Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3111502"
m (→Loading cytotoxic cargo) |
m (→Loading cytotoxic cargo) |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K3111502 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K3111502 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | T. maritima encapsulin (6-His) and DARPin929 fusion protein co-expressed with miniSOG in order to report targeting of HER2+ cells and cause a cytotoxic effect in them upon illumination. | + | <i>T. maritima</i> encapsulin (6-His) and DARPin929 fusion protein co-expressed with miniSOG in order to report targeting of HER2+ cells and cause a cytotoxic effect in them upon illumination. |
<!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | <!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
===Composite Part Design=== | ===Composite Part Design=== | ||
| − | T. maritima encapsulin surface display and cargo loading were previously | + | <i>T. maritima</i> encapsulin surface display and cargo loading were previously shown in BioBricks <partinfo>BBa_K3111501</partinfo> and <partinfo>BBa_K3111402</partinfo>. In these experiments we looked at how we can use these properties for the construction of a drug delivery platform. |
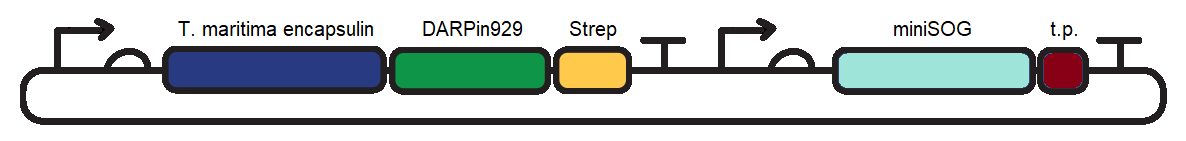
| − | To induce cytotoxic action, we proceeded with loading of the encapsulin system with a fluorescent photosensitiser protein, miniSOG (<partinfo>BBa_K3111032</partinfo>). Under blue-light illumination, miniSOG is activated and generates reactive oxygen species which are damaging to | + | To induce cytotoxic action, we proceeded with loading of the encapsulin system with a fluorescent photosensitiser protein, miniSOG (<partinfo>BBa_K3111032</partinfo>). Under blue-light illumination, miniSOG is activated and generates reactive oxygen species which are damaging to cells (1). To achieve this we cloned <partinfo>BBa_K3111501</partinfo> and <partinfo>BBa_K3111302</partinfo> together to construct the plasmid observed in Figure 1. |
| − | [[Image:TmEncH_DARPin929_miniSOG1.png|600px|thumb|center|'''Figure 1:''' pSB1C3 plasmid containing the T. maritima encapsulin monomer, DARPin929 and miniSOG coding sequences. t.p. - T. maritima encapsulin targeting peptide]] | + | [[Image:TmEncH_DARPin929_miniSOG1.png|600px|thumb|center|'''Figure 1:''' pSB1C3 plasmid containing the <i>T. maritima</i> encapsulin monomer, DARPin929 and miniSOG coding sequences. t.p. - <i>T. maritima</i> encapsulin targeting peptide]] |
===Related Parts=== | ===Related Parts=== | ||
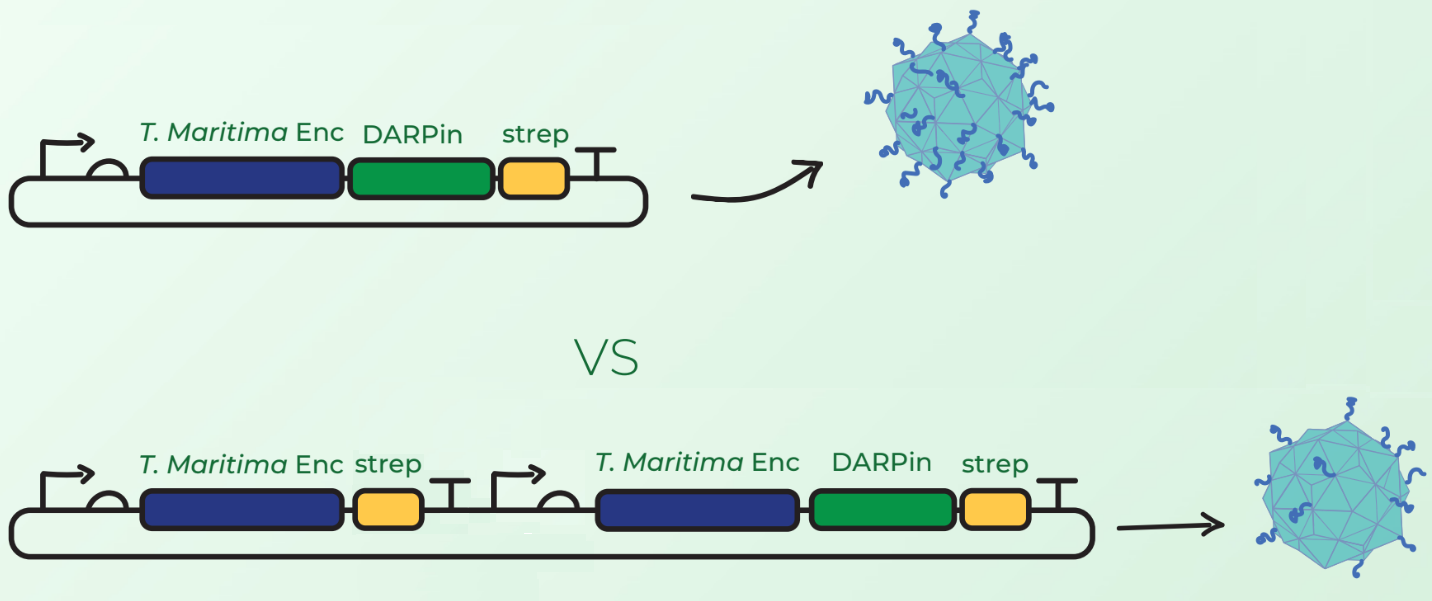
