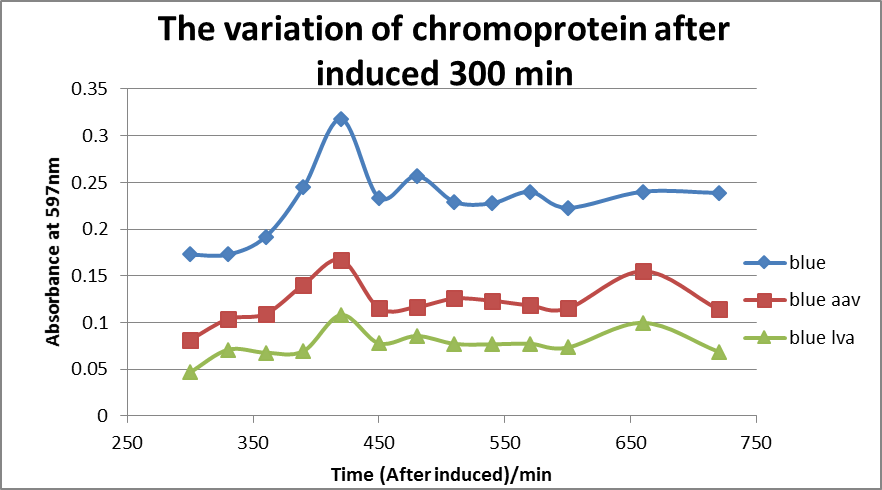
Figure 2: The variation of chromoprotein after induced 300 mins.
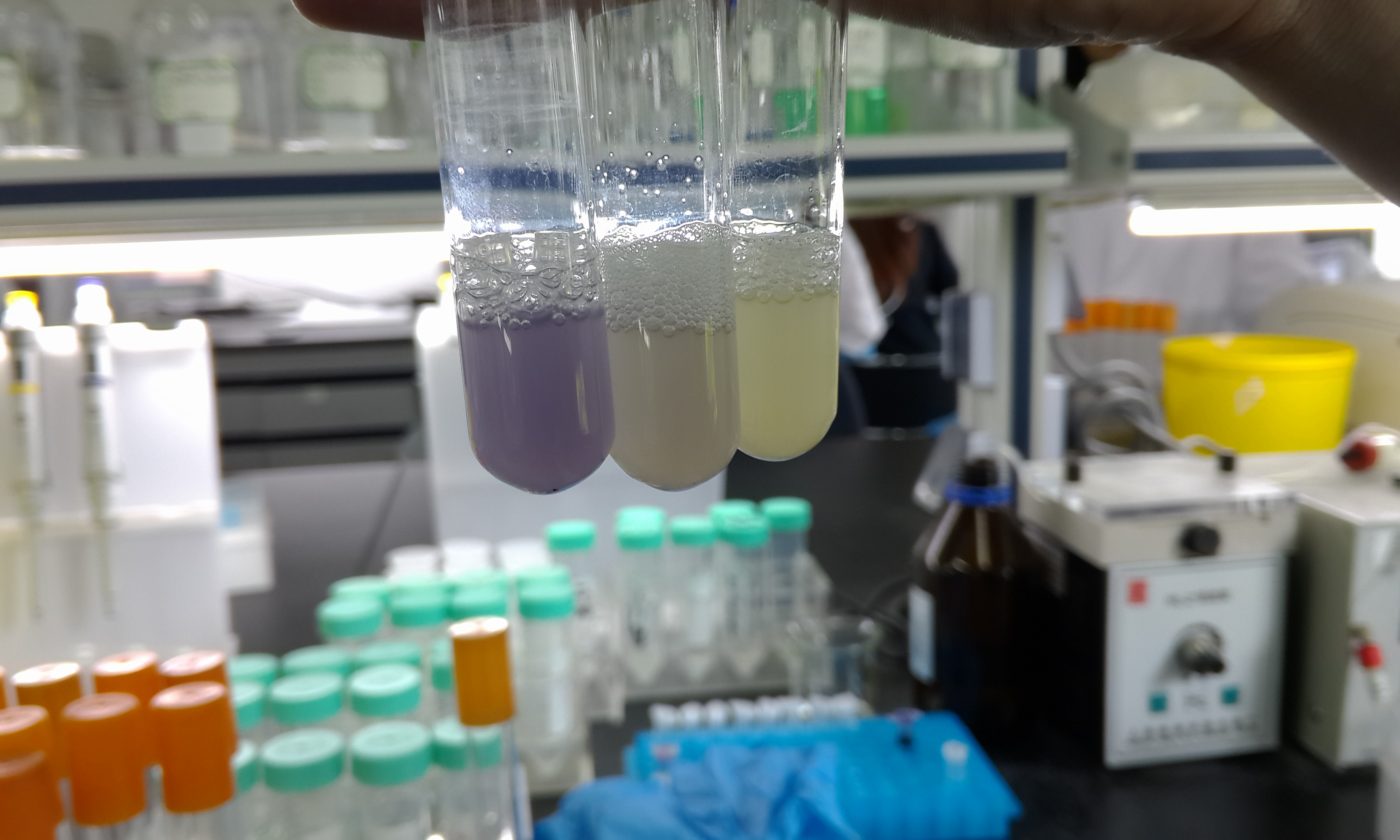

Figure 3: The color of non-tag, AAV tail and LVA tail after induced 720 minutes.
As shown in the Figure 2, both blue chromoprotein with LVA tail and AAV tail had less accumulation amount than the group of no-tail, which indicated both LVA tail and AAV tail raised the degradation rate. In addition, blue chromoprotein with LVA tail had an even lower accumulation in host cells compared to blue chromoprotein with AAV tail. It was speculated that the LVA tail provided a higher degradation rate. In conclusion, the tails can speed up the degradation of chromoprotein, and LVA tail is highly effective in protein degradation, whereas in our project the AAV tag was chosen to gain a balance between clear color performance and high speed of degradation.
References
Anderson,J. (1998) ‘New unstable variants of green fluorescent protein for studies of transient gene expression in bacteria’, Applied and environmental microbiology, 64(6), June, pp.2240-2246.
Usage and Biology
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
