Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K2259027"
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K2259027 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K2259027 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | This | + | This is an intermediate construct to the full SynORI constitutive copy number device. It consists of an Anderson promoter and ColE1 RNA I gene (without promoter). It can be combined with [[part:BBa_K2259000]] replication initiation part. |
| − | When combined with RNA II | + | When combined with RNA II this device sets a defined copy number for a plasmid (see:[[part:BBa_K2259069]]). |
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
===ColE1 plasmid replication overview=== | ===ColE1 plasmid replication overview=== | ||
| − | [[Image:Cole1 horizontal cropped.png|center| | + | [[Image:Cole1 horizontal cropped.png|300px| center|]] |
| − | + | <b><center>Figure 1. Main principles of ColE1 plasmid family replication</center> | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ColE1-type plasmid replication begins with the synthesis of plasmid encoded RNA II</b> (also called primer transcript) by RNA polymerase which initiates transcription at a site 555bp upstream of origin of replication. The RNA transcript forms a RNA - DNA hybrid with template DNA near the origin of replication. Hybridized RNA is then cleaved at the replication origin by RNAse H and serves as a primer for DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase I (Figure 1. A).<ref>Itoh, T. and Tomizawa, J. (1980). Formation of an RNA primer for initiation of replication of ColE1 DNA by ribonuclease H. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 77(5), pp.2450-2454.</ref> | |
| − | + | <b>Initiation of replication can be inhibited by plasmid encoded small RNA, called RNA I </b>. Synthesis of RNA I starts 445 bp upstream of the replication origin and proceeds in the direction opposite to that of RNA II synthesis and terminates near the RNA II transcription initiation site. <b>RNA I binds to RNA II</b> and thereby prevents the formation of a secondary structure of RNA II that is necessary for hybridization of RNA II to the template DNA (Figure 1. B).<ref>Tomizawa, J. (1984). Control of cole 1 plasmid replication: The process of binding of RNA I to the primer transcript. Cell, 38(3), pp.861-870.</ref> | |
| − | + | For RNA I to inhibit primer formation, it must bind before the nascent RNA II transcript extends to the replication origin. Consequently, the concentration of RNA I and the rate of binding of RNA I to RNA II is critical for regulation of primer formation and thus for plasmid replication. <ref>Tomizawa, J. (1984). Control of cole 1 plasmid replication: The process of binding of RNA I to the primer transcript. Cell, 38(3), pp.861-870.</ref> | |
| + | |||
| + | The interaction between RNA I and RNA II can be amplified by Rop protein, see [[part:BBa_K2259010]]. | ||
==Usage with SynORI (Framework for multi-plasmid systems)== | ==Usage with SynORI (Framework for multi-plasmid systems)== | ||
===About SynORI=== | ===About SynORI=== | ||
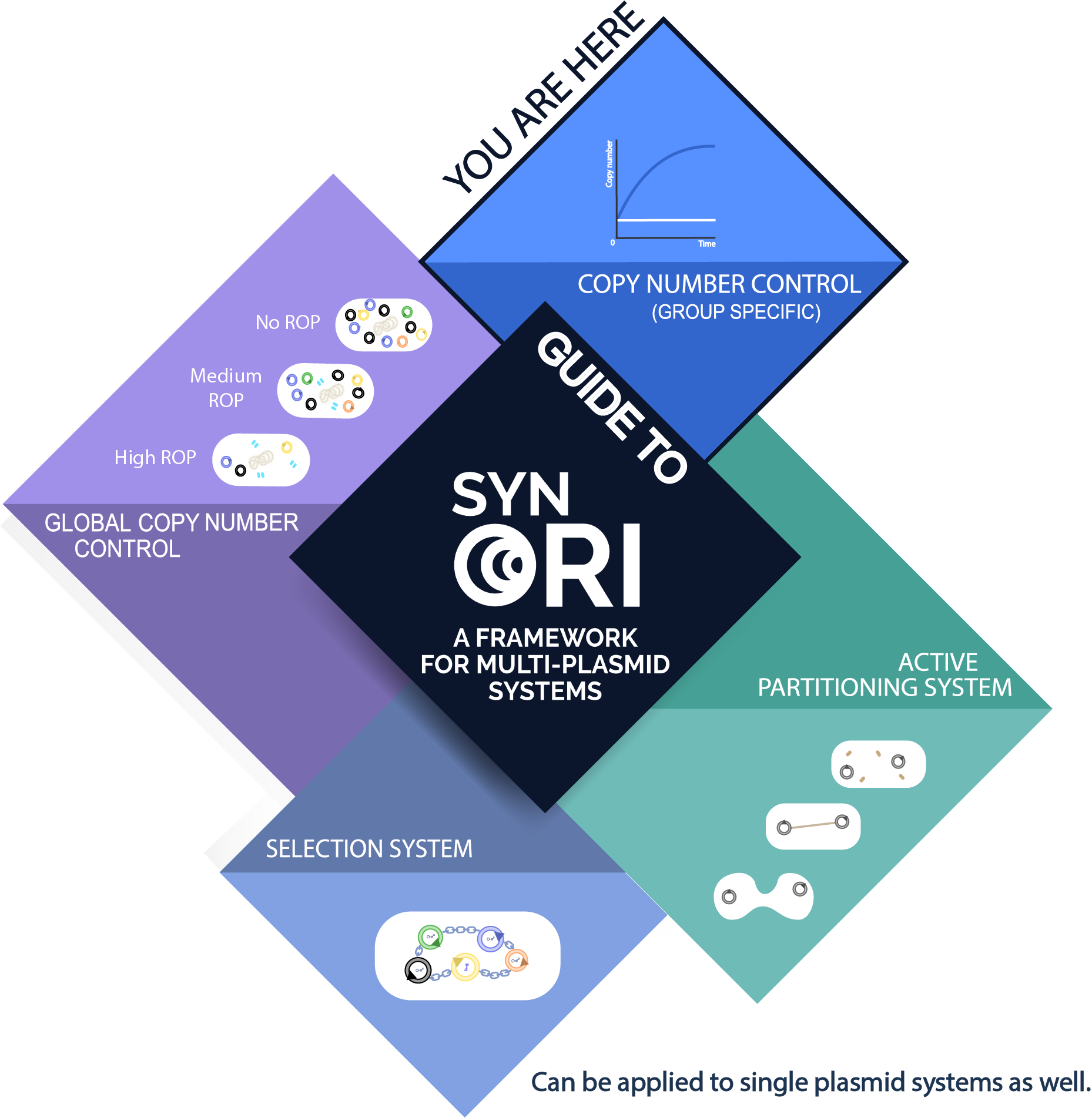
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Groupspec.png|600px|center|]] |
SynORI is a framework for multi-plasmid systems created by ''Vilnius-Lithuania 2017'' which enables quick and easy workflow with multiple plasmids, while also allowing to freely pick and modulate copy number for every unique plasmid group! Read more about [http://2017.igem.org/Team:Vilnius-Lithuania SynORI here]! | SynORI is a framework for multi-plasmid systems created by ''Vilnius-Lithuania 2017'' which enables quick and easy workflow with multiple plasmids, while also allowing to freely pick and modulate copy number for every unique plasmid group! Read more about [http://2017.igem.org/Team:Vilnius-Lithuania SynORI here]! | ||