| − | In addition to this device, we tested a different configuration of Encapsulin-DARPin assembly. Surface display of large peptides on encapsulin C-terminus has not been previously described. Our major concern was that the fusion of DARPins on the T. maritima encapsulin monomer would hinder the assembly of 60-mer encapsulin. Our first design in Figure 2 (top) involved C-terminal fusion of the DARPin on the encapsulin coding sequence. However, after discussions with Prof. Steve Brocchini we considered a second cloning strategy observed in Figure 2 (bottom). This involved the downstream cloning of an additional T. maritima encapsulin monomer under its own T7 promoter and ribosome binding site. The rationale was that simultaneous expression of fused and non-fused encapsulin monomers would allow the assembly of an encapsulin with a mixture of the 2 monomers. This would consequently reduce the DARPin load and potentially facilitate the assembly compared to original case where each monomer would have a fused DARPin. | + | In addition to this device, we tested a different configuration of Encapsulin-DARPin assembly. Surface display of large peptides on encapsulin C-terminus has not been previously described. Our major concern was that the fusion of DARPins on the <i>T. maritima</i> encapsulin monomer would hinder the assembly of 60-mer encapsulin. Our first design in Figure 2 (top) involved C-terminal fusion of the DARPin on the encapsulin coding sequence. However, after discussions with Prof. Steve Brocchini we considered a second cloning strategy observed in Figure 2 (bottom). This involved the downstream cloning of an additional <i>T. maritima</i> encapsulin monomer under its own T7 promoter and ribosome binding site. The rationale was that simultaneous expression of fused and non-fused encapsulin monomers would allow the assembly of an encapsulin with a mixture of the 2 monomers. This would consequently reduce the DARPin load and potentially facilitate the assembly compared to original case where each monomer would have a fused DARPin. |
[[Image:TmEnc_device_cloning.png|600px|thumb|center|'''Figure 2:''' Top: <partinfo>BBa_K3111501</partinfo>, which when cloned with <partinfo>BBa_K3111032</partinfo> creates this BioBrick; Bottom: <partinfo>BBa_K3111501</partinfo> + <partinfo>BBa_K3111103</partinfo>, which when cloned with <partinfo>BBa_K3111032</partinfo> creates <partinfo>BBa_K3111503</partinfo>.]] | [[Image:TmEnc_device_cloning.png|600px|thumb|center|'''Figure 2:''' Top: <partinfo>BBa_K3111501</partinfo>, which when cloned with <partinfo>BBa_K3111032</partinfo> creates this BioBrick; Bottom: <partinfo>BBa_K3111501</partinfo> + <partinfo>BBa_K3111103</partinfo>, which when cloned with <partinfo>BBa_K3111032</partinfo> creates <partinfo>BBa_K3111503</partinfo>.]] | ||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
===Loading cytotoxic cargo=== | ===Loading cytotoxic cargo=== | ||
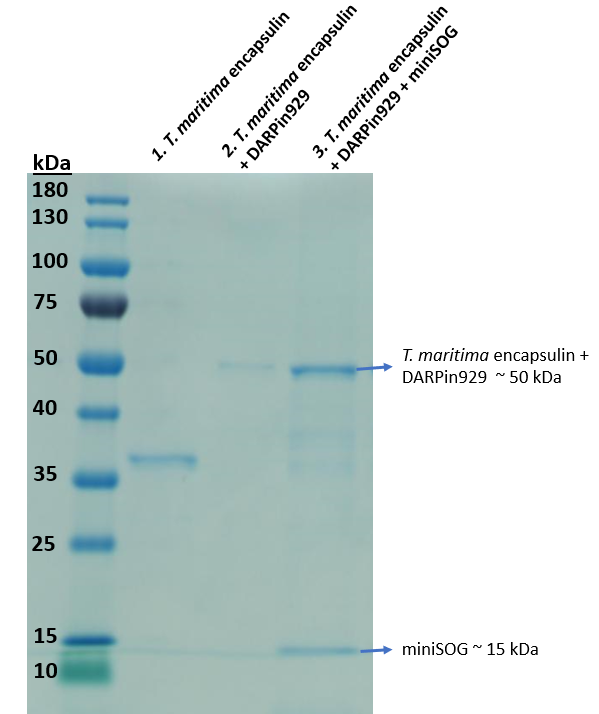
| − | [[Image:TmEncH_DARPin929_miniSOG2.png|300px|thumb|right|'''Figure 3:''' SDS-PAGE analysis of the multicomponent drug delivery vehicle composed of T. maritima encapsulin, surface displayed DARPin929 and loaded miniSOG.]] | + | [[Image:TmEncH_DARPin929_miniSOG2.png|300px|thumb|right|'''Figure 3:''' SDS-PAGE analysis of the purified elution of multicomponent drug delivery vehicle, which is composed of <i>T. maritima</i> encapsulin, surface displayed DARPin929 and loaded miniSOG.]] |
