Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K863022"
(→Substrate Analysis) |
|||
| Line 99: | Line 99: | ||
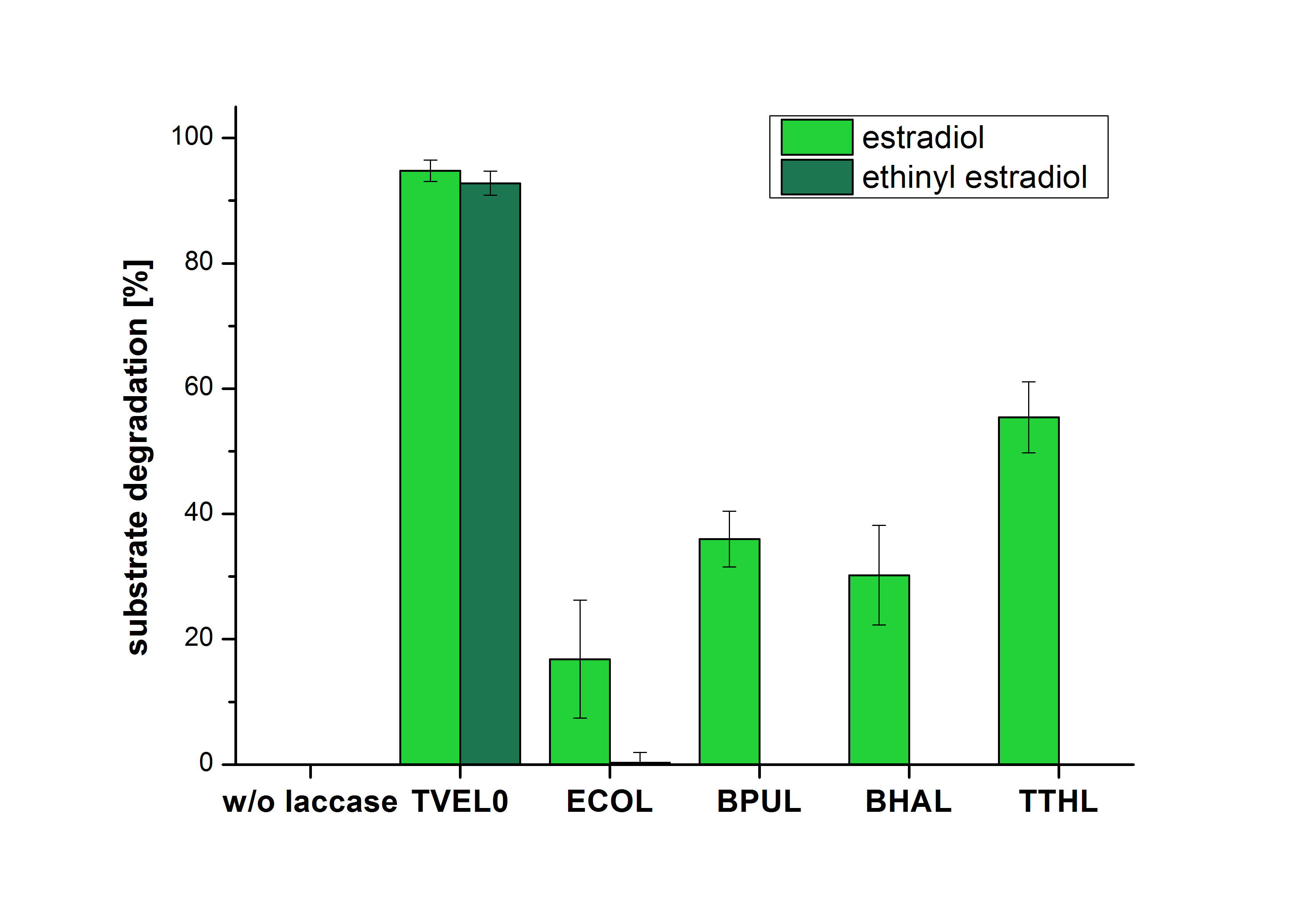
[[Image:Bielefeld2012_Ohne_ABTS.jpg|400px|thumb|left|'''Figure 2: Degradation of estradiol (dark green) and ethinyl estradiol (light green) with the different laccases after 5 hours without ABTS.''' In the graph it is shown that the bought laccase TVEL0 which was used as positive control is able to degrade more than 90 percent of the used substrates. None of the bacterial laccases are able to degrade ethinyl estradiol without ABTS but estradiol is degraded in a range from 16 %(ECOL) to 55 % (TTHL). The original concentrations of substrates were 2 µg per approach. (n = 4)]] | [[Image:Bielefeld2012_Ohne_ABTS.jpg|400px|thumb|left|'''Figure 2: Degradation of estradiol (dark green) and ethinyl estradiol (light green) with the different laccases after 5 hours without ABTS.''' In the graph it is shown that the bought laccase TVEL0 which was used as positive control is able to degrade more than 90 percent of the used substrates. None of the bacterial laccases are able to degrade ethinyl estradiol without ABTS but estradiol is degraded in a range from 16 %(ECOL) to 55 % (TTHL). The original concentrations of substrates were 2 µg per approach. (n = 4)]] | ||
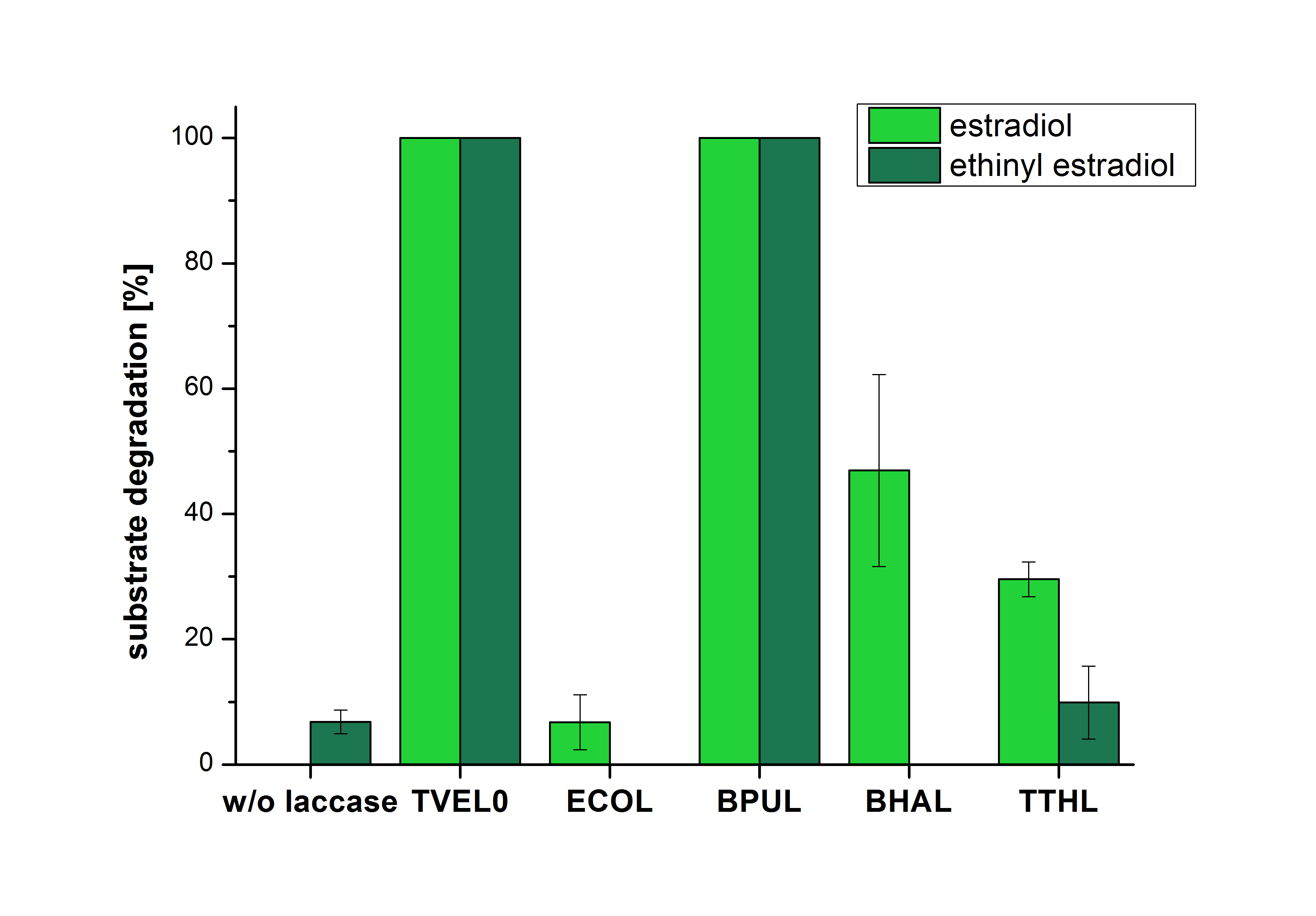
[[Image:Bielefeld2012_Mit_ABTS.jpg|400px|thumb|right|'''Figure 3: Degradation of estradiol (blue) and ethinyl estradiol (red) with the different laccases after 10 minutes hours with ABTS added.''' The commercial laccase TVEL0 which was used as positive control is able to degrade all of the used substrates. The bacterial laccase BPUL degraded 100 % of ethinyl estradiol and estradiol. ECOL the laccase from ''E. coli'' degraded 6.7 % estradiol and none of the used ethinyl estradiol. BHAL degraded 46.9 % of estradiol but no ethinyl estradiol. The laccase TTHL from ''Thermus thermophilus'' degraded 29.5 % of estradiol and 9.8 % ethinyl estradiol. The original concentrations of substrates were 2 µg per