Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K2224001:Experience"
(→Experiment Abstract) |
(→Applications of BBa_K2224001) |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
====Part Description:==== | ====Part Description:==== | ||
This is the experiment report of SMS_Shenzhen team in August, 2017. | This is the experiment report of SMS_Shenzhen team in August, 2017. | ||
| + | [[File:BBa K2224001 Plate Streaking.jpeg|600px|thumb|left|Fig.1 Plate streaking result of BBa K2224001]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''''Figure 1 The result of plate streaking of BioBrick BBa_K2224001''''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
We, 2017 SMS iGEM Team, have submitted this part AND characterized the function and effectiveness of this part. | We, 2017 SMS iGEM Team, have submitted this part AND characterized the function and effectiveness of this part. | ||
BBa_K2224001 is a composite part with the backbone pSB1C3. The CDS of this part is '''''Lecanicillium lecanii strain 432 endochitinase (chit1)''''', a chitinase originate from ''verticillium lecanii'', a kind of '''entomogenous fungus'''. With a GeneBank identifier '''DQ412944''' in NCBI. This enzyme helps catalyze chitin. SMS students optimized the codons and removed introns to fit the original sequence into E. coli expression system. | BBa_K2224001 is a composite part with the backbone pSB1C3. The CDS of this part is '''''Lecanicillium lecanii strain 432 endochitinase (chit1)''''', a chitinase originate from ''verticillium lecanii'', a kind of '''entomogenous fungus'''. With a GeneBank identifier '''DQ412944''' in NCBI. This enzyme helps catalyze chitin. SMS students optimized the codons and removed introns to fit the original sequence into E. coli expression system. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
====Experiment Abstract==== | ====Experiment Abstract==== | ||
| Line 22: | Line 45: | ||
''(ABS is for absorbance, U is for active unit)'' | ''(ABS is for absorbance, U is for active unit)'' | ||
[[File:Chitinase Activity.png|200px|thumb|left|Chitinase Activity scatter diagram]] | [[File:Chitinase Activity.png|200px|thumb|left|Chitinase Activity scatter diagram]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | =====Measurement of OD600 ===== | ||
| + | To obtain the bacteria quantity in sample for active unit measurement, we constructed a standard bacteria concentration diagram. | ||
| + | We used Flat colony counting method to obtain the Standard Calibration Curve for Bacterial Concentration: | ||
| + | #Prepare LB medium. | ||
| + | #Take the available preserved TOP10 strain, pick the bacteria strain by using a platinum ring beside a fire and then draw lines on solid LB medium. | ||
| + | #Culture the inoculated medium in constant temperature incubator for 24h, temperature at '''37 ℃ ±1 ℃''' in incubator. Pick monoclonal bacteria colonies, inject in '''20mL''' liquid LB medium, shake the medium in constant temperature shaking incubator '''(110r/ min, 3cm oscillation amplitude)''' for '''24h'''. | ||
| + | #Take '''0.4mL''' cultured bacteria fluid in logarithmic growth phase, cultured in 20mL nutrient bacteria medium, then shake the medium for '''4h''' to get bacteria fluid in stable phase. | ||
| + | #Dilute the cultured bacteria fluid in stable phase with liquid LB medium '''(for 5, 10, 20, 40 times)'''. In '''660nm''' standard wavelength, measure the absorbance (ABS) of this group of samples different bacteria concentration. (Zeroing before testing with 1x liquid LB medium). | ||
| + | #Determine the colony numbers of four different dilution times in turns in a sterile room next to the flame. Each sample was formulated in several concentration gradients, and''' 1 mL''' of each sample was injected into the dish with sterilized pipette. Inject about '''15 mL ,45~50 ℃''' solid LB medium, then turn the dish so that the sample with the medium can be fully mixed. When medium solidified, turn the plate. Place the medium in '''37 ℃±1 ℃''' incubator to culture for '''24h''', count the number of colonies. With eye observation, the colony number was counted and recorded. The average colony number of each dilution plate can then be obtained. | ||
| + | [[File:Dilution of top10 bacteria which contains BioBrick BBa K2224001 results.jpeg|300px|thumb|left|Fig.2 Dilution of top10 bacteria which contains BioBrick BBa K2224001 results]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Using the spectrophotometer to get the estimated value of optical density of the samples,we made a conversion to the concentration of the bacterial suspension. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''''Figure 2 the results of the colony counting of 10^6 and 10^7 times diluted bacteria fluid(the fluid was coated on solid LB medium to grow visible colonies)''''' | ||
| + | |||
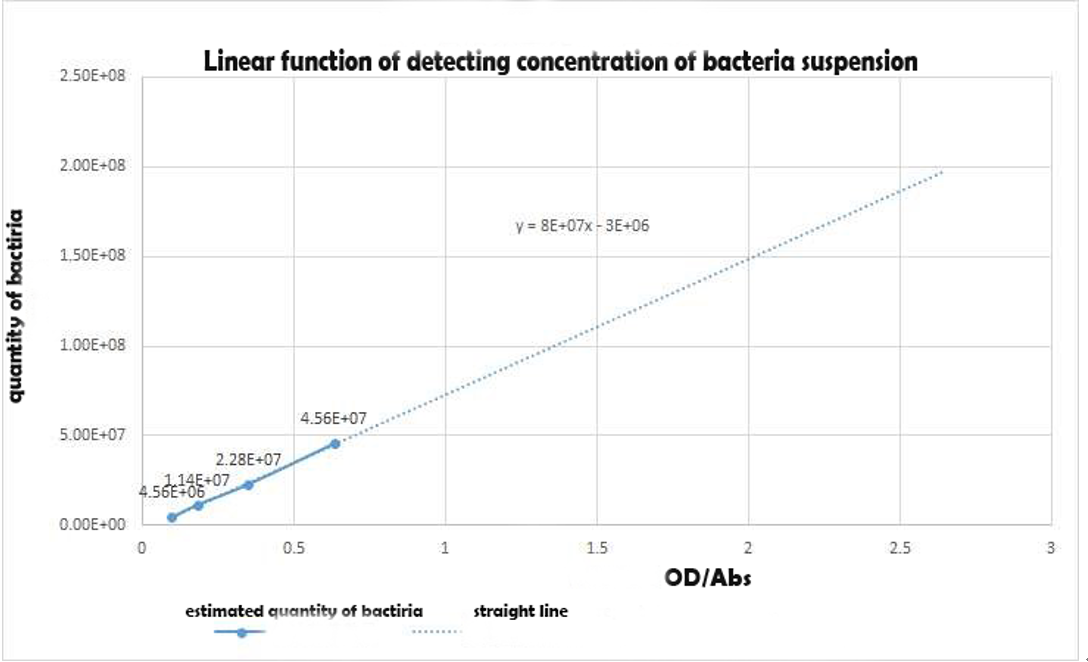
| + | [[File:SMS4.png|300px|thumb|right|Fig.3 Bacteria Concentration related to ABS diagram]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''''Figure 3 Linear function of detecting concentration of bacteria suspension in experiment 1''''' | ||
===User Reviews=== | ===User Reviews=== | ||
Latest revision as of 05:33, 28 October 2017
This experience page is provided so that any user may enter their experience using this part.