| − | To enable cargo loading we utilised a short native C-terminal targeting peptide ( | + | To enable cargo loading we utilised a short native C-terminal targeting peptide (2) that was previously described to allow foreign cargo loading. Thus, miniSOG was fused to the C-terminal targeting peptide downstream via a flexible linker. Once cloning was proven successful, we used BL21 (DE3) cells for protein expression in a 50mL shake flask culture. Then we purified the soluble cell lysate and obtained a sample to run on an SDS-PAGE to investigate cargo loading. |
| − | In Figure 3, we | + | In Lane 3 of Figure 3, we can see that bands representing both the Encapsulin-DARPin hybrid construct (~50 kDa) and photosensitiser miniSOG (~15 kDa) can be seen in this purified elution. As miniSOG does not possess a Strep-tag, we would not expect to see it in this fraction unless it was bound to the inside of an assembled <i>T. maritima</i> encapsulin. Fluorescence spectrophotometric analysis of the purified elution indicated fluorescence compared to non-loaded encapsulins as well, confirming that there's miniSOG present. Protocol for quantifying cargo loading found on team UCL 2019 website: https://2019.igem.org/Team:UCL/Experiments#Proteins. |
| − | [[Image:TmEncH_loading.png|400px|thumb|center|'''Figure 4:''' | + | [[Image:TmEncH_loading.png|400px|thumb|center|'''Figure 4:''' Quantification of <i>T. maritima</i> encapsulin loading. Error bars show 95% confidence interval.]] |
| − | Figure 4 shows the cargo loading capacity obtained from producing the multicomponent drug delivery platform using BBa_K3111502 and <partinfo>BBa_K3111503</partinfo> cloning strategies. | + | Figure 4 shows the cargo loading capacity obtained from producing the multicomponent drug delivery platform using BBa_K3111502 and <partinfo>BBa_K3111503</partinfo> cloning strategies. Loading capacity for BBa_K3111502 was estimated to be 13.61+-0.36 molecules of miniSOG. In contrast, <partinfo>BBa_K3111503</partinfo> was shown to be loading 8.19+-0.21 miniSOG molecules per encapsulin. We hypothesise that this difference is caused by the surface display of DARPins slowing down the assembly of encapsulins and giving the targeting peptide present on miniSOG more time to form hydrophobic interactions to the inner shell of encapsulin monomers. Due to high error, no significant difference was shown between loading sfGFP and miniSOG, although it was hypothesised that more miniSOG molecules could be loaded due to it being noticeably smaller than sfGFP. Analysis on the methodology used to calculate the number of loaded cargo proteins can be found on <partinfo>BBa_K3111402</partinfo> registry page. |
===Binding and cytotoxicity assay=== | ===Binding and cytotoxicity assay=== | ||
