Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K525223"
(→Expression in E. coli) |
|||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
The CspB gen was fused with a monomeric RFP ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_E1010 BBa_E1010]) using [http://2011.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols#Gibson_assembly Gibson assembly] for characterization. | The CspB gen was fused with a monomeric RFP ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_E1010 BBa_E1010]) using [http://2011.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols#Gibson_assembly Gibson assembly] for characterization. | ||
| − | The | + | The mRFP|CspB fusion protein was overexpressed in E. coli KRX after induction of T7 polymerase by supplementation of 0,1 % L-rhamnose using the [http://2011.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Downstream-processing#Expression_of_S-layer_genes_in_E._coli autinduction protocol] from promega. |
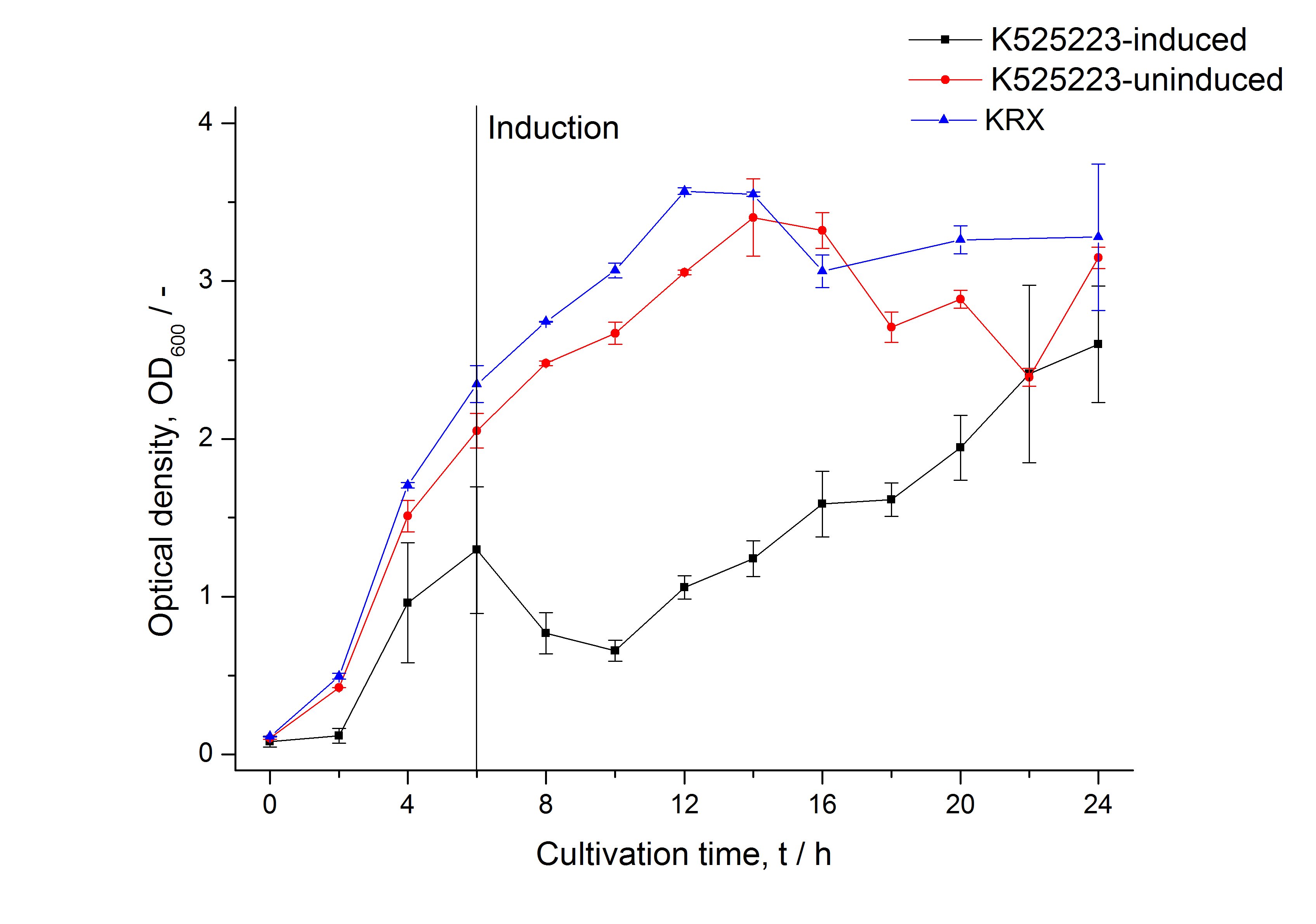
[[Image:Bielefeld_2011_CH3_Growthcurve.png|600px|center|thumb| '''Figure 1: Growthcurve of ''E. coli'' KRX expressing the fusion protein of CspB and mRFP with and without induction. A curve depicting KRX wildtype is shown for comparsion.''']] | [[Image:Bielefeld_2011_CH3_Growthcurve.png|600px|center|thumb| '''Figure 1: Growthcurve of ''E. coli'' KRX expressing the fusion protein of CspB and mRFP with and without induction. A curve depicting KRX wildtype is shown for comparsion.''']] | ||
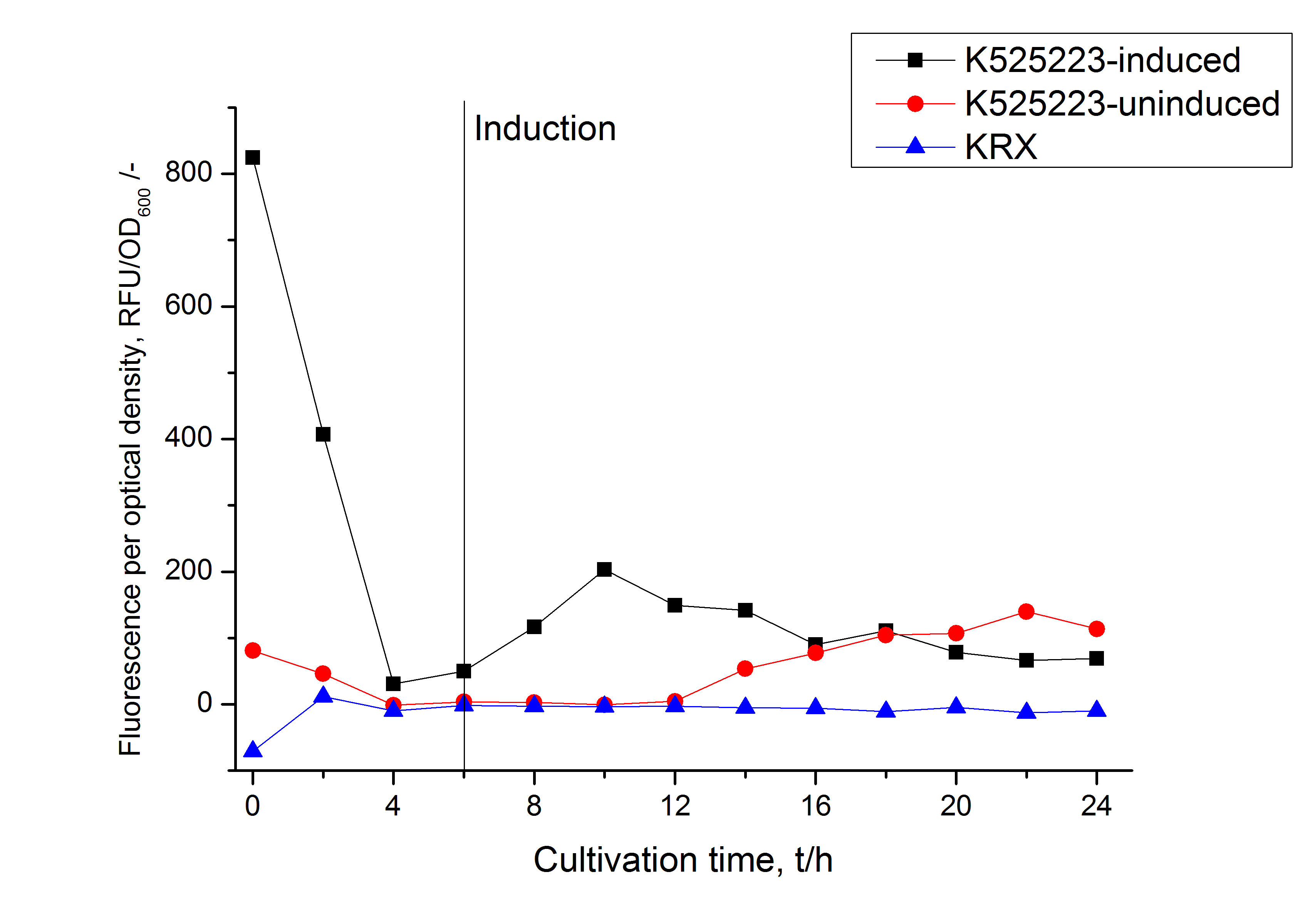
