Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K801080:Experience"
(Undo revision 149113 by Fabian Froehlich (Talk)) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
| − | This | + | ===Expression of Thaumatin=== |
| − | + | ==== Ion exchange chromatography ==== | |
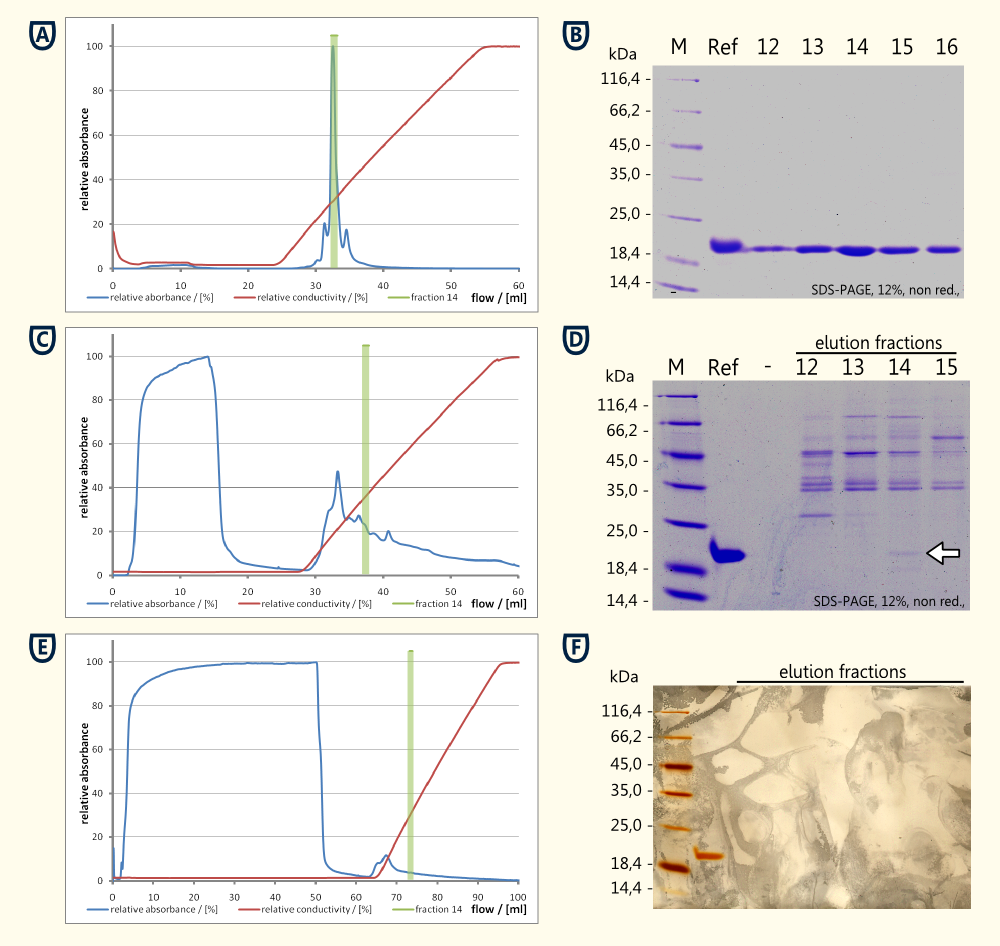
| + | [[File:TUM12_ThaumatinIEC.png|500px|thump|right|Experimental Results]] | ||
| + | Preprothaumatin becomes posttranslationally modified by cleaving a part of the N- and the C-terminal polypeptide. Therefore it was not possible to add a tag for affinity chromatography. For this reason it was necessary to purify the protein from the cytoplasm of the desintegrated yeast cells using ion exchange chromatography to have a proove of principle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Experimental details:''' | ||
| + | *Samples: cell lysate, supernatant from culture, reference for thaumatin (MedHerbs) | ||
| + | *Dialysis against 20mM MES Buffer pH 6.0 (twice) using a 12-16 kDa dialysis membrane | ||
| + | *Chromatography with a Äkta purifier equipped with a Ressource S 6ml (S: Methyl sulfonate (strong cation exchanger)) | ||
| + | *Sample was applied using a super-loop | ||
| + | *Wash with two colum volumes 20mM MES Buffer pH 6.0 | ||
| + | *Elution with a gradient of 0 - 500 mM NaCl over 5 column volumes | ||
| + | *Fractions of 1 ml were collected during the elution<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Experimental results:''' | ||
| + | *Reference Thaumatin (see figure A and B) | ||
| + | **nealy no protein in the flow through during sample application (see figure A) | ||
| + | **a major peak eluting at ~14 mS*cm-1 which corresponds to fraction Nr. 14 see figure A) | ||
| + | ** The corresponding SDS-PAGE showed a clear band around fraction Nr. 14 corresponding matching the expected 22 kDa | ||
| + | *Cell lysate | ||
| + | **high concentration of protein in the flow through (see figure C and D) | ||
| + | **no clear peak arround fraction 14 could be detected | ||
| + | **The SDS-PAGE performed from the reference and the fractions 12 to 15 showed a weak band at the height of the reference. This band having the same size as the reference (see running propperties on SDS-PAGE in figure D) and the same isoelectric point (both eluted in fraction 14) is very likely to be thaumatin which was produced by the yeast cells. | ||
| + | *Supernatant of yeast culture (see figure E and F) | ||
| + | **Export of the protein in high concentrations was unlikely to happen, therefore 48 ml of supernatant were loaded on the column | ||
| + | **Ratio between frowthrough and eluted protein was less favourable compared to the cell lysate. | ||
| + | **Total protein quantities were to low to be detected by Coomassie stain, therefore a silver stain was performed (see figure F) | ||
| + | **Beside the reference no additional proteinbands could be detected on the silver stained SDS-PAGE<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Conclusion from this experiment:'''<br> | ||
| + | A '''proof of principle for the expression of Thaumatin was achieved using ion exchange chromotography and comparison of bands optained on an SDS-PAGE relative to a standard of Thaumatin'''. <br> | ||