| − | |||
=Characterization= | =Characterization= | ||
| − | In order to characterize this construct it must be cloned next to RNA II gene. Please see [[part:BBa_K2259069]]. | + | In order to characterize this construct, it must be cloned next to RNA II gene. Please see [[part:BBa_K2259069]]. |
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Latest revision as of 17:05, 1 November 2017
SynORI constitutive plasmid copy number device intermediate (0.86 Anderson)
This is an intermediate construct to the full SynORI constitutive copy number device. It consists of an Anderson promoter and ColE1 RNA I gene (without promoter). It can be combined with part:BBa_K2259000 replication initiation part.
When combined with RNA II this device sets a defined copy number for a plasmid (see:part:BBa_K2259069).
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 7
Illegal NheI site found at 30 - 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Contents
Introduction
Biology
ColE1 plasmid replication overview
ColE1-type plasmid replication begins with the synthesis of plasmid encoded RNA II (also called primer transcript) by RNA polymerase which initiates transcription at a site 555bp upstream of origin of replication. The RNA transcript forms a RNA - DNA hybrid with template DNA near the origin of replication. Hybridized RNA is then cleaved at the replication origin by RNAse H and serves as a primer for DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase I (Figure 1. A).[1]
Initiation of replication can be inhibited by plasmid encoded small RNA, called RNA I . Synthesis of RNA I starts 445 bp upstream of the replication origin and proceeds in the direction opposite to that of RNA II synthesis and terminates near the RNA II transcription initiation site. RNA I binds to RNA II and thereby prevents the formation of a secondary structure of RNA II that is necessary for hybridization of RNA II to the template DNA (Figure 1. B).[2]
For RNA I to inhibit primer formation, it must bind before the nascent RNA II transcript extends to the replication origin. Consequently, the concentration of RNA I and the rate of binding of RNA I to RNA II is critical for regulation of primer formation and thus for plasmid replication. [3]
The interaction between RNA I and RNA II can be amplified by Rop protein, see part:BBa_K2259010.
Usage with SynORI (Framework for multi-plasmid systems)
About SynORI
SynORI is a framework for multi-plasmid systems created by Vilnius-Lithuania 2017 which enables quick and easy workflow with multiple plasmids, while also allowing to freely pick and modulate copy number for every unique plasmid group! Read more about [http://2017.igem.org/Team:Vilnius-Lithuania SynORI here]!
Characterization
In order to characterize this construct, it must be cloned next to RNA II gene. Please see part:BBa_K2259069.
References
- ↑ Itoh, T. and Tomizawa, J. (1980). Formation of an RNA primer for initiation of replication of ColE1 DNA by ribonuclease H. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 77(5), pp.2450-2454.
- ↑ Tomizawa, J. (1984). Control of cole 1 plasmid replication: The process of binding of RNA I to the primer transcript. Cell, 38(3), pp.861-870.
- ↑ Tomizawa, J. (1984). Control of cole 1 plasmid replication: The process of binding of RNA I to the primer transcript. Cell, 38(3), pp.861-870.