Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K2172010"
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
[[File:T--CIEI-BJ--colony1.jpg|600px|thumb|center]] | [[File:T--CIEI-BJ--colony1.jpg|600px|thumb|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then we used the optimal condition to produce our target recombinant proteins. During the enrichment of the bacterial process, we checked the GFP fluorescence of the bacterial. And the result showed that the GFP fluorescence was observaed. It indicated that our SmCPS1-GFP recombinant protein has been expressed in the bacteria. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:T--CIEI-BJ--tu14.png|600px|thumb|center|Fig. The GFP fluorescence of the bacterial precipitation]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | After ultrasonication, we used the SDS-PAGE electrophoresis to detect our target protein, and the result showed that we succesfully produced our the recombinant protein. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:T--CIEI-BJ--Pic001.png|600px|thumb|center|Fig. The SDS-PAGE electrophoresis of recombinant protein]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lane 1, total protein without IPTG induction; Lane 2, supernatant without IPTG induction; Lane 3, total protein with IPTG induction; Lane 4, supernatant with IPTG induction. Black arrow shows the targeted recombinant proteins. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In order to verify the successful expression of SmCPS1 with our device, we performed sonication on E. coli cells and smashed them. Then the supernatant fluid and total protein were collected for the SDS protein electrophoresis. The results of the SDS-PAGE showed that with induction of IPTG, the protein SmCPS1 can be successfully expressed by our device, with size of 136 KD, which is in accordance with our expectation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Next we committed Western Blot method to detect the exitence of GST tag by using GST antibody. The results showed that, under both situations, bacteria successfully expressed our recombinant protein. It also showed that, the concentration of soluble SmCPS1 produced by the IPTG-induced bacteria is much greater than that of the protein produced by the non-IPTG-induced one. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:T--CIEI-BJ--Pic002.png|600px|thumb|center|Fig. Western blot result using GST antibody. Lane a, total protein without IPTG induction; Lane b, total protein with IPTG induction; Lane c, supernatant without IPTG induction; Lane d, supernatant with IPTG induction.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
'''Tac Promoter (29bp): ''' | '''Tac Promoter (29bp): ''' | ||
| Line 231: | Line 249: | ||
'''Three Site-directed mutagenesis:''' | '''Three Site-directed mutagenesis:''' | ||
[[File:T--CIEI-BJ--partLily1.jpg|600px|thumb|center]] | [[File:T--CIEI-BJ--partLily1.jpg|600px|thumb|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- --> | ||
| + | <span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | ||
| + | <partinfo>BBa_K2172010 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- Uncomment this to enable Functional Parameter display | ||
| + | ===Functional Parameters=== | ||
| + | <partinfo>BBa_K2172010 parameters</partinfo> | ||
| + | <!-- --> | ||
Latest revision as of 03:02, 20 October 2016
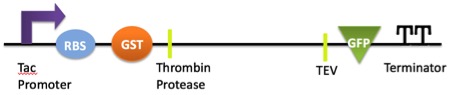
Tac Promoter-RBS-GST-Thrombin Protease-TEV-GFP-Terminator
This part is a gene circuit that can be used to test whether it is being expressed or not. It comprises of a ribosome binding site (RBS) for ribosomes to bind, a GST label for purification, a thrombin protease cleavage site plus a TEV protease cleavage site, a GFP detection unit, and a terminator. When transformed into bacteria, e.g. E. coli, it can be used to test whether the bacteria are expressing the part not. Other parts, such as the gene SmCPS1, can be inserted into this part via digestion on the thrombin site and the TEV site.
This circuit is responsible for the function of all sequence with a terminator waiting for the SmCPS1 protein to insert among Thrombin protease and TEV restriction cleavage sites. The above circuit without target gene SmCPS1 is constructed mainly to test whether it produces SmCPS1. If the circuit do work, it would result in the expression of the GFP gene and emission of green fluorescent light.