approach. (n = 4)]] | [[Image:Bielefeld2012_Mit_ABTS.jpg|400px|thumb|right|'''Figure 3: Degradation of estradiol (blue) and ethinyl estradiol (red) with the different laccases after 10 minutes hours with ABTS added.''' The commercial laccase TVEL0 which was used as positive control is able to degrade all of the used substrates. The bacterial laccase BPUL degraded 100 % of ethinyl estradiol and estradiol. ECOL the laccase from ''E. coli'' degraded 6.7 % estradiol and none of the used ethinyl estradiol. BHAL degraded 46.9 % of estradiol but no ethinyl estradiol. The laccase TTHL from ''Thermus thermophilus'' degraded 29.5 % of estradiol and 9.8 % ethinyl estradiol. The original concentrations of substrates were 2 µg per approach. (n = 4)]] | ||
| + | <br style="clear: both" /> | ||
| + | == Immobilization == | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:File:Bielefeld2012-Immobilized_proteins.jpg|500px|left|thumb|'''Figure 20''': The percentage of laccases immobilized to CPC-Beads. 99 % of ECOL, 97 % of BPUL and 79 % of BHAL and TTHL laccases were bound to the beads.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:justify;"> | ||
| + | Figure 20 shows the percentage of laccases bound after incubation with CPC-beads, relative to the original concentration. The concentration of laccases in the supernatant after incubation was measured using Roti®-Nanoquant. The results showed that only 21% of BHAL laccases was still present in the supernatant. This illustrates that BHAL was successfully immobilized on the CPC-beads. | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <br style="clear: both" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
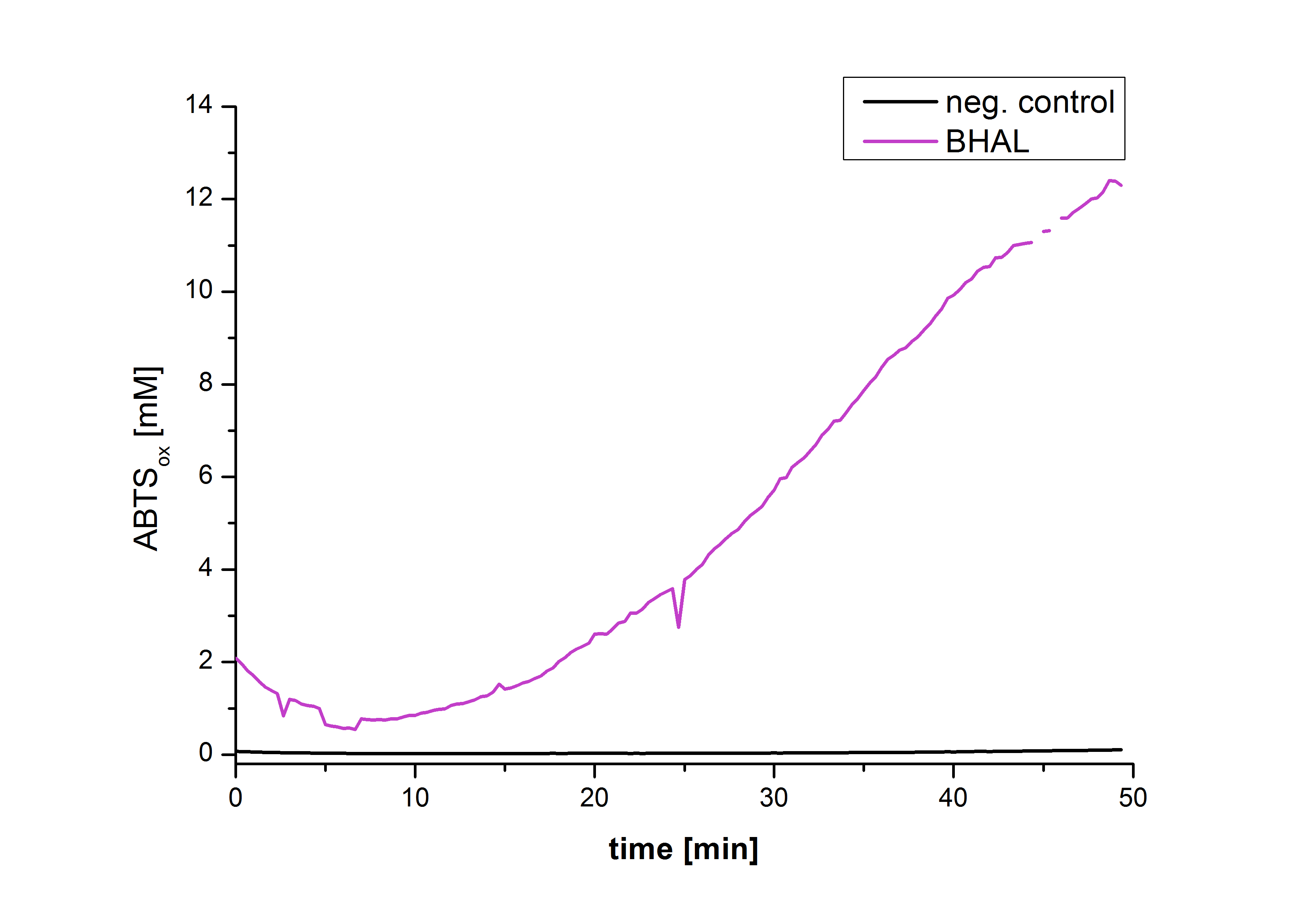
| + | [[Image:Bielefeld2012-Graphen_Bead_Halo.jpg|500px|left|thumb|'''Figure 22''': Illustration of ABTS oxidation by BHAL with time compared to the negative control. The increase in ABTS oxidized proves laccase activity.]] | ||
| + | <div style="text-align:justify;"> | ||