| − | Once the construction of the multicomponent drug delivery vehicle was proven successful through SDS-PAGE and fluorescent spectrophotometric analysis we proceeded with mammalian cell culture studies. We used SK-BR-3 breast adenocarcinoma cells that are overexpressing HER2 receptor, which we had prieviously shown to be targeted by DARPin929 (<partinfo>BBa_K3111011</partinfo>). | + | Once the construction of the multicomponent drug delivery vehicle was proven successful through SDS-PAGE and fluorescent spectrophotometric analysis we proceeded with mammalian cell culture studies. We used SK-BR-3 breast adenocarcinoma cells that are overexpressing HER2 receptor (3), which we had prieviously shown to be targeted by DARPin929 (<partinfo>BBa_K3111011</partinfo>). |
| + | |||
| + | Preliminary cytotoxicity tests using cell proliferation reagent WST-1 revealed that BBa_K3111502 outperformed <partinfo>BBa_K3111503</partinfo>, with 30% and 21% of reduction in cell viability after 30 minutes of illumination respectively. Therefore, additional experiments were only performed on BBa_K3111502. | ||
The cells were first incubated with the Encapsulin-DARPin929-miniSOG drug delivery construct for 30 min, then they were illuminated with white light at 40 lumens/cm2 for 30 mins in order to activate the cytotoxic effect of the encapsulated miniSOG at 37 °C and 20% oxygen. At the end of the experiment, the cells were visualised with EVOS FL microscope to observe uptake of the encapsulins. Following that, all the cell samples were stained using the Annexin V – Propidium Iodide staining kit for determination of potential cell death and percentage loss in viability using flow cytometry. Moreover, we wanted to examine the specificity of the cytotoxic effect thus we replicated the experimental set-up and conditions with Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs), which do not possess the HER2 receptor. We also included two controls which comprised of the SK-BR-3 and MSCs alone. | The cells were first incubated with the Encapsulin-DARPin929-miniSOG drug delivery construct for 30 min, then they were illuminated with white light at 40 lumens/cm2 for 30 mins in order to activate the cytotoxic effect of the encapsulated miniSOG at 37 °C and 20% oxygen. At the end of the experiment, the cells were visualised with EVOS FL microscope to observe uptake of the encapsulins. Following that, all the cell samples were stained using the Annexin V – Propidium Iodide staining kit for determination of potential cell death and percentage loss in viability using flow cytometry. Moreover, we wanted to examine the specificity of the cytotoxic effect thus we replicated the experimental set-up and conditions with Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs), which do not possess the HER2 receptor. We also included two controls which comprised of the SK-BR-3 and MSCs alone. | ||
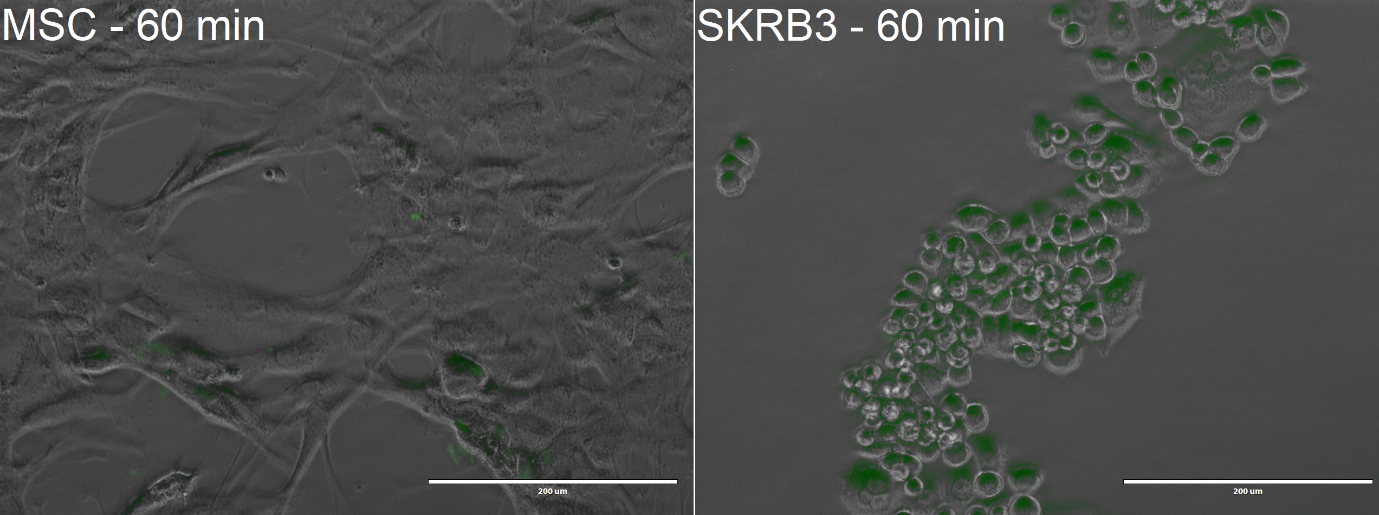
| − | [[Image:TmEncH_DARPin929_miniSOG3.png|500px|thumb|center|'''Figure 5:''' Confocal Microscopy image of MSCs and SK-BR-3 after | + | [[Image:TmEncH_DARPin929_miniSOG3.png|500px|thumb|center|'''Figure 5:''' Confocal Microscopy image of MSCs and SK-BR-3 after 60-minute incubation; Scalebar: 200 μm.]] |
