Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K733003"
Feisun0718 (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
<!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | <!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | ||
===Usage and Biology=== | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
| + | Characterization by UCAS iGEM 2016 team | ||
| + | This is we used the ydcD and ydcE genes to build a kill-switch. | ||
| + | By measuring the growth curve of E. coli expressing the antitoxin and toxin, we showed that toxin EndoA can be effectively neutralized by its antitoxin EndoB. | ||
| + | However, if the expression of EndoA is too strong (for example, induced by 5µg/mL aTc in our case), toxin will not be neutralized by antitoxin. | ||
| + | [[file:T--UCAS--ydcD1.png|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the figure above, toxin is induced at 0 min by 1.7µg/mL aTc, and antitoxin is induced by 8mM of IPTG after incubation for 4 hours. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[file:T--UCAS--ydcD2.png|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the figure above, toxin and antitoxin are both induced at 0 min. | ||
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
<span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | <span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | ||
Revision as of 01:50, 20 October 2016
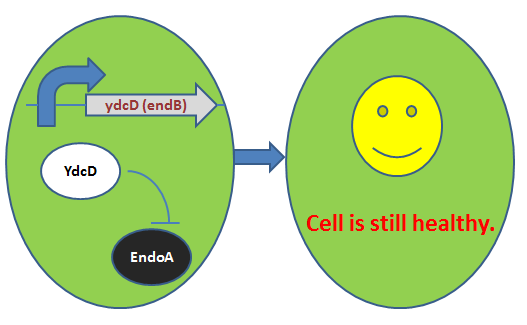
RBS+ydcD: antitoxin gene
ydcD has another name endB. This gene encodes a labile antidote –YdcD - for ydcE(ndoA) gene. YdcD can directly inhibit EndoA in vitro, so that the bacteria will not be vitiated under low level expression of YdcE. (Pellegrini et al., 2005) For reasons why we include this gene in our cell growth inhibition device, please click:BBa_K733012.
Sequence and Features
Assembly Compatibility:
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Reference
Pellegrini O, Mathy N, Gogos A, Shapiro L, and Condon C. "The Bacillus subtilis ydcDE operon encodes an endoribonuclease of the MazF/PemK family and its inhibitor.." Molecular microbiology. 56.5 (2005): 1139-1148. Print.