| + | Figure 22 shows the illustration of ABTS oxidation by BHAL with time compared to the negative control. The increase in ABTS oxidized proves laccase activity even if a direct comparison with the original and not immobilized laccase solution was not possible due to the very low concentration of purified BHAL. | ||
<br style="clear: both" /> | <br style="clear: both" /> | ||
Revision as of 02:55, 27 October 2012
bhal laccase from Bacillus halodurans with constitutive promoter J23100, RBS and HIS tag
bhal laccase with constitutive promoter J23100, RBS and HIS tag
Sequence and Features
- 10INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]Illegal XbaI site found at 38
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 8
Illegal NheI site found at 31 - 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal XhoI site found at 219
- 23INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]Illegal XbaI site found at 38
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal XbaI site found at 38
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
First some trials of shaking flask cultivations were made with various parameters to identify the best conditions for production of the His tagged laccase Lbh1 from [http://www.dsmz.de/catalogues/details/culture/DSM-18197.html?tx_dsmzresources_pi5 Bacillus halodurans C-125 ] named BHAL. Due to inactivity of the enzyme in the cell lysate a purification method was established (using Ni-NTA-Histag resin). BHAL could not be detected by SDS-PAGE (theoretical molecular weight of 56 kDa) or activity test by using the BioBrick BBa_K863020 and E. coli KRX as expression system. Due to this results the new BioBrick BBa_K863022 was constructed and expressed E. coli Rossetta-Gami 2. With this expression system the laccase could be produced and analysed via SDS-PAGE. A small scale Ni-NTA-column was used to purify the laccase. The fractionated samples were tested regarding their activity with ABTS and showed ability in oxidizing ABTS. A scale up was not yet performed.
Contents
Cultivation, Purification and SDS-PAGE
Cultivation