From the confocal microscopy imaging in Figure 5, we could see that after 1-hour incubation green fluorescence from miniSOG was detected in both samples. Fluorescence was not expected for the MSCs, since from our previous experiments with <partinfo>BBa_K3111201</partinfo> we have not observed any unspecific binding. We hypothesise that the concentration of construct that we loaded was too high, thus non-specific passive uptake was initiated. However, since significantly more fluorescence was observed in SK-BR-3 cells, we can deem that the system is indeed selective. | From the confocal microscopy imaging in Figure 5, we could see that after 1-hour incubation green fluorescence from miniSOG was detected in both samples. Fluorescence was not expected for the MSCs, since from our previous experiments with <partinfo>BBa_K3111201</partinfo> we have not observed any unspecific binding. We hypothesise that the concentration of construct that we loaded was too high, thus non-specific passive uptake was initiated. However, since significantly more fluorescence was observed in SK-BR-3 cells, we can deem that the system is indeed selective. | ||
| − | [[Image:TmEncH_DARPin929_miniSOG4.png|600px|thumb|center|'''Figure 6:''' Cell death flow cytometry analysis for different illumination conditions | + | [[Image:TmEncH_DARPin929_miniSOG4.png|600px|thumb|center|'''Figure 6:''' Cell death flow cytometry analysis for different illumination conditions. Note that MSCs shown here were illuminated for 60 minutes unlike described previously.]] |
The plots in Figure 6 are separated in 4 quadrants over which the cell population is distributed. The upper left quadrant indicated the percentage of necrotic cells, the upper right the percentage of late apoptotic cells, the lower left shows the percentage of viable cells and the lower right the percentage of early apoptotic cells. Cell controls in Figure 6 (a) and (d) helped to define the normal boundaries for their respective cell type | The plots in Figure 6 are separated in 4 quadrants over which the cell population is distributed. The upper left quadrant indicated the percentage of necrotic cells, the upper right the percentage of late apoptotic cells, the lower left shows the percentage of viable cells and the lower right the percentage of early apoptotic cells. Cell controls in Figure 6 (a) and (d) helped to define the normal boundaries for their respective cell type | ||
| − | From Figure 6 ( | + | From Figure 6 (b) we could observe a shift in cell population majorly towards the lower right quadrant indicating early apoptosis of the cell before illumination compared to our control cell population in 6 (a). While this was not expected, we speculate that light falling on the well plates during sample processing could have induced miniSOG, thus resulting in a loss of cell viability. MSCs however presented only a minimal percentage of early apoptotic cells. After