Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1033206"
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
The backbone pSBLbC is a shuttle vector between E. coli, Lacotbacillus, and probably other lactic acid bacteria <i>(LaB)</i> like <i>Lactococcus lactis</i>. It has been used for subcloning in <i>E. coli</i> and to express the chromoprotein [[Part:BBa_K1033209|amilCP]]. | The backbone pSBLbC is a shuttle vector between E. coli, Lacotbacillus, and probably other lactic acid bacteria <i>(LaB)</i> like <i>Lactococcus lactis</i>. It has been used for subcloning in <i>E. coli</i> and to express the chromoprotein [[Part:BBa_K1033209|amilCP]]. | ||
| − | It is meant to be used for working in <i>E. coli</i> and different lactic acid bacteria, when it is very useful to do preliminary work in <i>E. coli</i>, and transfer finished constructs to LAB. But for that use we recommend the version with erythromycin resistance ([[Part:BBa_K1033207|pSBLbE]]) since that has been successfully used to transform Lactobacillus as well. | + | It's replicon is known to replicate in a wide range of gram positive and gram negative species<sup>[[#Footnote 1|[1]]]</sup>, and the backbone is meant to be used for working in <i>E. coli</i> and different lactic acid bacteria, when it is very useful to do preliminary work in <i>E. coli</i>, and transfer finished constructs to <i>LAB</i>. But for that use we recommend the version with erythromycin resistance ([[Part:BBa_K1033207|pSBLbE]]) since that has been successfully used to transform Lactobacillus as well. |
https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/1/18/Uppsala2013_Shuttle_Vector_pSBLBC_cp29_amilCP1.png | https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/1/18/Uppsala2013_Shuttle_Vector_pSBLBC_cp29_amilCP1.png | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
<h3>Construction</h3> | <h3>Construction</h3> | ||
| − | It was made by replacing the replicon of the BioBrick compatible plasmid ([[Part:BBa_K864001|pSB4C15]]) with a broad range replicon from the engineered plasmid pJP059. The replicon is also referred to as pSH71 and is related to pWV01 and that family of rolling circle replicating plasmids.<sup>[[#Footnote | + | It was made by replacing the replicon of the BioBrick compatible plasmid ([[Part:BBa_K864001|pSB4C15]]) with a broad range replicon from the engineered plasmid pJP059. The replicon is also referred to as pSH71 and is related to pWV01 and that family of rolling circle replicating plasmids.<sup>[[#Footnote 2|[2]]]</sup> |
We also had to change the promotor of the chloramphenicol resistance cassette to one that would initiate transcription effectively in <i>Lactobacillus</i>. We tried several constitutive promotors but finally got [[Part:BBa_K1033222|CP29]] to work. | We also had to change the promotor of the chloramphenicol resistance cassette to one that would initiate transcription effectively in <i>Lactobacillus</i>. We tried several constitutive promotors but finally got [[Part:BBa_K1033222|CP29]] to work. | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
<h3>References</h3> | <h3>References</h3> | ||
| − | <div id="Footnote 1"></div> | + | <div id="Footnote 1"></div> [1] I. Pérez-Arellano, M. Zúñiga, and G. Pérez-Martínez (2001), Construction of Compatible Wide-Host-Range Shuttle Vectors for Lactic Acid Bacteria and Escherichia coli, Plasmid 46 (2) 106-116. |
| − | <div id="Footnote 2"></div> | + | <div id="Footnote 2"></div> [2] I. Pérez-Arellano, M. Zúñiga, and G. Pérez-Martínez (2001), Construction of Compatible Wide-Host-Range Shuttle Vectors for Lactic Acid Bacteria and Escherichia coli, Plasmid 46 (2) 106-116. |
<!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | <!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | ||
Revision as of 23:11, 3 October 2013
Lactobacillus shuttle vector pSBLbC
The backbone pSBLbC is a shuttle vector between E. coli, Lacotbacillus, and probably other lactic acid bacteria (LaB) like Lactococcus lactis. It has been used for subcloning in E. coli and to express the chromoprotein amilCP.
It's replicon is known to replicate in a wide range of gram positive and gram negative species[1], and the backbone is meant to be used for working in E. coli and different lactic acid bacteria, when it is very useful to do preliminary work in E. coli, and transfer finished constructs to LAB. But for that use we recommend the version with erythromycin resistance (pSBLbE) since that has been successfully used to transform Lactobacillus as well.
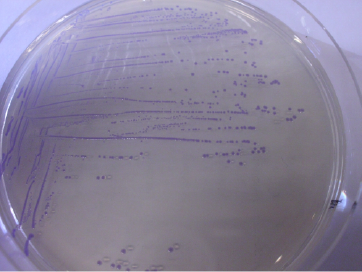
Fig 1: E. coli D5-alpha carrying pSBLbC with blue chromoprotein amilCP, and lactobacillus promotor CP29
Construction
It was made by replacing the replicon of the BioBrick compatible plasmid (pSB4C15) with a broad range replicon from the engineered plasmid pJP059. The replicon is also referred to as pSH71 and is related to pWV01 and that family of rolling circle replicating plasmids.[2]
We also had to change the promotor of the chloramphenicol resistance cassette to one that would initiate transcription effectively in Lactobacillus. We tried several constitutive promotors but finally got CP29 to work.
See design subpage for more details.
Results
We have successfully subcloned small constructs into pSBLbC and used it to transform E. coli D5-alpha. Judging from levels of expression, copy number in E. coli is lower than pSB3K3. Despite several attempts we have not managed to transform Lactobacillus reuteri or Lactobacillus plantarum. We strongly suspect the resistance cassette is at fault since positive controls on antibiotic free agar plates have grown, but we have not had enough time to work out a solution. Please see our shuttle vector with erythromycin resistance, which has met with more success in that area.
References
[1] I. Pérez-Arellano, M. Zúñiga, and G. Pérez-Martínez (2001), Construction of Compatible Wide-Host-Range Shuttle Vectors for Lactic Acid Bacteria and Escherichia coli, Plasmid 46 (2) 106-116. [2] I. Pérez-Arellano, M. Zúñiga, and G. Pérez-Martínez (2001), Construction of Compatible Wide-Host-Range Shuttle Vectors for Lactic Acid Bacteria and Escherichia coli, Plasmid 46 (2) 106-116.Sequence and Features
- 10INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]Illegal prefix found in sequence at 3036
Illegal suffix found in sequence at 1 - 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal EcoRI site found at 3036
Illegal NheI site found at 1981
Illegal SpeI site found at 2
Illegal PstI site found at 16
Illegal NotI site found at 9
Illegal NotI site found at 3042 - 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal EcoRI site found at 3036
Illegal BamHI site found at 1960 - 23INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]Illegal prefix found in sequence at 3036
Illegal suffix found in sequence at 2 - 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal prefix found in sequence at 3036
Illegal XbaI site found at 3051
Illegal SpeI site found at 2
Illegal PstI site found at 16 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