The first trials to produce the Lbh1 - laccase from Bacillus halodurans (named BHAL) were performed in shaking flasks with various flask designs (from 100 mL-1 to 1 L flasks, with and without baffles) and under several conditions. The varied parameters in our screening experiments were temperature (27 °C,30 °C and 37 °C), concentration of chloramphenicol (20-170 µg mL-1), induction strategy (autoinduction and manual induction with 0,1 % rhamnose) and cultivation time (6 to 24 h). Furthermore we cultivated with and without 0.25 mM CuCl2 to provide a sufficient amount of copper, which is needed for the active center of the laccase. E.coli KRX was not able to produce active BHAL under the tested conditions, therefore another chassis was chosen. For further cultivations E. coli Rosetta-Gami 2 was transformed with BBa_K863012, because of its ability to translate rare codons. BHAL was produced under the following conditions:
- flask design: shaking flask without baffles
- medium: [http://2012.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Materials#LB_medium LB]-Medium
- antibiotics: 60 µg mL-1 chloramphenicol and 300 µg mL-1 ampicillin
- temperature: 37 °C
- cultivation time: 24 h
Purification
The cells were harvested and resuspended in Ni-NTA-equilibration buffer, mechanically lysed by sonification and centrifuged. After preparing the cell paste the BHALlaccase could not be purified with the 15 mL column, because of the column was not available. For this reason a small scale purification (6 mL) of the supernatant of the lysate was performed with a [http://2012.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Production#Syringe_method 1 mL Ni-NTA-column]. The elution was collected in 1 mL fractions.
SDS-PAGE
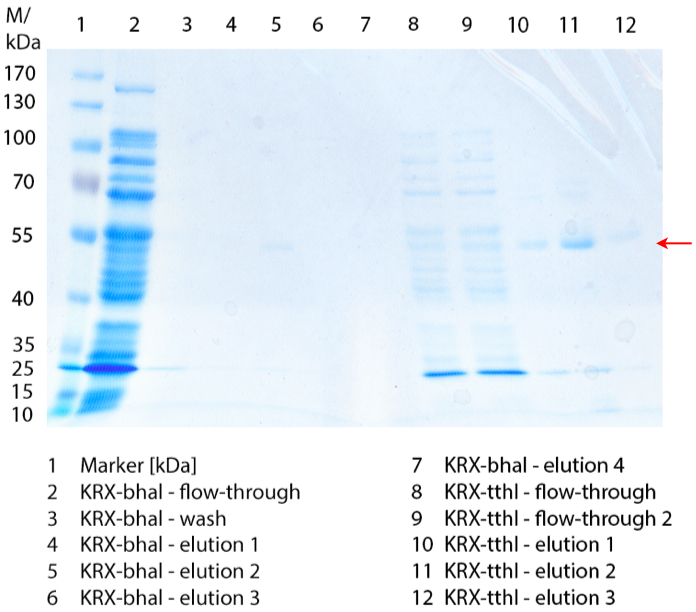
In figure 1 the different fractions of the purified cell lysate of E. coli Rosetta-Gami 2 with BBa_K863022 are shown in a SDS-PAGE. BHAL has a molecular weight of 56 kDa. In lane 5, which corresponds to the elution fraction 2, a faint band of 56 kDa is visible. Therefore the fractions were further analysed by activity test and MALDI-TOF.