Name: BBa_K2172010
TAC-F primer: TCTAGATGACAATTAATCATCGGCT
TE-R primer: ACTAGTATGTATTTAGAAAAATAAACAAATAGG
Description: Promoter and RBS added, GST labeled, coding with Thrombin and TEV restriction enzyme cleavage sites, GFP detector, and Terminator.
Function: See BBa_K2172010 in part registry.
Length: 1719bp
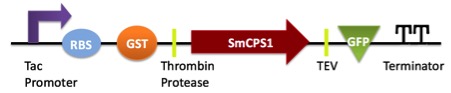
We separated target gene SmCPS1 from the whole circuit adding GFP detector and terminator as terminal signal to test its function, which ensure the further protein secretion.
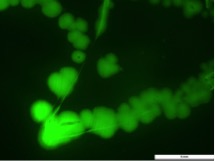
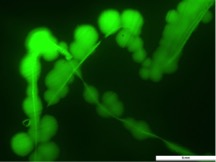
Green fluorescent light of E. coli under microscope. The E. coli transformed from white to fluorescent Green, because GFP segment inserted into plasmid result in unique detective color. We obtained the average expressive value of the green fluorescence in the biobrick part.
Tac Promoter (29bp) ---RBS (14bp) ---GST (757) ---Thrombin protease (18bp) ---SmCPS1 (2382bp) ---TEV (21bp) ---GFP (720bp) ---Terminator (160bp)
We constructed this complete circuit in pGEX-KG vector finally to express our gene SmCPS1 and secrete its protein from E. coli BL21. The whole gene circuit consists of K2172010 part with SmCPS1. Thus we labeled GFP segment to test functions. As pure protein SmCPS1 have successfully been extracted, we are able to synthesize one process of the compounds production.
Then we used the optimal condition to produce our target recombinant proteins. During the enrichment of the bacterial process, we checked the GFP fluorescence of the bacterial. And the result showed that the GFP fluorescence was observaed. It indicated that our SmCPS1-GFP recombinant protein has been expressed in the bacteria.
After ultrasonication, we used the SDS-PAGE electrophoresis to detect our target protein, and the result showed that we succesfully produced our the recombinant protein.
Lane 1, total protein without IPTG induction; Lane 2, supernatant without IPTG induction; Lane 3, total protein with IPTG induction; Lane 4, supernatant with IPTG induction. Black arrow shows the targeted recombinant proteins.
In order to verify the successful expression of SmCPS1 with our device, we performed sonication on E. coli cells and smashed them. Then the supernatant fluid and total protein were collected for the SDS protein electrophoresis. The results of the SDS-PAGE showed that with induction of IPTG, the protein SmCPS1 can be successfully expressed by our device, with size of 136 KD, which is in accordance with our expectation.
Next we committed Western Blot method to detect the exitence of GST tag by using GST antibody. The results showed that, under both situations, bacteria successfully expressed our recombinant protein. It also showed that, the concentration of soluble SmCPS1 produced by the IPTG-induced bacteria is much greater than that of the protein produced by the non-IPTG-induced one.
Tac Promoter (29bp):
Function: The tac promoter, a strong hybrid promoter, is used to control and increase the expression levels of a target gene and is used in the over-expression of recombinant proteins, produced from the combination of promoters from the trp and lac operons.
Sequence: tgacaattaatcatcggctcgtataatgt
RBS (14bp):
Function: A ribosome binding site (RBS) is a sequence of mRNA. It is used to lead the ribosome to the right position on the mRNA during the beginning of translation
Sequence:
tcacacaggaaaca
GST (757bp):
Function: By inserting the GST DNA coding sequence next to protein of interest, the GST can be added to a protein of interest to purify the fusion protein from solution in a process known as a pull-down assay. The strong binding affinity of GFP beads coated with the compound can be added to the protein mixture. As a result, the protein of interest attached to the GST will stick to the beads, isolating the protein from the rest of those in solution.