Please enter
how you used this part and how it worked out.
Applications of BBa_K2224001
Part Description:
This is the experiment report of SMS_Shenzhen team in August, 2017.
Figure 1 The result of plate streaking of BioBrick BBa_K2224001
We, 2017 SMS iGEM Team, have submitted this part AND characterized the function and effectiveness of this part.
BBa_K2224001 is a composite part with the backbone pSB1C3. The CDS of this part is Lecanicillium lecanii strain 432 endochitinase (chit1), a chitinase originate from verticillium lecanii, a kind of entomogenous fungus. With a GeneBank identifier DQ412944 in NCBI. This enzyme helps catalyze chitin. SMS students optimized the codons and removed introns to fit the original sequence into E. coli expression system.
Experiment Abstract
The main purpose of this experiment is to measure the activity of a target enzyme, Lecanicillium lecanii strain 432 endochitinase (chit1), in TOP10 expression system.Testing the effectiveness of these enzymes’ expression in E. coli expression system is a fundamental portion of the whole project. According to previous researches, we expected that the expression activity of this chitinase in Top10 system should appear effective and show a co-relation to time. The data we obtained in this experiment include bacteria density in culture(in ABS) and enzyme activity(in U/10^4 cells). As our speculation, the expression results should confirm our expectation.
The original gene sequence of this chitinase DQ412944 was published on NCPI. SMS students have processed the CDS. Designed primer with restriction sites, modified the CDS for standardization. We then synthesized this plasmid with the backbone pSB1C3.
Experiment Princeple
We used a Chitinase activity measurement kit to measure the activity of this chitinase quantitatively. The enzyme activity was defined by the amount of N- acetyl glucosamine that produced by Chitinase' s hydrolysis to chitin divided by the amount of cells. Since the product, N- acetyl glucosamine, can lead to light absorbtion peak at 585nm and the light absorption can be detected by Spectrophotometer, we can figure out the relative activity of enzyme DQ412944. Enzyme activity in TOP10 E. coli expression system related to time shown below. (ABS is for absorbance, U is for active unit)
Measurement of OD600
To obtain the bacteria quantity in sample for active unit measurement, we constructed a standard bacteria concentration diagram. We used Flat colony counting method to obtain the Standard Calibration Curve for Bacterial Concentration:
- Prepare LB medium.
- Take the available preserved TOP10 strain, pick the bacteria strain by using a platinum ring beside a fire and then draw lines on solid LB medium.
- Culture the inoculated medium in constant temperature incubator for 24h, temperature at 37 ℃ ±1 ℃ in incubator. Pick monoclonal bacteria colonies, inject in 20mL liquid LB medium, shake the medium in constant temperature shaking incubator (110r/ min, 3cm oscillation amplitude) for 24h.
- Take 0.4mL cultured bacteria fluid in logarithmic growth phase, cultured in 20mL nutrient bacteria medium, then shake the medium for 4h to get bacteria fluid in stable phase.
- Dilute the cultured bacteria fluid in stable phase with liquid LB medium (for 5, 10, 20, 40 times). In 660nm standard wavelength, measure the absorbance (ABS) of this group of samples different bacteria concentration. (Zeroing before testing with 1x liquid LB medium).
- Determine the colony numbers of four different dilution times in turns in a sterile room next to the flame. Each sample was formulated in several concentration gradients, and 1 mL of each sample was injected into the dish with sterilized pipette. Inject about 15 mL ,45~50 ℃ solid LB medium, then turn the dish so that the sample with the medium can be fully mixed. When medium solidified, turn the plate. Place the medium in 37 ℃±1 ℃ incubator to culture for 24h, count the number of colonies. With eye observation, the colony number was counted and recorded. The average colony number of each dilution plate can then be obtained.
Using the spectrophotometer to get the estimated value of optical density of the samples,we made a conversion to the concentration of the bacterial suspension.
Figure 2 the results of the colony counting of 10^6 and 10^7 times diluted bacteria fluid(the fluid was coated on solid LB medium to grow visible colonies)
Figure 3 Linear function of detecting concentration of bacteria suspension in experiment 1
User Reviews
UNIQ87d718e4a54f4b22-partinfo-00000000-QINU UNIQ87d718e4a54f4b22-partinfo-00000001-QINU