Activity Analysis of BHAL
Initial activity tests of purified fractions
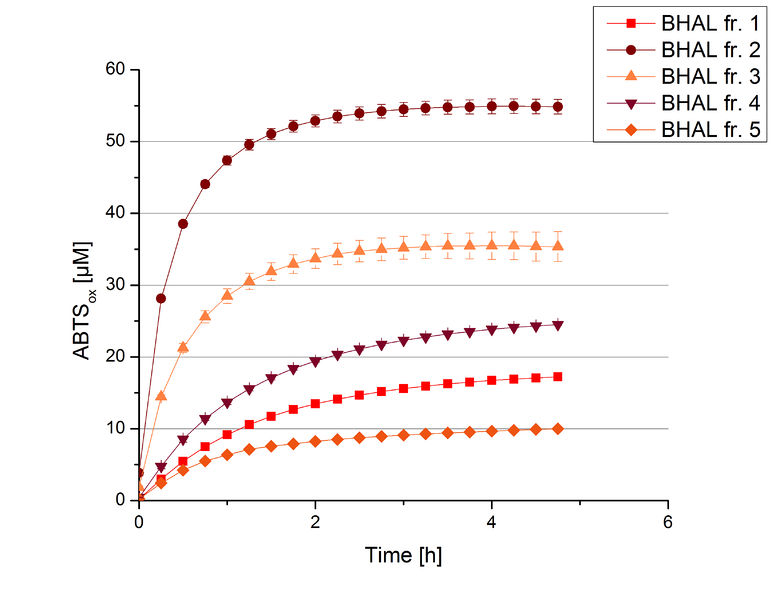
The resulting fractions of the cultivation and purification of BHAL (fraction 1 to 5) were analysed with activity tests. After rebuffering into deionized H2O and incubation with 0.4 mM CuCl2 for 2 hours, the samples were measured with 140 µL sample, 0.1 mM ABTS, 100 mM sodium acetate buffer to a final volume of 200 µL. The change in optical density was measured at 420 nm, reporting the oxidation of ABTS for 5 hours at 25°C. An increase in ABTSox can be seen (Figure 4), indicating produced BHAL laccase in each fraction. Fraction 2 shows the highest amount of ABTSox (55%) reaching saturation after 3 hours. Similar to BPUL laccase, BHAL is capable to reach saturation after 3 hours with approximately oxidizing 55% of the supplied ABTS. Therefore BHAL is going to be characterized further.
Initial activity tests of purified fractions
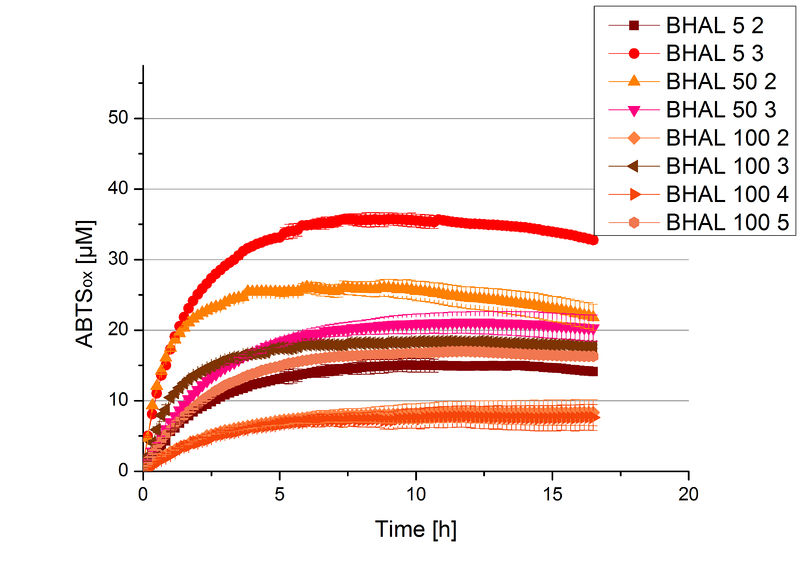
Different fractions of the purification of a new cultivation since the Regional Jamborees in Amsterdam were tested regarding their activity of the produced BHAL. Before and after re-buffering the protein concentration was determined. The initial activity tests were done in Britton-Robinson buffer (pH 5) with 0.1 mM ABTS at 25 °C. The protein amount was adjusted in each sample for a comparison. One distinct fraction showed the highest activity: fraction 5% 3 (Fig. 5). The contained laccase amount was calculated by assuming that the most active fraction contains 90 % laccase. This leads to a BHAL concentration of 10,9 ng mL-1.
