Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K864401"
(→Source) |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
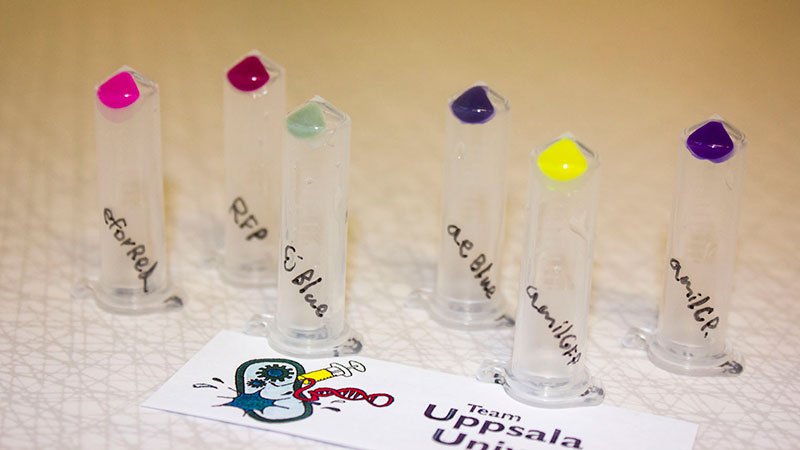
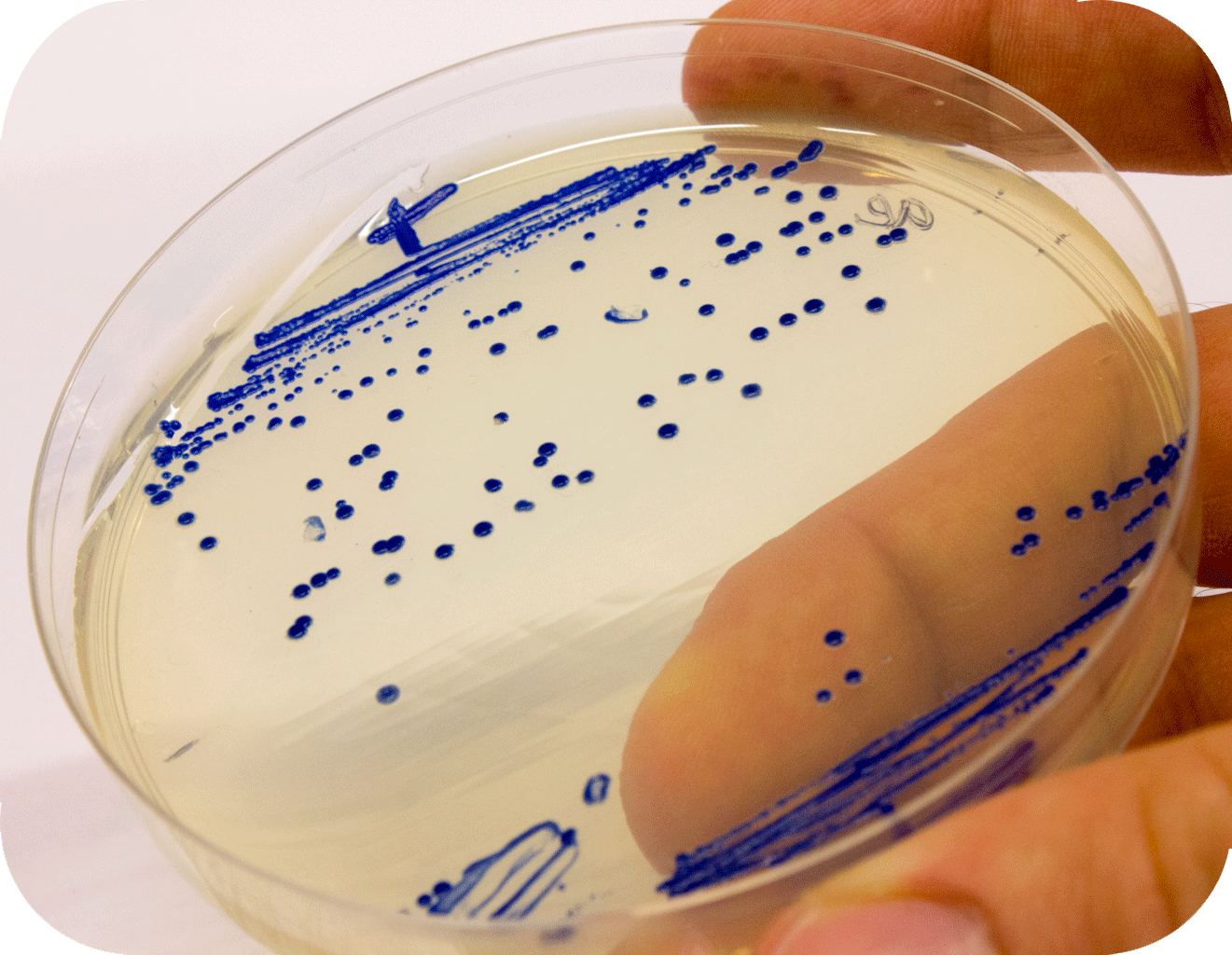
Below to the left is the expressed aeBlue in ''E.coli''. To the right comparison of aeBlue with other chromoproteins. | Below to the left is the expressed aeBlue in ''E.coli''. To the right comparison of aeBlue with other chromoproteins. | ||
| − | [[Image:Aeblue_plate_small.jpg.png| | + | [[Image:Aeblue_plate_small.jpg.png|360px]] |
[[Image:UUChromo.jpg|500px]] | [[Image:UUChromo.jpg|500px]] | ||
Revision as of 23:50, 29 September 2012
aeBlue blue chromoprotein
aeBlue is a blue chromoprotein extracted from the basal disk of a beadlet anemone Actinia equina. The protein has an absorption maximum at 597nm and a deep blue colour. The protein aeBlue has significant sequence homologies with proteins in the GFP family.
Source
The protein was first extracted and characterized in (Shkrob et. al., 2005) under the name aeCP597. This version is codon optimized for E.coli
Shkrob et. al. reported that the sum of the following substitutions compared to wild-type resulted in a far-red-shifted but radiation sensitive fluorescent protein: (K6T, K7E. Y101S, C143S, M146I, S158A)
Adding these following substitutions created a more thermostable and photostable product than the above product: (S3P, V19I, Y101S, M146I, N168D)
Below to the left is the expressed aeBlue in E.coli. To the right comparison of aeBlue with other chromoproteins.

References
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1316306/]Shkrob, M.A., Yanushevich, Y.G., Chudakov, D.M., Gurskaya, N.G., Labas, Y.A., Poponov, S.Y., Mudrik, N.N., Lukyanov, S., Lukyanov, K.A., 2005. Far-red fluorescent proteins evolved from a blue chromoprotein from Actinia equina. Biochem. J. 392, 649–654.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
