Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K2656002"
Alejovigno (Talk | contribs) |
Alejovigno (Talk | contribs) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | __NOTOC__ | |
<partinfo>BBa_K2656002 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K2656002 short</partinfo> | ||
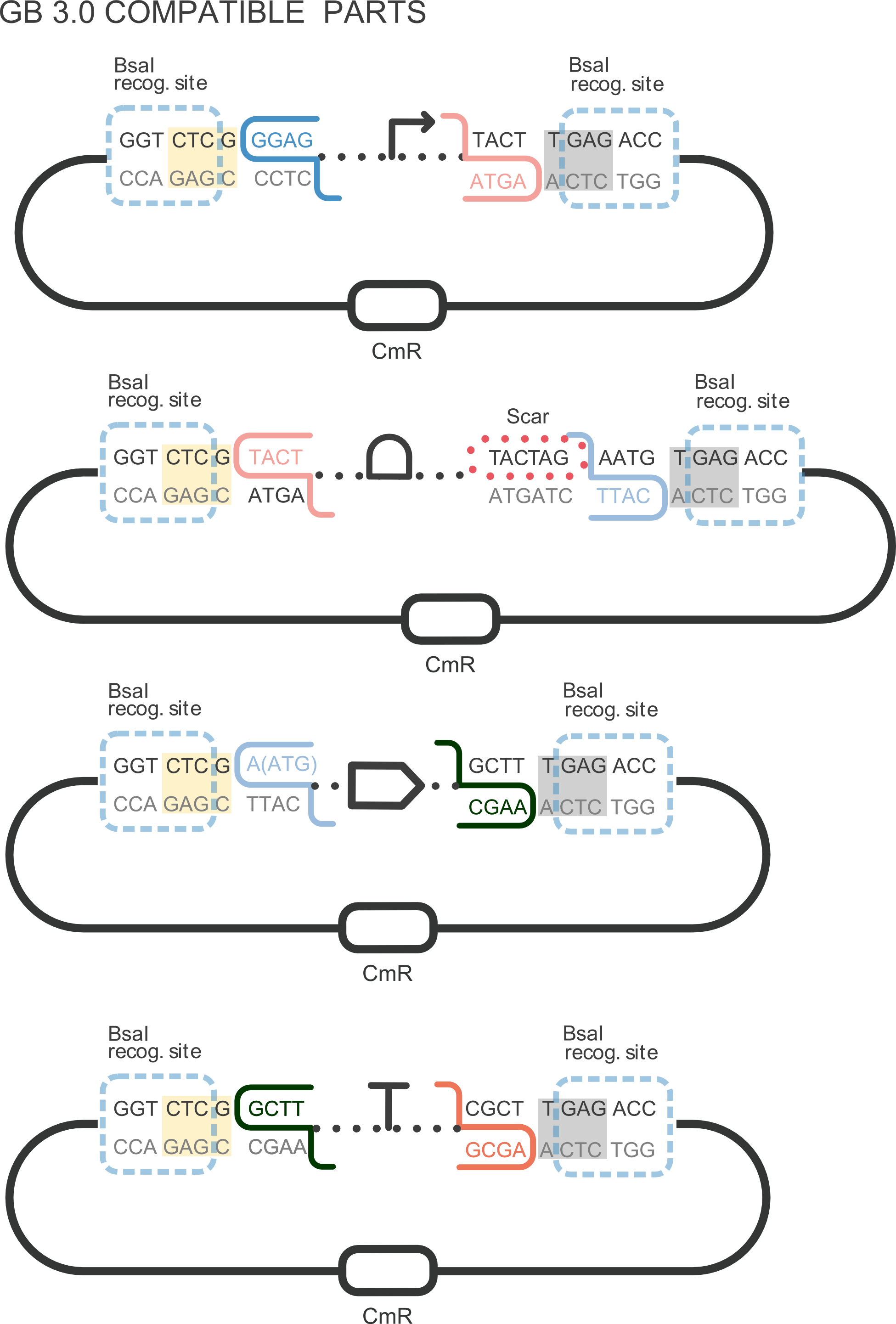
[[File:T--Valencia_UPV--im11UPV2018.png|250px|thumb|centro|alt=domestication.|Figure 1. DNA basic parts domestication. First construction refers to promoter GB domestication. ]] | [[File:T--Valencia_UPV--im11UPV2018.png|250px|thumb|centro|alt=domestication.|Figure 1. DNA basic parts domestication. First construction refers to promoter GB domestication. ]] | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
repressible promoter PluxR designed in (Egland and Greenberg, 2000). | repressible promoter PluxR designed in (Egland and Greenberg, 2000). | ||
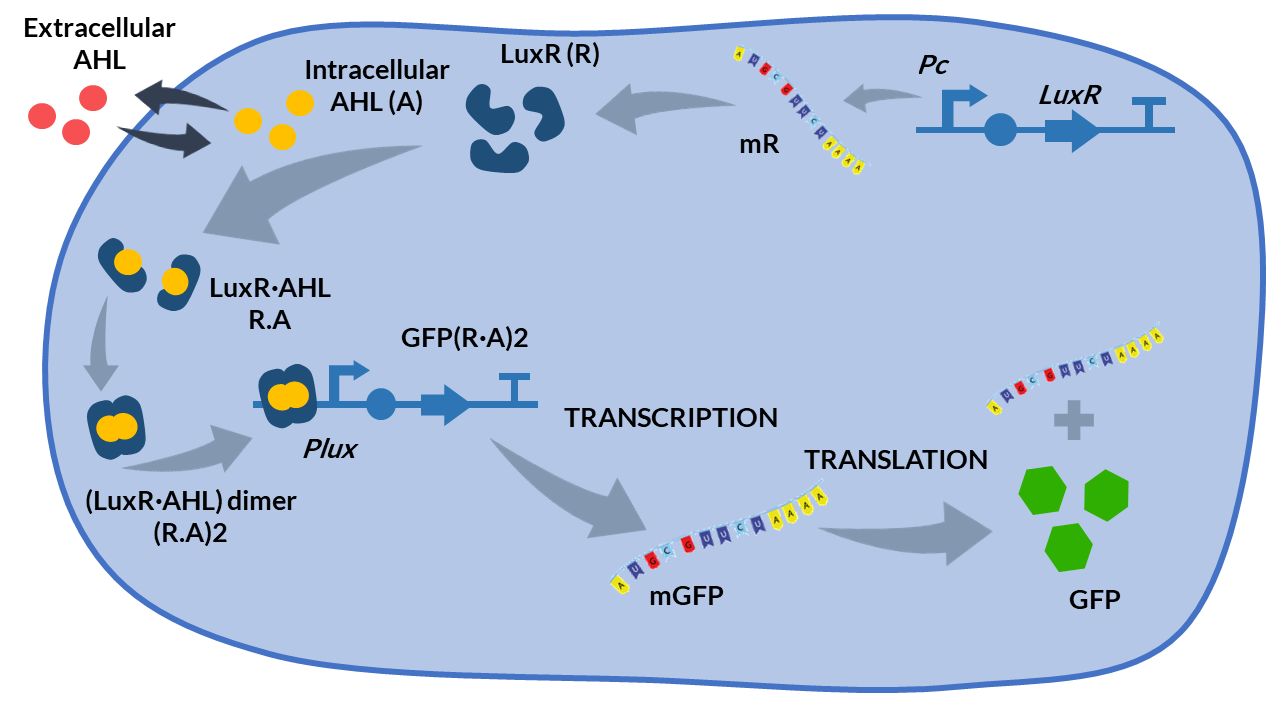
| − | [[File:T--Valencia UPV--luxR luxI schemaUPV2018.png.png| | + | [[File:T--Valencia UPV--luxR luxI schemaUPV2018.png.png|400px|thumb|none|alt=LuxR represible promoter and QS.|Figure 2. Schema of the LuxR promoter functioning.]] |
This part can be combined with other compatible parts from our [http://2018.igem.org/Team:Valencia_UPV/Part_Collection Valencia UPV IGEM 2018 Printeria Collection] to assemble transcriptional units with the <html><a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/parts/b/bc/T--Valencia_UPV--protocols.pdf#page=27"> Golden Gate assembly protocol </a></html>. | This part can be combined with other compatible parts from our [http://2018.igem.org/Team:Valencia_UPV/Part_Collection Valencia UPV IGEM 2018 Printeria Collection] to assemble transcriptional units with the <html><a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/parts/b/bc/T--Valencia_UPV--protocols.pdf#page=27"> Golden Gate assembly protocol </a></html>. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
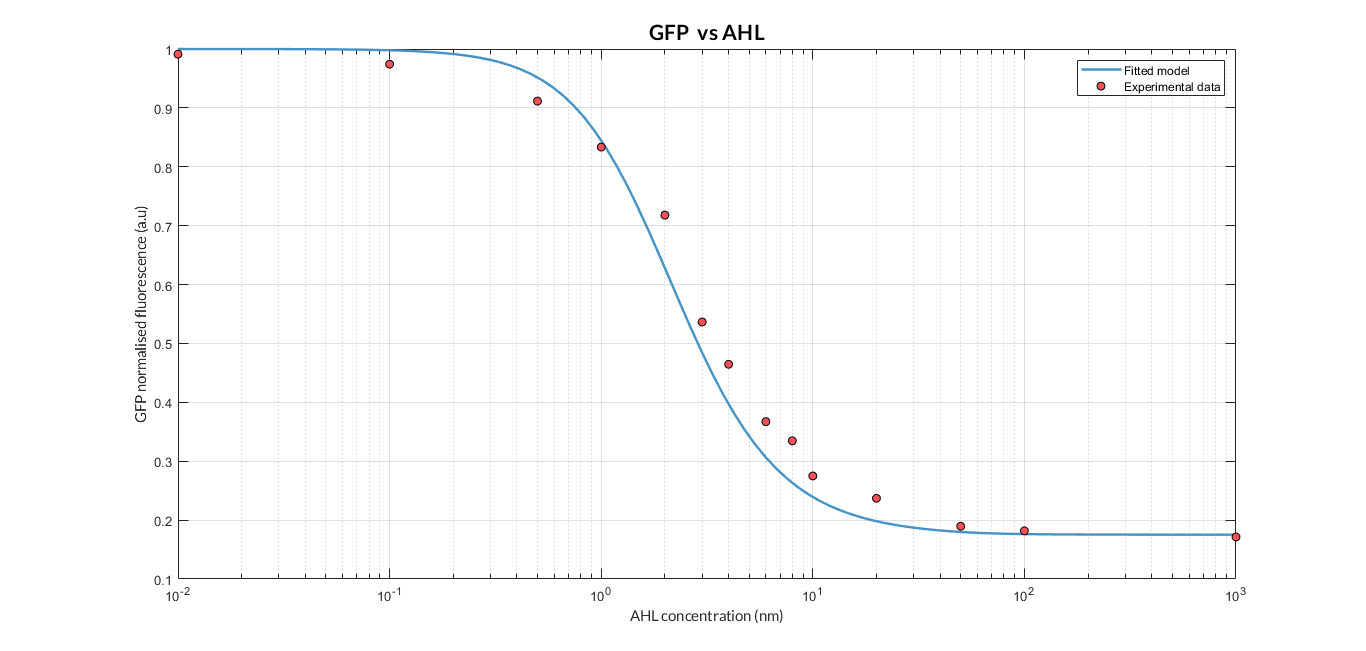
By using this [http://2018.igem.org/Team:Valencia_UPV/Experiments#exp_protocol experimental protocol] and inducing at different AHL concentrations, we have obtained the following experimental measures (in blue dots). This measurements were compared with our [http://2018.igem.org/Team:Valencia_UPV/Modeling#models constitutive AHL-LuxR model] to test it. | By using this [http://2018.igem.org/Team:Valencia_UPV/Experiments#exp_protocol experimental protocol] and inducing at different AHL concentrations, we have obtained the following experimental measures (in blue dots). This measurements were compared with our [http://2018.igem.org/Team:Valencia_UPV/Modeling#models constitutive AHL-LuxR model] to test it. | ||
| − | |||
[[File:T--Valencia_UPV_AHL_UPV2018.png|900px|thumb|none|alt=AHL experiment.|Figure 3. AHL induction experiment and comparison with our model simulation.]] | [[File:T--Valencia_UPV_AHL_UPV2018.png|900px|thumb|none|alt=AHL experiment.|Figure 3. AHL induction experiment and comparison with our model simulation.]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | <!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | ||
Latest revision as of 03:48, 18 October 2018
Promoter HSL-mediated luxR repressor
Part BBa_K2656002 is the repressible promoter BBa_R0061 compatible with both Biobrick and [http://2018.igem.org/Team:Valencia_UPV/Design GoldenBraid 3.0] assemply methods.
