Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3349002"
Kristiturton (Talk | contribs) |
Kristiturton (Talk | contribs) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K3349002 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K3349002 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | The PelC Pectin Lyase is originally from <i> Paenabacillus amylolyticus </i>. This particular pectin lyase is more specific to methylated pectin or homogalacturonan substrates rather than polygalacturonic acid [1]. This protein also works with both PelB(BBa_K3349001) and Pnl(BBa_K3349001) in this organism to effectively break down pectin. PelC has an optimal activity at 55°C and a pH of 10. The Km | + | The PelC Pectin Lyase is originally from <i> Paenabacillus amylolyticus</i>. This particular pectin lyase is more specific to methylated pectin or homogalacturonan substrates rather than polygalacturonic acid [1]. This protein also works with both PelB (BBa_K3349001) and Pnl (BBa_K3349001) in this organism to effectively break down pectin. PelC has an optimal activity at 55°C and a pH of 10. The Km in terms of 80% methylated substrates was determined to be 0.41 +/-0.06mg/ml. Calcium is a cofactor for this protein and is therefore necessary within the buffer conditions [1]. |
For purification purposes, this gene has a C-terminal hexa-histidine tag. For more information on our design and use please see our webpage https://2020.igem.org/Team:Lethbridge_HS. | For purification purposes, this gene has a C-terminal hexa-histidine tag. For more information on our design and use please see our webpage https://2020.igem.org/Team:Lethbridge_HS. | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
<b>Figure 1:</b> Homology modelling of PelC from <i>P. amylolyticus </i>. The protein structure was done using iTASSER [2] and SWISS-Model [3]. The two structures were then aligned and compared. A more in depth analysis can be found on our webpage. | <b>Figure 1:</b> Homology modelling of PelC from <i>P. amylolyticus </i>. The protein structure was done using iTASSER [2] and SWISS-Model [3]. The two structures were then aligned and compared. A more in depth analysis can be found on our webpage. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | For wetlab results we were able to start preparing for subcloning our parts into pSB1C3. The following Figure shows our digestion of the genes from pUC57-Kan using EcoRI and PstI. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <img src= "https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/c/c9/T--Lethbridge_HS--insertdigest2020.png" alt="pnl modelling" style="width:500px;height:700px;"> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <b>Figure 2: </b> Restriction digest of PelB and PelC DNA from the pUC57 plasmid using EcoRI and PstI enzymes run on a 1% agarose gel. The red boxes show the band corresponding to that of our DNA constructs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
Latest revision as of 16:48, 24 October 2020
Pectin Lyase PelC
The PelC Pectin Lyase is originally from Paenabacillus amylolyticus. This particular pectin lyase is more specific to methylated pectin or homogalacturonan substrates rather than polygalacturonic acid [1]. This protein also works with both PelB (BBa_K3349001) and Pnl (BBa_K3349001) in this organism to effectively break down pectin. PelC has an optimal activity at 55°C and a pH of 10. The Km in terms of 80% methylated substrates was determined to be 0.41 +/-0.06mg/ml. Calcium is a cofactor for this protein and is therefore necessary within the buffer conditions [1].
For purification purposes, this gene has a C-terminal hexa-histidine tag. For more information on our design and use please see our webpage https://2020.igem.org/Team:Lethbridge_HS.
In the beginning of our project we decided to do homology modelling of our pectin lyase enzymes in order to inform our thermostability modelling.

Figure 1: Homology modelling of PelC from P. amylolyticus . The protein structure was done using iTASSER [2] and SWISS-Model [3]. The two structures were then aligned and compared. A more in depth analysis can be found on our webpage.
For wetlab results we were able to start preparing for subcloning our parts into pSB1C3. The following Figure shows our digestion of the genes from pUC57-Kan using EcoRI and PstI.
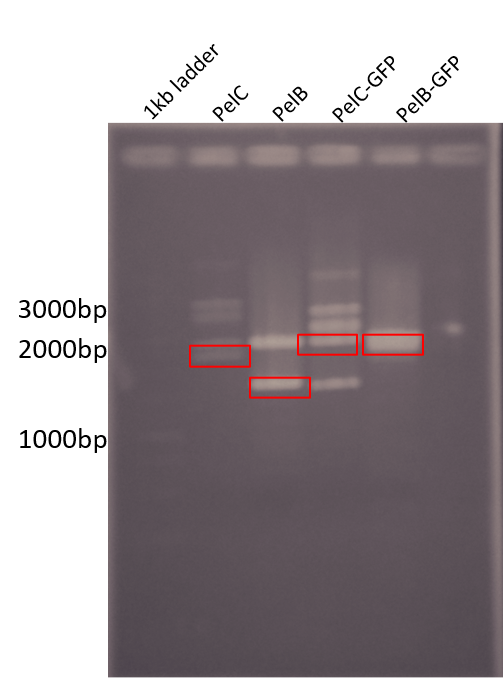
Figure 2: Restriction digest of PelB and PelC DNA from the pUC57 plasmid using EcoRI and PstI enzymes run on a 1% agarose gel. The red boxes show the band corresponding to that of our DNA constructs.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 829
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 215
