Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3142013"
(→SZPT-China) |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K3142013 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K3142013 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | + | AcmA is an Endo-βN-acetylmuramidase that dissociates the reducing group of N-acetylmuramic acid from Gram-positive bacteria to autolyze the lactic acid bacteria. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
<!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | <!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | ||
| Line 24: | Line 18: | ||
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
==SZPT-China== | ==SZPT-China== | ||
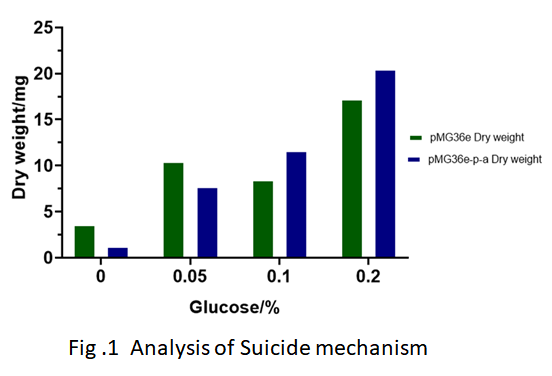
| − | + | The results of ''LAB'' MG1363 and ''LAB'' MG1363 with pMG36e-p - a after induction of recombinant bacteria by different glucose concentrations are shown in Fig. 1. The results showed that when the concentration of glucose in the environment was less than 0.05%, the growth of recombinant bacteria was significantly inhibited. | |
| − | [[file: | + | [[file:Acmaa.png|center|500px]] |
| + | |||
| + | ===Reference=== | ||
| + | *Coolbear, T., Pillidge, C. J., & Crow, V. L. (1994). The diversity of potential cheese ripeningcharacteristics of ''lactic acid starter bacteria'': Resistance to cell lysis and levels of cellular distribution of proteinase activities. International Dairy Journal, 4,697–721. | ||
Latest revision as of 02:57, 22 October 2019
acmA
AcmA is an Endo-βN-acetylmuramidase that dissociates the reducing group of N-acetylmuramic acid from Gram-positive bacteria to autolyze the lactic acid bacteria.
Sequence and Features
Assembly Compatibility:
- 10INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]Illegal XbaI site found at 627
Illegal PstI site found at 151 - 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal PstI site found at 151
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 579
- 23INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]Illegal XbaI site found at 627
Illegal PstI site found at 151 - 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal XbaI site found at 627
Illegal PstI site found at 151 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
SZPT-China
The results of LAB MG1363 and LAB MG1363 with pMG36e-p - a after induction of recombinant bacteria by different glucose concentrations are shown in Fig. 1. The results showed that when the concentration of glucose in the environment was less than 0.05%, the growth of recombinant bacteria was significantly inhibited.
Reference
- Coolbear, T., Pillidge, C. J., & Crow, V. L. (1994). The diversity of potential cheese ripeningcharacteristics of lactic acid starter bacteria: Resistance to cell lysis and levels of cellular distribution of proteinase activities. International Dairy Journal, 4,697–721.