When LuxR protein is present, the Quorum Sensing responsible small molecule AHL (Acyl-homoserine-lactone) binds forming the heterodimer (LuxR.AHL), which subsequently dimerizes as the heterotetramer (LuxR.AHL)2 (Boada et al, 2017) as shown in Figure 2. This complex is the active transcription factor that represses this synthetic
repressible promoter PluxR designed in (Egland and Greenberg, 2000).
This part can be combined with other compatible parts from our [http://2018.igem.org/Team:Valencia_UPV/Part_Collection Valencia UPV IGEM 2018 Printeria Collection] to assemble transcriptional units with the Golden Gate assembly protocol .
In order characterize this promoter we constructed the composite part BBa_K2656116 using the following RBS, CDS and terminator:
- RBS BBa_K2656009: the B0030 RBS in its Golden Braid compatible version from our [http://2018.igem.org/Team:Valencia_UPV/Part_Collection Part Collection]
- CDS BBa_K2656022: the E0040 GFPmut3b sequence in its Golden Braid standardized version from our [http://2018.igem.org/Team:Valencia_UPV/Part_Collection Part Collection]
- Terminator BBa_K2656026: the B0015 transcriptional terminator in its Golden Braid compatible version from our [http://2018.igem.org/Team:Valencia_UPV/Part_Collection Part Collection]
By using this [http://2018.igem.org/Team:Valencia_UPV/Experiments#exp_protocol experimental protocol] and inducing at different AHL concentrations, we have obtained the following experimental measures (in blue dots). This measurements were compared with our [http://2018.igem.org/Team:Valencia_UPV/Modeling#models constitutive AHL-LuxR model] to test it.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]