Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K823036"
(→Methods) |
|||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
| − | Visit our project page for more usefull parts of our [http://2012.igem.org/Team:LMU-Munich/Bacillus_BioBricks '''''BacillusB'''''io'''B'''rick'''B'''ox]. | + | Visit our project page for more usefull parts of our [http://2012.igem.org/Team:LMU-Munich/Bacillus_BioBricks '''''BacillusB'''''io'''B'''rick'''B'''ox]. This part was also evaluated in the publication [http://www.jbioleng.org/content/7/1/29 The ''Bacillus'' BioBrick Box: generation and evaluation of essential genetic building blocks for standardized work with ''Bacillus subtilis''] by Radeck ''et al.''. |
===Evaluation=== | ===Evaluation=== | ||
Revision as of 17:06, 3 February 2014
cMyc-tag (Freiburg standard+RBS)
cMyc-tag with RBS in Freiburg standard.
Find out more about the design of our prefix with ribosome binding site.
prefix:GAATTCCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGATAAGGAGGAACTACTATGGCCGGC
suffix:ACCGGTTAATACTAGTAGCGGCCGCTGCAGT
The cMyc-tag is a tag derived from the cMyc gene product. Antibodies were derived from the immunisation with synthetic peptides from the cMyc sequence [http://mcb.asm.org/content/5/12/3610.short Mol. Cell. Biol. 5,3610-3616]). The aminoacid sequence is EQKLISEEDL.
This is a part created by the LMU-Munich 2012 team. We added five tags to the registry, all in the Freiburg standard for N-and C-terminal fusions:
- cMyc - tag
Visit our project page for more usefull parts of our [http://2012.igem.org/Team:LMU-Munich/Bacillus_BioBricks BacillusBioBrickBox]. This part was also evaluated in the publication [http://www.jbioleng.org/content/7/1/29 The Bacillus BioBrick Box: generation and evaluation of essential genetic building blocks for standardized work with Bacillus subtilis] by Radeck et al..
Evaluation
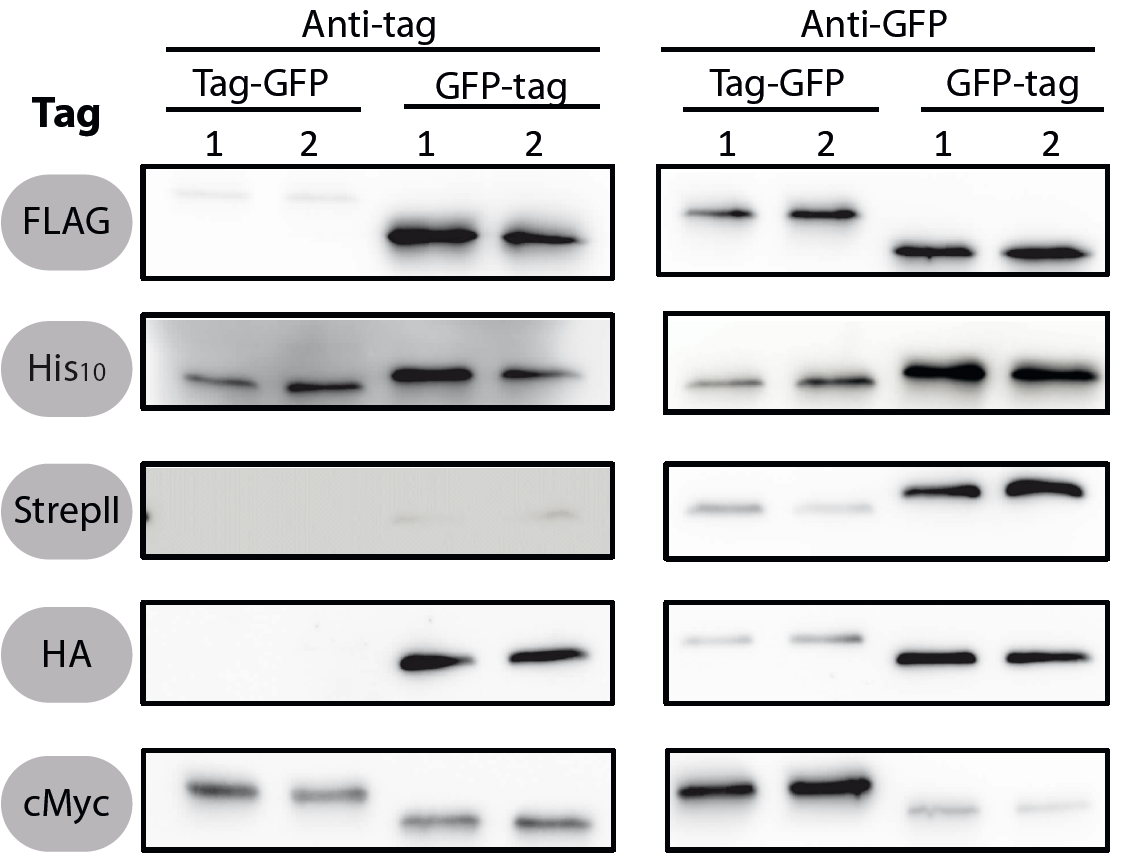
All 5 epitope tags were fused C- and N-terminally to GFP using the NgoMIV and AgeI restriction sites. These constructs were expressed in Bacillus subtils using pSBBs0K-Pspac. This vector did not need to be induced by IPTG due to a premature stop codon in the lacI gene.
|
Methods
To verify the functionality of the epitope tags, Western blot analyses of the strains TMB1920-TMB1929 were performed. LB medium (15 ml) was inoculated 1:100 from overnight culture and grown at 37°C and 200 rpm to OD600 ~ 0.5. Of this, 10 ml were harvested by centrifugation (8000 × g, 5 min) and the pellets stored at -20°C. Pellets were resuspended in 1 ml disruption buffer (50 mM Tris–HCl pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl) and lysed by sonication. Samples (12 μl of lysate) were loaded per lane on two 12.5% SDS-polyacrylamide gels and SDS-PAGE was performed according standard procedure [60]. One gel was stained with colloidal coomassie, the other one was used for protein transfer to a PVDF membrane (Merck Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) by submerged blotting procedure (Mini Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA)). After protein transfer, the membranes were treated with the following antibodies and conditions. Detailed protocols can be found [http://www.jbioleng.org/content/7/1/29/suppl/S3 here].
GFP
Probing with primary antibodies takes place with rabbit anti-GFP antibodies (1:3000, Epitomics, No. 1533). Horseradish-peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated anti-rabbit antibodies (1:2000, Promega, W401B) were used as secondary antibody. Hybridization of both antibodies was carried out in Blotto-buffer (2.5% (w/v) skim milk powder, 1 × TBS (50 mM Tris–HCl pH 7.6, 0.15 M NaCl)).
cMyc
Rabbit anti-Myc (1:2000, Abcan, ab9106) in TBS, 0.05% (w/v) Tween20, 5% (w/v) skim milk powder and anti-rabbit-HRP (1:2000, Promega, W401B) in Blotto-buffer were used.
Chemiluminescence signals were detected after addition of the HRP-substrate Ace Glow (Peqlab, Erlangen, Germany) using a FusionTM imaging system (Peqlab).
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 24
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]