BHAL activity depending on different ABTS concentrations
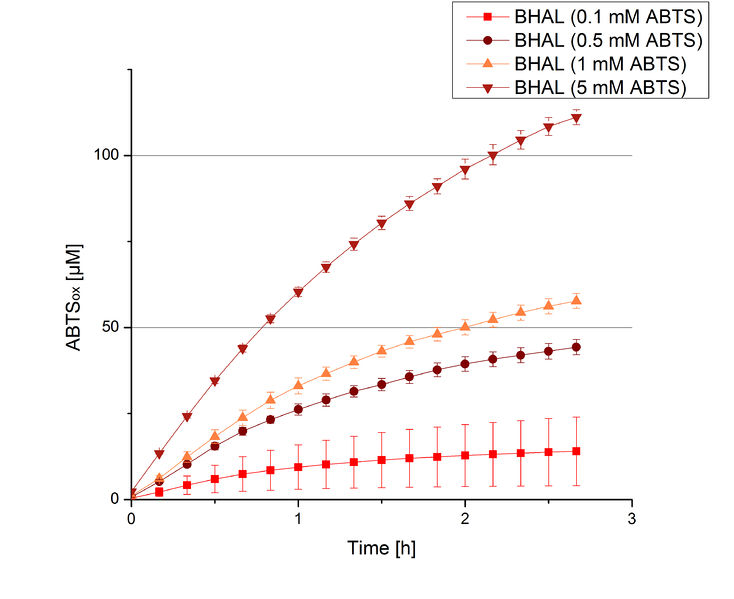
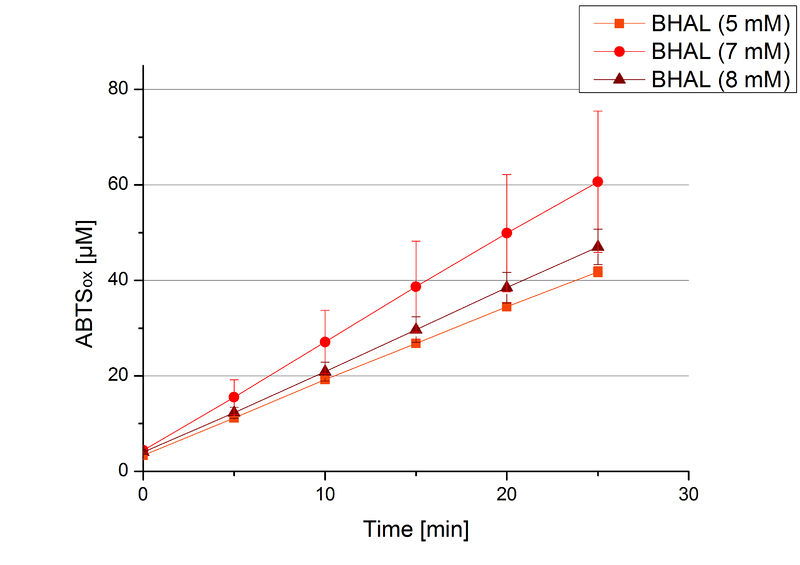
To be able to calculate the activity in Units mg-1, measurements had to be done under substrate saturation. This allows the comparison of Units mg-1 with other laccase activities and data found in literature. For this purpose ABTS concentrations ranging from 0.1 mM to 8 mM were applied in an experimental setup containing Britton-Robinson buffer (pH) and a temperature of 25 °C. For measurements with 0.1 mM to 5 mM ABTS 616 ng BHAL were used (Fig. 6). For measurements with 5 mM to 8 mM ABTS only 308 ng BHAL were applied (Fig. 7). Applying less than 7 mM ABTS a static increase in oxidized ABTS was given. Measurements with 8 mM ABTS showed a slower increase in oxidized ABTS as with 7 mM ABTS (Fig. 7). This may be due to a substrate toxication. The most compromising ABTS concentration was 7 mM with the highest increase in oxidized ABTS. Therefore a substrate saturation was reached with 7 mM ABTS.
