Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3962350"
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K3962350 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K3962350 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | + | HOK is the toxin of the HOK/SOK toxin-antitoxin system. The HOK/SOK is a type I toxin-antitoxin system originating from the R1 plasmid in E. coli. The SOK transcript can bind to a homologous region on HOK mRNA and prevent toxin expression. When E. coli undergoes cell division, the two daughter cells inherit the long-lived HOK toxin from the parent cell. Due to the short half-life of the SOK antitoxin, daughter cells inherit only small amounts and it is quickly degraded. | |
| + | |||
| + | The gel electrophoresis of pSB1A3-HOK is shown in Figure 1. The result in lane 18 shows that HOK is present in the biobrick. | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://2021.igem.org/wiki/images/6/6d/T--Leiden--Parts-HOK.png | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''''Figure 1''''' ''The gel result of pSB1A3-HOK (lane 18)'' | ||
<!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | <!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | ||
Latest revision as of 23:40, 21 October 2021
HOK - Toxin in Hok/Sok
HOK is the toxin of the HOK/SOK toxin-antitoxin system. The HOK/SOK is a type I toxin-antitoxin system originating from the R1 plasmid in E. coli. The SOK transcript can bind to a homologous region on HOK mRNA and prevent toxin expression. When E. coli undergoes cell division, the two daughter cells inherit the long-lived HOK toxin from the parent cell. Due to the short half-life of the SOK antitoxin, daughter cells inherit only small amounts and it is quickly degraded.
The gel electrophoresis of pSB1A3-HOK is shown in Figure 1. The result in lane 18 shows that HOK is present in the biobrick.
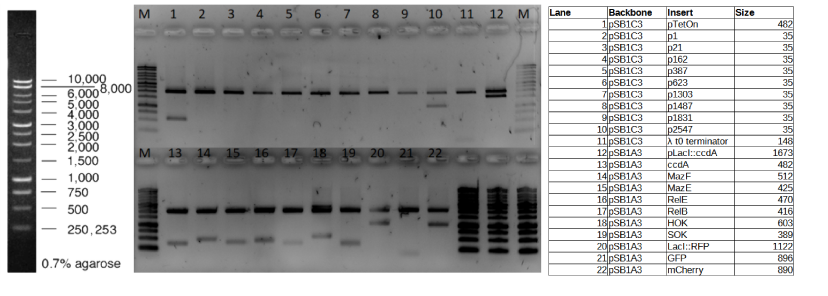
Figure 1 The gel result of pSB1A3-HOK (lane 18)
Sequence and Features
Assembly Compatibility:
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
