Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3113068"
Theresakeil (Talk | contribs) |
Theresakeil (Talk | contribs) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K3113068 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K3113068 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | DHD154a is a | + | DHD154a is a heterodimeric coiled-coil structure. |
<h2>Usage</h2> | <h2>Usage</h2> | ||
| − | To increase the modularity of our system we decided to test coiled coil proteins. These coiled coils mimic the interactions of DNA helix-helix interactions. The coiled-coil protein interaction allows the loading of more than one protein and larger proteins. We are using these helical structures to load RNA binding proteins into exosomes or virus-like | + | To increase the modularity of our system we decided to test coiled-coil proteins. These coiled-coils mimic the interactions of DNA helix-helix interactions. The coiled-coil protein interaction allows the loading of more than one protein and larger proteins. We are using these helical structures to load RNA binding proteins into exosomes or virus-like particles. |
<h2>Biology</h2> | <h2>Biology</h2> | ||
| − | We generated helical bundle heterodimers in which each monomer is a helix–turn–helix starting from four-helix backbones produced using a generalization of the Crick coiled-coil parameterization.<ref>Chen, Zibo ; Boyken, Scott E; Jia, Mengxuan ; Busch, Florian ; Flores-Solis, David ; Bick, Matthew J; Lu, Peilong ; VanAernum, Zachary L; Sahasrabuddhe, Aniruddha ; Langan, Robert A; Bermeo, Sherry ; Brunette, T J; Mulligan, Vikram Khipple ; Carter, Lauren P; DiMaio, Frank ; Sgourakis, Nikolaos G; Wysocki, Vicki H; Baker, David, Programmable design of orthogonal protein heterodimers Nature, 2018, ISSN: 1476-4687.</ref> | + | "We generated helical bundle heterodimers in which each monomer is a helix–turn–helix starting from four-helix backbones produced using a generalization of the Crick coiled-coil parameterization."<ref>Chen, Zibo ; Boyken, Scott E; Jia, Mengxuan ; Busch, Florian ; Flores-Solis, David ; Bick, Matthew J; Lu, Peilong ; VanAernum, Zachary L; Sahasrabuddhe, Aniruddha ; Langan, Robert A; Bermeo, Sherry ; Brunette, T J; Mulligan, Vikram Khipple ; Carter, Lauren P; DiMaio, Frank ; Sgourakis, Nikolaos G; Wysocki, Vicki H; Baker, David, Programmable design of orthogonal protein heterodimers Nature, 2018, ISSN: 1476-4687.</ref> |
<h2>Characterization</h2> | <h2>Characterization</h2> | ||
| − | + | <h3>Western Blot</h3> | |
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <figure class="figure"> | ||
| + | <img src="https://2019.igem.org/wiki/images/4/4f/T--Munich--WesternBlot_CC_test.png" width="50%" class="figure-img img-fluid rounded" alt=" "> | ||
| + | <figcaption style="font-size: 80%"> | ||
| + | <b>Figure 1: </b>The presence of vesicular components modularly composed with coiled-coils and directly fused could be proven by western blotting. Top left) the exosomal marker CD63 can be visualized with primary anti-CD63 mouse-antibody and secondary anti-mouse antibody - horse radish peroxidase (HRP) fusion. CDC63 does not run as a tight band on the blot because of glycosylation patterns and its nature as a membrane protein. Top right) Gag-protein is determined at around 70 kDa. The fusion construct Gag-HiBiT-L7Ae shows some degradation corresponding to the molecular weight of L7Ae cleavage. Bottom) MCP RNA-binding proteins can be shown with anti-MCP antibodies. | ||
| + | </figcaption> | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
Latest revision as of 01:59, 22 October 2019
DHD154a
DHD154a is a heterodimeric coiled-coil structure.
Usage
To increase the modularity of our system we decided to test coiled-coil proteins. These coiled-coils mimic the interactions of DNA helix-helix interactions. The coiled-coil protein interaction allows the loading of more than one protein and larger proteins. We are using these helical structures to load RNA binding proteins into exosomes or virus-like particles.