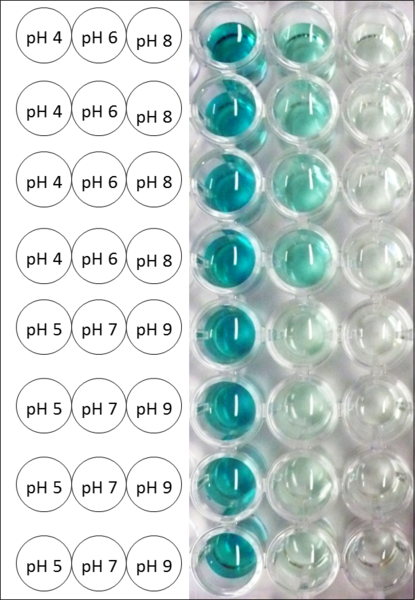
BHAL pH optimum
To determine the optimal experimental setup for BHAL activity measurements, the best pH had to be determined. Using Britton-Robinson buffer pHs between pH 4 and pH 9 had been adjusted. 308 ng BHAL per well had been tested under these pH conditions using 7 mM ABTS. The CuCl2 incubated and therefor activated BHAL showed a high activity at pH 4 and pH 5, where most of ABTS was oxidized (compared to Fig. 8 and 9). The calculated specific enzyme activity of BHAL showed high activity at both mentioned pHs (Fig. 10). While BHAL had an activity of ~8 U mg-1 at pH 4 and pH 5, the enzyme activity decreased at higher pHs. At a pH of 6 only 1/3 of enzyme activity could be detected compared to the activity at pH 4 and pH 5. While still active at pH 7, the BHAL is not as suitable as thought for an application at a waste water treatment plant because of its high activity in acidic environments.
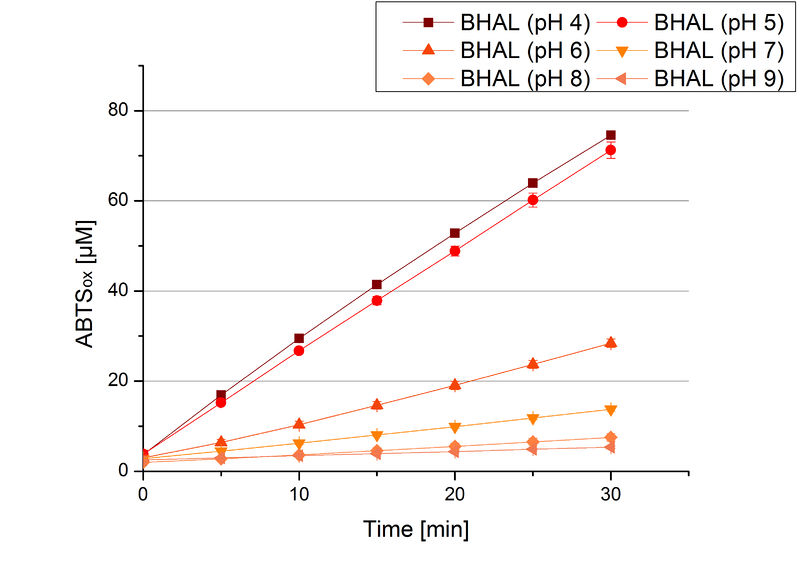
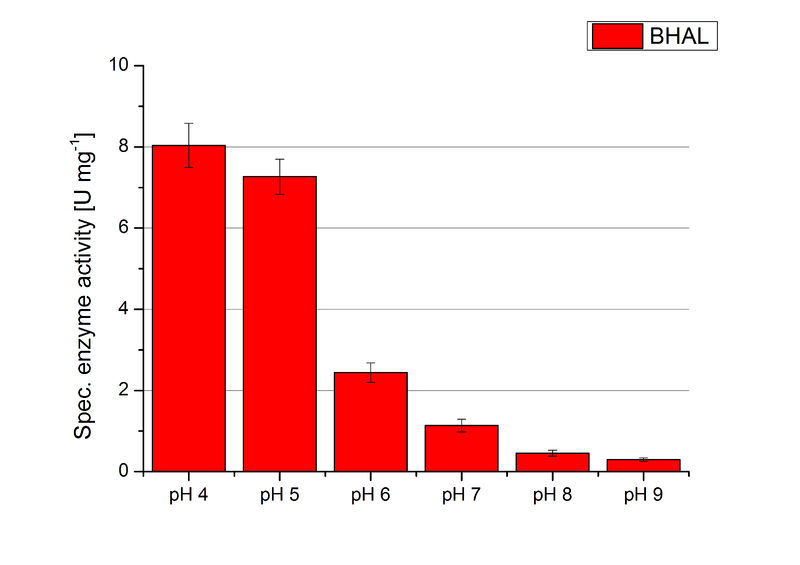
BHAL activity at different temperatures
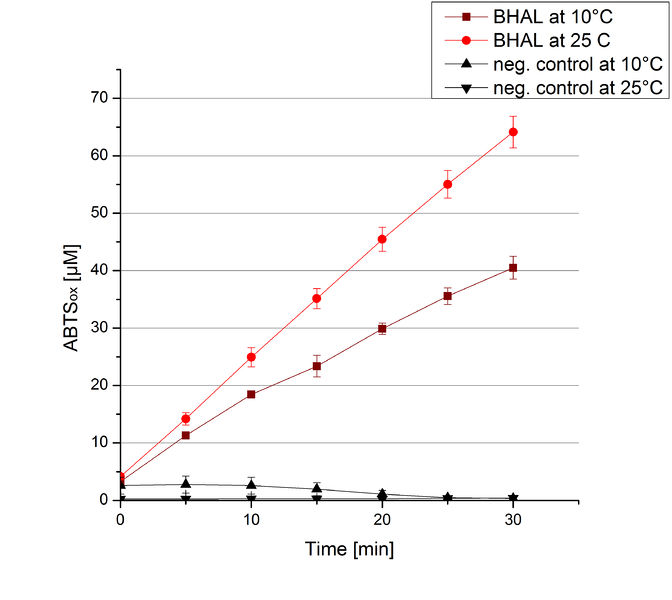
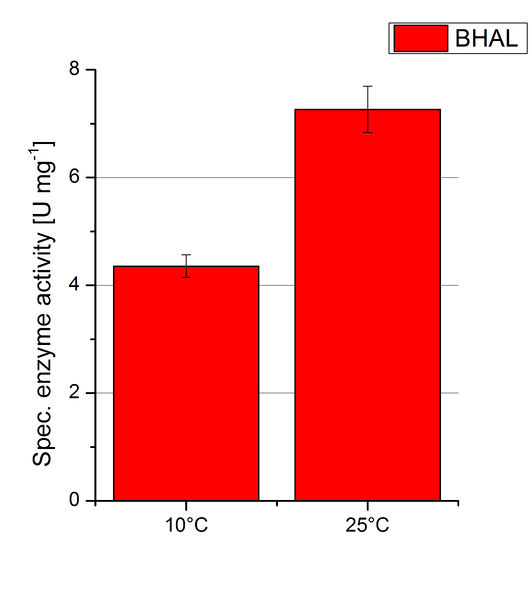
To investigate the activity of BHAL at temperatures that will apply at a waste water treatment plant throughout the year, activity tests were performed at 10 °C and 25 °C as described above. The measurements were conducted for 30 minutes. The obtained results revealed a lower activity of BHAL at 10 °C in comparison to 25 °C (see Fig. 11). The obtained results were used to calculate the specific enzyme activity which was at 4.2 and 7.2 U mg-1, respectively (see Figure 12). The negative control without BHAL but 0.4 mM CuCl2 at 10 °C and 25 °C showed a negligible oxidation of ABTS. The activity of BHAL was increased to about 60 % at 10 °C but nevertheless the observed activity at both conditions was great news for the possible application in waste water treatment plants.
Substrate Analysis
The measurements were made to test if the produced laccases were able to degrade different hormones. Therefore the produced laccases were inserted in the same concentrations (3 µg mL-1) to the different measurement approaches. To work with the correct pH value (which were measured by the Team Activity Test) Britton Robinson buffer at pH 5 was used for all measurements. The initial substrate concentration was 5 µg mL-1. The results