Sequence:
atgtcccctatactaggttattggaaaattaagggccttgtgcaacccactcgacttcttttggaatatcttgaagaaaaatatgaagagcatttgtatgagcgcgatgaaggtgataaatggcgaaacaaaaagtttgaattggg
tttggagtttcccaatcttccttattatattgatggtgatgttaaattaacacagtctatggccatcatacgttatatagctgacaagcacaacatgttgggtggttgtccaaaagagcgtgcagagatttcaatgcttgaaggagcg
gttttggatattagatacggtgtttcgagaattgcatatagtaaagactttgaaactctcaaagttgattttcttagcaagctacctgaaatgctgaaaatgttcgaagatcgtttatgtcataaaacatatttaaatggtgatcatgtaa
cccatcctgacttcatgttgtatgacgctcttgatgttgttttatacatggacccaatgtgcctggatgcgttcccaaaattagtttgttttaaaaaacgtattgaagctatcccacaaattgataagtacttgaaatccagcaagtata
tagcatggcctttgcagggctggcaagccacgtttggtggtggcgaccatcctccaaaatcggatctggttccgcgtggatccccgggaatttccggtggtggtggtggaattctagactccatgggtcgactcgagctcaag
cttattcatcgtgactgac
Thrombin protease (18bp):
Sequence: CTGGTTCCGCGTGGATCC
TEV (21bp):
Function: Thrombin protease, a DNA segment of pGEX-KG vector containing Bam Hl cloning site after GST, and TEV added at front of the GFP, are the two type of restriction enzyme cleavage sites inserted into tanshinone gene circuit in order to purify the SmCPS1 enzyme.
Sequence: GAAAACCTGTATTTTCAGGGC
GFP (720bp):
Function: The gene for the production of GFP is incorporated into the genome of the organism in the region of the DNA that codes for the target proteins and that is controlled by the same regulatory sequence; that is, the gene's regulatory sequence now controls the production of GFP, where expression of GFP can be used as a detection device for a particular characteristic.
Sequence:
ATGGTGAGCAAGGGCGAGGAGCTGTTCACCGGGGTGGTGCCCATCCTGGTCGAGCTGGACGGCGACGTAAACGGCCACAAGTTCAGCGTGTCC
GGCGAGGGCGAGGGCGATGCCACCTACGGCAAGCTGACCCTGAAGTTCATCTGCACCACCGGCAAGCTGCCCGTGCCCTGGCCCACCCTCGTG
ACCACCCTGACCTACGGCGTGCAGTGCTTCAGCCGCTACCCCGACCACATGAAGCAGCACGACTTCTTCAAGTCCGCCATGCCCGAAGGCTACG
TCCAGGAGCGCACCATCTTCTTCAAGGACGACGGCAACTACAAGACCCGCGCCGAGGTGAAGTTCGAGGGCGACACCCTGGTGAACCGCATCGA
GCTGAAGGGCATCGACTTCAAGGAGGACGGCAACATCCTGGGGCACAAGCTGGAGTACAACTACAACAGCCACAACGTCTATATCATGGCCGACA
AGCAGAAGAACGGCATCAAGGTGAACTTCAAGATCCGCCACAACATCGAGGACGGCAGCGTGCAGCTCGCCGACCACTACCAGCAGAACACCCC
CATCGGCGACGGCCCCGTGCTGCTGCCCGACAACCACTACCTGAGCACCCAGTCCGCCCTGAGCAAAGACCCCAACGAGAAGCGCGATCACATG