Biology
"We generated helical bundle heterodimers in which each monomer is a helix–turn–helix starting from four-helix backbones produced using a generalization of the Crick coiled-coil parameterization."[1]
Characterization
Western Blot
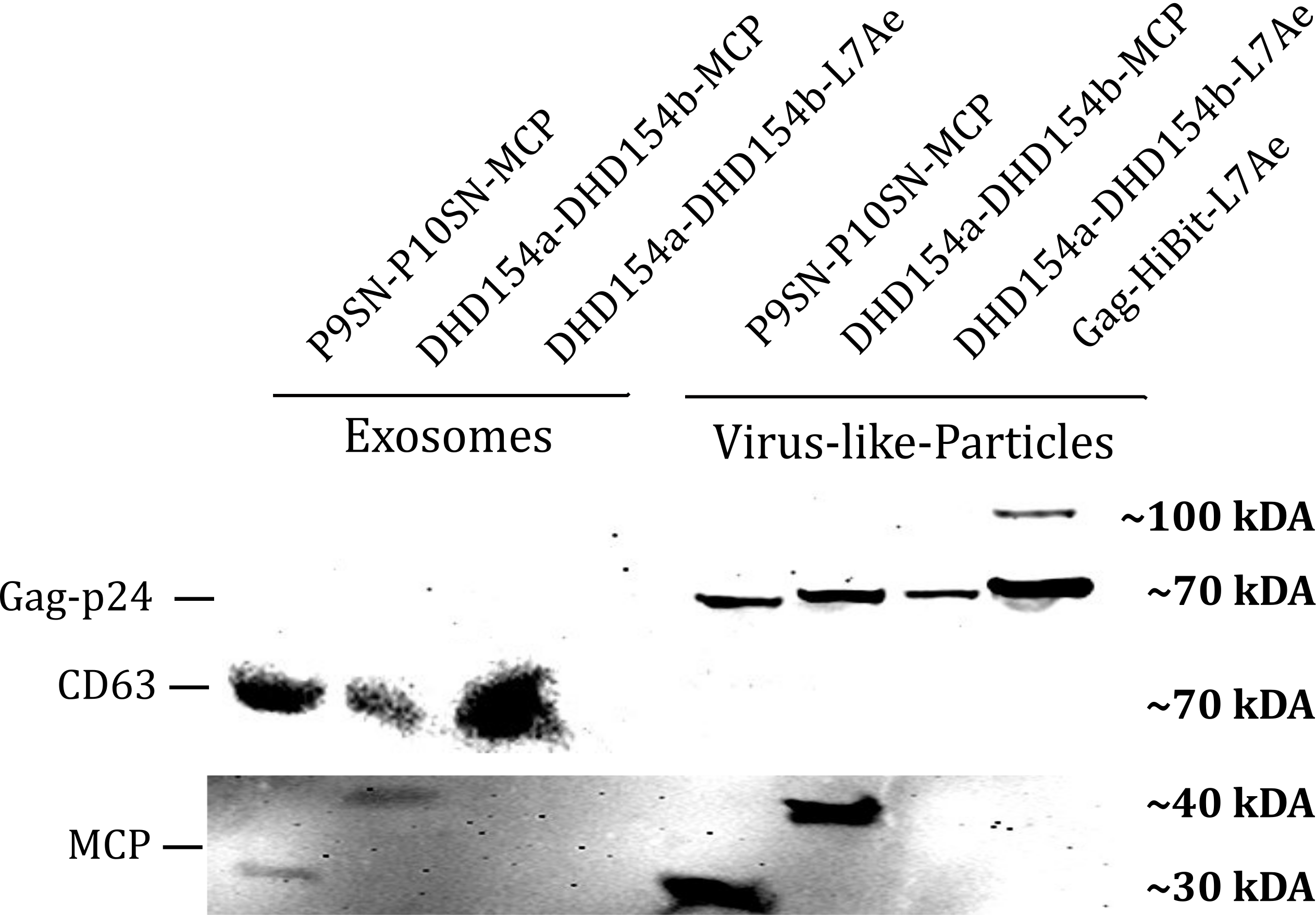
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
References
- ↑ Chen, Zibo ; Boyken, Scott E; Jia, Mengxuan ; Busch, Florian ; Flores-Solis, David ; Bick, Matthew J; Lu, Peilong ; VanAernum, Zachary L; Sahasrabuddhe, Aniruddha ; Langan, Robert A; Bermeo, Sherry ; Brunette, T J; Mulligan, Vikram Khipple ; Carter, Lauren P; DiMaio, Frank ; Sgourakis, Nikolaos G; Wysocki, Vicki H; Baker, David, Programmable design of orthogonal protein heterodimers Nature, 2018, ISSN: 1476-4687.