of the reactions without ABTS are shown in Figure 2. On the Y-axis the percentages of degraded estradiol (blue) and ethinyl estradiol (red) are indicated. The X-axis displays the different tested laccases. The degradation was measured at t0 and after five hours of incubation at 30 °C. The negative control was the substrate in Britton Robinson buffer and showed no degradation of the substrates. The bought laccase TVEL0 which is used as positive control is able to degrade 94.7 % estradiol and 92.7 % ethinyl estradiol. The laccase BPUL (from Bacillus pumilus) degraded 35.9 % of used estradiol after five hours. ECOL was able to degrade 16.8 % estradiol. BHAL degraded 30.2 % estradiol. The best results were determined with TTHL (laccase from Thermus thermophilus). Here the percentage of degradation amounted 55.4 %.
The results of the reactions of the laccases with addition of ABTS are shown in Figure 3. The experimental set ups were the same as the reaction approach without ABTS described above. The X-axis displays the different tested laccases. On the Y-axis the percentages of degraded estradiol (blue) and ethinyl estradiol (red) are shown. The degradation was measured at t0 and after five hours of incubation at 20 °C. The negative control showed no degradation of estradiol. 6.8 % of ethinyl estradiol was decayed. The positive control TVEL0 is able to degrade 100 % estradiol and ethinyl estradiol. The laccase BPUL (from Bacillus pumilus) degraded 46.9 % of used estradiol after ten minutes incubation. ECOL was able to degrade 6.7 % estradiol. BHAL degraded 46.9 % estradiol. With TTHL (laccase from Thermus thermophilus)a degradation 29.5 % were determined.
Immobilization
Figure 20 shows the percentage of laccases bound after incubation with CPC-beads, relative to the original concentration. The concentration of laccases in the supernatant after incubation was measured using Roti®-Nanoquant. The results showed that only 21% of BHAL laccases was still present in the supernatant. This illustrates that BHAL was successfully immobilized on the CPC-beads.
Figure 22 shows the illustration of ABTS oxidation by BHAL with time compared to the negative control. The increase in ABTS oxidized proves laccase activity even if a direct comparison with the original and not immobilized laccase solution was not possible due to the very low concentration of purified BHAL.