[[Image:Bielefeld_2011_CH3_RFU_OD.png|600px|center|thumb| '''Figure 2: RFU to OD<sub>600</sub> ratio of ''E. coli'' KRX expressing the fusion protein of CspB and mRFP with and without induction. A curve depicting KRX wildtype is shown for comparsion.''']] | [[Image:Bielefeld_2011_CH3_RFU_OD.png|600px|center|thumb| '''Figure 2: RFU to OD<sub>600</sub> ratio of ''E. coli'' KRX expressing the fusion protein of CspB and mRFP with and without induction. A curve depicting KRX wildtype is shown for comparsion.''']] | ||
Revision as of 22:24, 21 September 2011
S-layer cspB from Corynebacterium halotolerans with lipid anchor, PT7 and RBS
S-layers (crystalline bacterial surface layer) are crystal-like layers consisting of multiple protein monomers and can be found in various (archae-)bacteria. They constitute the outermost part of the cell wall. Especially their ability for self-assembly into distinct geometries is of scientific interest. At phase boundaries, in solutions and on a variety of surfaces they form different lattice structures. The geometry and arrangement is determined by the C-terminal self assembly-domain, which is specific for each S-layer protein. The most common lattice geometries are oblique, square and hexagonal. By modifying the characteristics of the S-layer through combination with functional groups and protein domains as well as their defined position and orientation to eachother (determined by the S-layer geometry) it is possible to realize various practical applications ([http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00573.x/full Sleytr et al., 2007]).
Usage and Biology
S-layer proteins can be used as scaffold for nanobiotechnological applications and devices by e.g. fusing the S-layer's self-assembly domain to other functional protein domains. It is possible to coat surfaces and liposomes with S-layers. A big advantage of S-layers: after expressing in E. coli and purification, the nanobiotechnological system is cell-free. This enhances the biological security of a device.
Important parameters
| Experiment | Characteristic | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Expression (E. coli) | Localisation | Cell membrane |
| Compatibility | E. coli KRX | |
| Induction of expression | L-rhamnose for induction of T7 polymerase | |
| Specific growth rate (un-/induced) | 0.248 h-1 / 0.098 h-1 | |
| Doubling time (un-/induced) | 2.79 h / 7.07 h |
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 1102
Illegal XhoI site found at 558 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 225
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 1314
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 1425
Illegal AgeI site found at 216
Illegal AgeI site found at 457
Illegal AgeI site found at 504 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI site found at 906
Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 213
Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 591
Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 993
Expression in E. coli
The CspB gen was fused with a monomeric RFP (BBa_E1010) using [http://2011.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols#Gibson_assembly Gibson assembly] for characterization.
The mRFP|CspB fusion protein was overexpressed in E. coli KRX after induction of T7 polymerase by supplementation of 0,1 % L-rhamnose using the [http://2011.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Downstream-processing#Expression_of_S-layer_genes_in_E._coli autinduction protocol] from promega.