Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K404223"
| (9 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
<partinfo>BBa_K404223 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K404223 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | <br><b>The RGD integrin binding motif, inserted into [[ | + | {| style="color:black" cellpadding="6" cellspacing="1" border="2" align="left" |
| + | ! colspan="2" style="background:#66bbff;"|[https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K404223 (AAV2)-Rep-VP123_p5-TATAless (ViralBrick-453-RGD)] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |'''BioBrick Nr.''' | ||
| + | |[https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K404223 BBa_K404223] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |'''RFC standard''' | ||
| + | |[https://parts.igem.org/Help:Assembly_standard_25 RFC 25] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |'''Requirement''' | ||
| + | |pSB1C3<br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |'''Source''' | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |'''Submitted by''' | ||
| + | |[http://2010.igem.org/Team:Freiburg_Bioware FreiGEM 2010] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
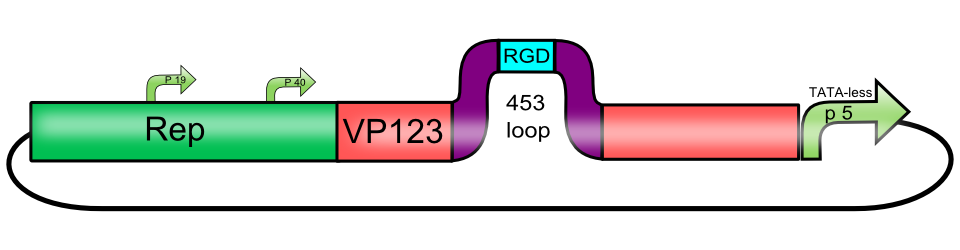
| + | <br><b>The RGD integrin binding motif, inserted into the 453 loop of [[Part:BBa_K404002|[AAV2]-Rep-VP123_p5-TATAless]]</b> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
[[Image:Freiburg10_Rep-VP123_P5-TATA-less 453-RGD.png|thumb|center|480px]]<br> | [[Image:Freiburg10_Rep-VP123_P5-TATA-less 453-RGD.png|thumb|center|480px]]<br> | ||
| Line 9: | Line 29: | ||
https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/parts/f/f6/Freiburg10_ViralBrick_motif_RGD.png | https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/parts/f/f6/Freiburg10_ViralBrick_motif_RGD.png | ||
| + | <br/><html> | ||
| + | <h3>Capsid</h3> | ||
| + | The AAV capsid consists of 60 capsid protein subunits. The three cap proteins VP1, VP2, and VP3 are encoded in an overlapping reading frame. Arranged in a stoichiometric ratio of 1:1:10, they form an icosahedral symmetry. The mRNA encoding for the cap proteins is transcribed from p40 and alternative spliced to minor and major products. Alternative splicing and translation initiation of VP2 at a nonconventional ACG initiation codon promote the expression of VP1, VP2 and VP3. The VP proteins share a common C terminus and stop codon, but begin with a different start codon. The N termini of VP1 and VP2 play important roles in infection and contain motifs that are highly homologous to the phospholipase A2 (PLA2) domain and nuclear localization signals (BR)(+). | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h3>References</h3> | ||
| + | <b>DiPrimio, Asokan, Govindasamy, Agbandje-McKenna, & Samulski</b>, June 2008. Surface loop dynamics in adeno-associated virus capsid assembly. Journal of virology, 167(1), 5178–5189 <br /> | ||
| + | <center><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/parts/a/a7/Freiburg10_Cap_proteins_VP1_2%263.png" width="600" | ||
| + | height="auto"/></center></html><br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
Latest revision as of 02:48, 28 October 2010
[AAV2]-Rep-VP123_p5-TATAless (ViralBrick-453-RGD)
| (AAV2)-Rep-VP123_p5-TATAless (ViralBrick-453-RGD) | |
|---|---|
| BioBrick Nr. | BBa_K404223 |
| RFC standard | RFC 25 |
| Requirement | pSB1C3 |
| Source | |
| Submitted by | [http://2010.igem.org/Team:Freiburg_Bioware FreiGEM 2010] |
The RGD integrin binding motif, inserted into the 453 loop of [AAV2]-Rep-VP123_p5-TATAless
Usage and Biology
Integrins are transmembrane proteins that, among other functions, mediate cell attachment to surrounding tissues. They bind to a motif consisting of the amino acids arginine, glycine and aspartic acid (RGD in one-letter code). Because Integrin is highly expressed in many tumor cell lines (Albelda et al., 1990), (Damjanovich, Albelda, Mette, & Buck, 1992), (Lessey et al., 1995), (Smythe, LeBel, Bavaria, Kaiser, & Albelda, 1995), (Gladson & Cheresh, 1991), AAV particles displaying the RGD motif on various positions in their capsid proteins have been created by (Shi et al., 2003). Particles displaying RGD at amino acid positions 584 & 588 as well as 453 or 587 (Boucas et al., 2009) showed transduction efficiencies similar to wt AAV, even when the cells’ HSPG receptors were blocked by heparin sulfate or when the natural HSPG binding motif on the capsid surface was knocked out. To further broaden the area of therapeutic application, we created a ViralBrick containing the RGD motive to specifically target cells with low HSPG-/high Integrin expression.

Capsid
The AAV capsid consists of 60 capsid protein subunits. The three cap proteins VP1, VP2, and VP3 are encoded in an overlapping reading frame. Arranged in a stoichiometric ratio of 1:1:10, they form an icosahedral symmetry. The mRNA encoding for the cap proteins is transcribed from p40 and alternative spliced to minor and major products. Alternative splicing and translation initiation of VP2 at a nonconventional ACG initiation codon promote the expression of VP1, VP2 and VP3. The VP proteins share a common C terminus and stop codon, but begin with a different start codon. The N termini of VP1 and VP2 play important roles in infection and contain motifs that are highly homologous to the phospholipase A2 (PLA2) domain and nuclear localization signals (BR)(+).References
DiPrimio, Asokan, Govindasamy, Agbandje-McKenna, & Samulski, June 2008. Surface loop dynamics in adeno-associated virus capsid assembly. Journal of virology, 167(1), 5178–5189
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 3644
Illegal XhoI site found at 1913
Illegal XhoI site found at 2099 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI site found at 4170
Illegal BsaI site found at 4352
Illegal BsaI site found at 4389
Illegal SapI site found at 3048