| + | Further goals would include to increase the expression of the thaumatin and to investigate the secretion. This could be achieved by improving the purification protocol in order to load more than 10 ml of cell lysate on the column in order to purify sufficient protein for a mass spectrum of the produced thaumatin. Another aspect that should be investigated is the transport process that could be monitored in an ELISA or via quantitative western blotting using a polyclonal serum against thaumatin.<br> | ||
===Applications of BBa_K801080=== | ===Applications of BBa_K801080=== | ||
Revision as of 18:06, 26 September 2012
Expression of Thaumatin
Ion exchange chromatography
Preprothaumatin becomes posttranslationally modified by cleaving a part of the N- and the C-terminal polypeptide. Therefore it was not possible to add a tag for affinity chromatography. For this reason it was necessary to purify the protein from the cytoplasm of the desintegrated yeast cells using ion exchange chromatography to have a proove of principle.
Experimental details:
- Samples: cell lysate, supernatant from culture, reference for thaumatin (MedHerbs)
- Dialysis against 20mM MES Buffer pH 6.0 (twice) using a 12-16 kDa dialysis membrane
- Chromatography with a Äkta purifier equipped with a Ressource S 6ml (S: Methyl sulfonate (strong cation exchanger))
- Sample was applied using a super-loop
- Wash with two colum volumes 20mM MES Buffer pH 6.0
- Elution with a gradient of 0 - 500 mM NaCl over 5 column volumes
- Fractions of 1 ml were collected during the elution
Experimental results:
- Reference Thaumatin (see figure A and B)
- nealy no protein in the flow through during sample application (see figure A)
- a major peak eluting at ~14 mS*cm-1 which corresponds to fraction Nr. 14 see figure A)
- The corresponding SDS-PAGE showed a clear band around fraction Nr. 14 corresponding matching the expected 22 kDa
- Cell lysate
- high concentration of protein in the flow through (see figure C and D)
- no clear peak arround fraction 14 could be detected
- The SDS-PAGE performed from the reference and the fractions 12 to 15 showed a weak band at the height of the reference. This band having the same size as the reference (see running propperties on SDS-PAGE in figure D) and the same isoelectric point (both eluted in fraction 14) is very likely to be thaumatin which was produced by the yeast cells.
- Supernatant of yeast culture (see figure E and F)
- Export of the protein in high concentrations was unlikely to happen, therefore 48 ml of supernatant were loaded on the column
- Ratio between frowthrough and eluted protein was less favourable compared to the cell lysate.
- Total protein quantities were to low to be detected by Coomassie stain, therefore a silver stain was performed (see figure F)
- Beside the reference no additional proteinbands could be detected on the silver stained SDS-PAGE
Conclusion from this experiment:
A proof of principle for the expression of Thaumatin was achieved using ion exchange chromotography and comparison of bands optained on an SDS-PAGE relative to a standard of Thaumatin.
Further goals would include to increase the expression of the thaumatin and to investigate the secretion. This could be achieved by improving the purification protocol in order to load more than 10 ml of cell lysate on the column in order to purify sufficient protein for a mass spectrum of the produced thaumatin. Another aspect that should be investigated is the transport process that could be monitored in an ELISA or via quantitative western blotting using a polyclonal serum against thaumatin.
Applications of BBa_K801080
User Reviews
UNIQ752ff7ccddbd6999-partinfo-00000000-QINU UNIQ752ff7ccddbd6999-partinfo-00000001-QINU