illumination, we observed a considerable shift towards the upper and lower right quadrants in Figure 6 (c), indicating a high rate of apoptosis with a total of around 80% reduction in cell viability. The loss of viability in MSC through early apoptosis observed in Figure 6 (d, e and f) could be associated to the greater sensibility of stem cells to environmental condition fluctuation (in this instance, strong illumination) or the handling of the cells required for imaging and staining. |
| + | |||
| + | ===Conclusion=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | To conclude, these experiments show that our drug delivery platform successfully targets HER2 overexpressing SK-BR-3 cells and kills them at a significantly higher degree than MSCs once illuminated with light, thus demonstrating double selectivity in terms of cytotoxicity. | ||
| + | |||
| + | These experiments show that our drug delivery platform successfully targets HER2 overexpressing SK-BR-3 cells and kills them at a significantly higher degree than MSCs once illuminated with light, thus demonstrating double selectivity in terms of cytotoxicity. We believe this composite part has proven the concept of Encapsulin-DARPin drug delivery platform, and it can be further adapted upon by using different encapsulins, DARPins and cargo. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [1] Xu S, Chisholm AD. Highly efficient optogenetic cell ablation in C. elegans using membrane-targeted miniSOG. Sci Rep [Internet]. 2016 Feb [cited 2019 Oct 14];6(1). Available from: http://www.nature.com/articles/srep21271 | ||
| + | |||
| + | [2] Cassidy-Amstutz C, Oltrogge L, Going CC, Lee A, Teng P, Quintanilla D, et al. Identification of a Minimal Peptide Tag for in Vivo and in Vitro Loading of Encapsulin. Biochemistry. 2016 Jun 21;55(24):3461– | ||
| − | + | [3] Camacho-Leal MP, Sciortino M, Cabodi S. ErbB2 Receptor in Breast Cancer: Implications in Cancer Cell Migration, Invasion and Resistance to Targeted Therapy, Breast Cancer - From Biology to Medicine. Phuc Van Pham, IntechOpen. | |
Latest revision as of 20:16, 20 October 2019
TmEncH_DARPin929_StrepII + miniSOG_TP
T. maritima encapsulin (6-His) and DARPin929 fusion protein co-expressed with miniSOG in order to report targeting of HER2+ cells and cause a cytotoxic effect in them upon illumination.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 171
Illegal BglII site found at 586
Illegal BamHI site found at 950
Illegal BamHI site found at 2101 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI site found at 1677
Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 2321
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 520
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 551
Composite Part Design
T. maritima encapsulin surface display and cargo loading were previously shown in BioBricks BBa_K3111501 and BBa_K3111402. In these experiments we looked at how we can use these properties for the construction of a drug delivery platform.
