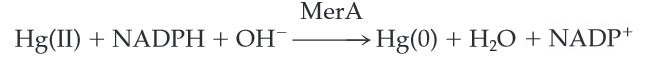Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1420001"
(→Function) |
(→Overview) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
| − | <p>MerA, a cytoplasmic mercuric ion reductase, is the essential component of bacterial mercury resistance. | + | <p>MerA, a cytoplasmic mercuric ion reductase, is the essential component of bacterial mercury resistance. MerA couples with the organomercurial lyase, MerB to reduce the toxicity of organic and inorganic mercury compounds. While MerA and MerB are the key mercury detoxification enzymes, they orchestrate with mercury transport proteins, MerT and MerP, to confer bacterial mercury resistance.</p> |
<p></p> | <p></p> | ||
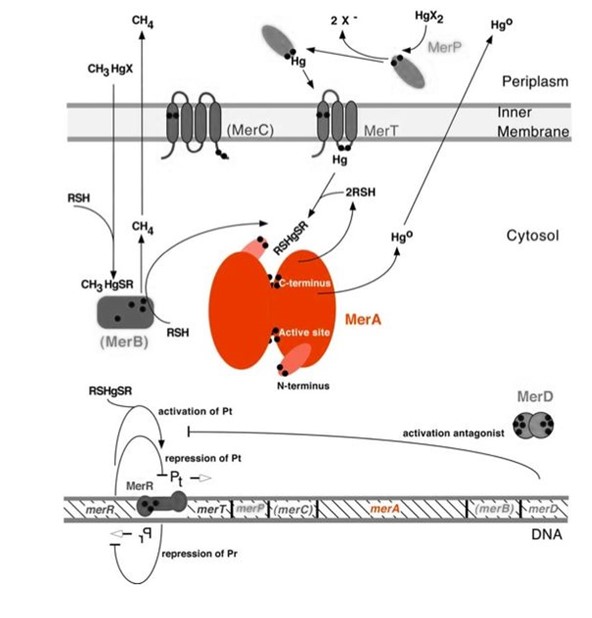
Figure 1 shows the interactions of MerA, mercury compounds, and other ''mer'' proteins. MerA and gene ''merA'' are highlighted in orange.''merA'' is located downstream of ''mer'' genes that encodes mercury transport proteins. | Figure 1 shows the interactions of MerA, mercury compounds, and other ''mer'' proteins. MerA and gene ''merA'' are highlighted in orange.''merA'' is located downstream of ''mer'' genes that encodes mercury transport proteins. | ||
[[File:MerA.jpg|center]] | [[File:MerA.jpg|center]] | ||
<p></p> | <p></p> | ||
| − | This figure is adapted from "Bacterial mercury resistance from atoms to ecosystems". Reference: ''T. Barkay et al''. FEMS Microbiology Reviews 27 (2003) 355-384. | + | Figure 1. Model of mercury resistance operon. The symbol • indicates a cystein residue. (This figure is adapted from "Bacterial mercury resistance from atoms to ecosystems". Reference: ''T. Barkay et al''. FEMS Microbiology Reviews 27 (2003) 355-384.) |
== Molecular Function == | == Molecular Function == | ||
Revision as of 23:46, 12 October 2014
merA, mercuric reductase from Serratia marcescens
Overview
MerA, a cytoplasmic mercuric ion reductase, is the essential component of bacterial mercury resistance. MerA couples with the organomercurial lyase, MerB to reduce the toxicity of organic and inorganic mercury compounds. While MerA and MerB are the key mercury detoxification enzymes, they orchestrate with mercury transport proteins, MerT and MerP, to confer bacterial mercury resistance.
Figure 1 shows the interactions of MerA, mercury compounds, and other mer proteins. MerA and gene merA are highlighted in orange.merA is located downstream of mer genes that encodes mercury transport proteins.
Figure 1. Model of mercury resistance operon. The symbol • indicates a cystein residue. (This figure is adapted from "Bacterial mercury resistance from atoms to ecosystems". Reference: T. Barkay et al. FEMS Microbiology Reviews 27 (2003) 355-384.)
Molecular Function
MerA catalyzes the reduction of mercuric ion to the relative inert, volatile monoatomic mercury in a NADPH dependent reaction.
Scheme 1. MerA Catalyzed Reaction
Structure and Mechanism
Characterization of merA
To test the effect of MerA to the level of mercury resistance, we generated a merA deletion mutant and characterized it by zone of inhibition test.
Zone of Inhibition Results
Figure 2. Zones of Inhibition Test For Mercury Resistance Activity. Three different plasmids were expressed in Escherichia coli strain K12 to compare level of mercury resistance. (A)Plates of ZOI test. Left, K12 conntaining pBBRBB::mer; center,K12 containing pBBRBB::gfp; right, K12 strain containing pBBRBB::merΔmerA, or the merA deletion mutant. (b) Graphical representation of the size of zones of inhibition diameter. The diameter of the Zone of Inhibition was measured in triplicate. Green corresponds to pBBRBB::gfp, blue to pBBRBB::mer, and red to pBBRBB::merΔmerA.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 1201
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 1249
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 1311
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 1522 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]