To induce cytotoxic action, we proceeded with loading of the encapsulin system with a fluorescent photosensitiser protein, miniSOG (BBa_K3111032). Under blue-light illumination, miniSOG is activated and generates reactive oxygen species which are damaging to cells (1). To achieve this we cloned BBa_K3111501 and BBa_K3111302 together to construct the plasmid observed in Figure 1.
Related Parts
In addition to this device, we tested a different configuration of Encapsulin-DARPin assembly. Surface display of large peptides on encapsulin C-terminus has not been previously described. Our major concern was that the fusion of DARPins on the T. maritima encapsulin monomer would hinder the assembly of 60-mer encapsulin. Our first design in Figure 2 (top) involved C-terminal fusion of the DARPin on the encapsulin coding sequence. However, after discussions with Prof. Steve Brocchini we considered a second cloning strategy observed in Figure 2 (bottom). This involved the downstream cloning of an additional T. maritima encapsulin monomer under its own T7 promoter and ribosome binding site. The rationale was that simultaneous expression of fused and non-fused encapsulin monomers would allow the assembly of an encapsulin with a mixture of the 2 monomers. This would consequently reduce the DARPin load and potentially facilitate the assembly compared to original case where each monomer would have a fused DARPin.
Experimental Results
Our ultimate aim for BBa_K3111502 was to test whether this device can illicit cytotoxic effect in SK-BR-3 cells with two layers of selectivity: DARPin binding and light induction.
Loading cytotoxic cargo
To enable cargo loading we utilised a short native C-terminal targeting peptide (2) that was previously described to allow foreign cargo loading. Thus, miniSOG was fused to the C-terminal targeting peptide downstream via a flexible linker. Once cloning was proven successful, we used BL21 (DE3) cells for protein expression in a 50mL shake flask culture. Then we purified the soluble cell lysate and obtained a sample to run on an SDS-PAGE to investigate cargo loading.
In Lane 3 of Figure 3, we can see that bands representing both the Encapsulin-DARPin hybrid construct (~50 kDa) and photosensitiser miniSOG (~15 kDa) can be seen in this purified elution. As miniSOG does not possess a Strep-tag, we would not expect to see it in this fraction unless it was bound to the inside of an assembled T. maritima encapsulin. Fluorescence spectrophotometric analysis of the purified elution indicated fluorescence compared to non-loaded encapsulins as well, confirming that there's miniSOG present. Protocol for quantifying cargo loading found on team UCL 2019 website: https://2019.igem.org/Team:UCL/Experiments#Proteins.
Figure 4 shows the cargo loading capacity obtained from producing the multicomponent drug delivery platform using BBa_K3111502 and BBa_K3111503 cloning strategies. Loading capacity for BBa_K3111502 was estimated to be 13.61+-0.36 molecules of miniSOG. In contrast, BBa_K3111503 was shown to be loading 8.19+-0.21 miniSOG molecules per encapsulin. We hypothesise that this difference is caused by the surface display of DARPins slowing down the assembly of encapsulins and giving the targeting peptide present on miniSOG more time to form hydrophobic interactions to the inner shell of encapsulin monomers. Due to high error, no significant difference was shown between loading sfGFP and miniSOG, although it was hypothesised that more miniSOG molecules could be loaded due to it being noticeably smaller than sfGFP. Analysis on the methodology used to calculate the number of loaded cargo proteins can be found on BBa_K3111402 registry page.
Binding and cytotoxicity assay
Once the construction of the multicomponent drug delivery vehicle was proven successful through SDS-PAGE and fluorescent spectrophotometric analysis we proceeded with mammalian cell culture studies. We used SK-BR-3 breast adenocarcinoma cells that are overexpressing HER2 receptor (3), which we had prieviously shown to be targeted by DARPin929 (BBa_K3111011).
Preliminary cytotoxicity tests using cell proliferation reagent WST-1 revealed that BBa_K3111502 outperformed BBa_K3111503, with 30% and 21% of reduction in cell viability after 30 minutes of illumination respectively. Therefore, additional experiments were only performed on BBa_K3111502.
The cells were first incubated with the Encapsulin-DARPin929-miniSOG drug delivery construct for 30 min, then they were illuminated with white light at 40 lumens/cm2 for 30 mins in order to activate the cytotoxic effect of the encapsulated miniSOG at 37 °C and 20% oxygen. At the end of the experiment, the cells were visualised with EVOS FL microscope to observe uptake of the encapsulins. Following that, all the cell samples were stained using the Annexin V – Propidium Iodide staining kit for determination of potential cell death and percentage loss in viability using flow cytometry. Moreover, we wanted to examine the specificity of the cytotoxic effect thus we replicated the experimental set-up and conditions with Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs), which do not possess the HER2 receptor. We also included two controls which comprised of the SK-BR-3 and MSCs alone.
From the confocal microscopy imaging in Figure 5, we could see that after 1-hour incubation green fluorescence from miniSOG was detected in both samples. Fluorescence was not expected for the MSCs, since from our previous experiments with BBa_K3111201 we have not observed any unspecific binding. We hypothesise that the concentration of construct that we loaded was too high, thus non-specific passive uptake was initiated. However, since significantly more fluorescence was observed in SK-BR-3 cells, we can deem that the system is indeed selective.
The plots in Figure 6 are separated in 4 quadrants over which the cell population is distributed. The upper left quadrant indicated the percentage of necrotic cells, the upper right the percentage of late apoptotic cells, the lower left shows the percentage of viable cells and the lower right the percentage of early apoptotic cells. Cell controls in Figure 6 (a) and (d) helped to define the normal boundaries for their respective cell type
From Figure 6 (b) we could observe a shift in cell population majorly towards the lower right quadrant indicating early apoptosis of the cell before illumination compared to our control cell population in 6 (a). While this was not expected, we speculate that light falling on the well plates during sample processing could have induced miniSOG, thus resulting in a loss of cell viability. MSCs however presented only a minimal percentage of early apoptotic cells. After illumination, we observed a considerable shift towards the upper and lower right quadrants in Figure 6 (c), indicating a high rate of apoptosis with a total of around 80% reduction in cell viability. The loss of viability in MSC through early apoptosis observed in Figure 6 (d, e and f) could be associated to the greater sensibility of stem cells to environmental condition fluctuation (in this instance, strong illumination) or the handling of the cells required for imaging and staining.
Conclusion
To conclude, these experiments show that our drug delivery platform successfully targets HER2 overexpressing SK-BR-3 cells and kills them at a significantly higher degree than MSCs once illuminated with light, thus demonstrating double selectivity in terms of cytotoxicity.
These experiments show that our drug delivery platform successfully targets HER2 overexpressing SK-BR-3 cells and kills them at a significantly higher degree than MSCs once illuminated with light, thus demonstrating double selectivity in terms of cytotoxicity. We believe this composite part has proven the concept of Encapsulin-DARPin drug delivery platform, and it can be further adapted upon by using different encapsulins, DARPins and cargo.
References
[1] Xu S, Chisholm AD. Highly efficient optogenetic cell ablation in C. elegans using membrane-targeted miniSOG. Sci Rep [Internet]. 2016 Feb [cited 2019 Oct 14];6(1). Available from: http://www.nature.com/articles/srep21271
[2] Cassidy-Amstutz C, Oltrogge L, Going CC, Lee A, Teng P, Quintanilla D, et al. Identification of a Minimal Peptide Tag for in Vivo and in Vitro Loading of Encapsulin. Biochemistry. 2016 Jun 21;55(24):3461–
[3] Camacho-Leal MP, Sciortino M, Cabodi S. ErbB2 Receptor in Breast Cancer: Implications in Cancer Cell Migration, Invasion and Resistance to Targeted Therapy, Breast Cancer - From Biology to Medicine. Phuc Van Pham, IntechOpen.