GTCCTGCTGGAGTTCGTGACCGCCGCCGGGATCACTCTCGGCATGGACGAGCTGTACAAGTAA
Terminator (160bp):
Function: Termination (T terminator) is the DNA sequence of the RNA polymerase termination signal of transcription, which is a structure at A structure in the poly (A) site downstream around 160bp
Sequence:
AGCGATAGCGGAGTGTATAATTCTTGAAGACGAAAGGGCCTCGTGATACGCCTATTTTTATAGGTTAATGTCATGATAATAATGGTTTCTTAGACGTCAG
GTGGCACTTTTCGGGGAAATGTGCGCGGAACCCCTATTTGTTTATTTTTCTAAATACATT
SmCPS1 sequencing result (before Site-directed mutagenesis): ATGGCCTCCTTATCCTCTACAATCCTCAGCCGCTCTCCGGCGGCCCGCCGCAGAATTACGCCGGCATCGGCTAAGCTTCACCTGCCGGAATGTTTC
GCCATCAGTGCATGGATGGGCAGCAGCACTAAAAACCTTTCTCTCAGCTACCAACTTAATCACAAGAAAATATCAGTTGCCACAGTAGATGCGCCGC
AGGTGCATGACCACGACGGCACTACCGTTCATCAAGGCCATGATGCGGTGAAGAATATTGAGGATCCCATTGAATACATCAGGACGTTGTTGAGGAC
GACGGGGGACGGGAGAATAAGCGTGTCGCCGTACGACACGGCGTGGGTGGCGATGATCAAGGACGTGGAGGGGCGGGACGGGCCCCAGTTCCC
CTCCAGCCTCGAGTGGATCGTGCAGAATCAACTCGAGGATGGATCGTGGGGCGATCAGAAGCTTTTCTGCGTCTACGATCGCCTCGTCAATACCATC
GCGTGCGTGGTAGCCTTGAGATCGTGGAATGTTCATGCTCACAAGGTCAAAAGAGGAGTGACGTACATCAAGGAAAATGTGGATAAACTTATGGAGG
GAAATGAGGAGCACATGACTTGTGGGTTCGAAGTGGTGTTTCCGGCGCTTCTACAAAAAGCGAAAAGCTTAGGCATCGAAGATCTTCCTTACGATTC
TCCGGCGGTGCAGGAGGTTTATCATGTCAGGGAACAAAAGTTGAAAAGGATTCCACTGGAGATTATGCACAAAATACCGACATCATTATTATTTAGTTT
GGAAGGGCTCGAAAATTTGGATTGGGACAAACTTTTGAAACTGCAGTCAGCCGACGGTTCCTTCCTCACCTCTCCCTCCTCCACCGCCTTCGCGTTC
ATGCAAACCAAGGATGAAAAATGCTACCAATTCATCAAGAACACGATAGACACTTTCAACGGAGGAGCGCCACACACTTATCCCGTCGACGTGTTTGGA
AGGCTCTGGGCGATCGACCGGCTGCAGCGCCTCGGAATTTCCCGCTTTTTTGAGCCGGAGATTGCTGATTGCTTAAGCCACATCCACAAATTTTGGAC
GGATAAGGGAGTTTTCAGTGGGAGAGAATCGGAGTTTTGCGACATTGACGATACATCCATGGGAATGAGGCTTATGAGGATGCATGGATATGATGTTGAT
CCAAATGTGCTGAGGAATTTCAAGCAGAAAGATGGTAAATTCTCTTGCTACGGCGGGCAGATGATCGAGTCGCCTTCTCCGATATACAATCTTTACAGAG
CTTCTCAGCTCCGATTTCCCGGCGAGGAAATCCTCGAAGATGCGAAGAAATTCGCCTACGATTTCTTGAAAGAAAAACTAGCCAACAATCAGATTCTGGA
TAAATGGGTTATTTCTAAGCACTTGCCTGATGAGATCAAGCTCGGGCTAGAGATGCCGTGGCTCGCCACCCTACCCCGCGTCGAGGCGAAGTACTACATC
CAGTACTACGCCGGCTCCGGCGACGTGTGGATCGGGAAGACGCTGTACAGGATGCCGGAGATCAGCAACGACACGTACCACGACCTAGCCAAGACGGAT
TTCAAGAGATGCCAAGCGAAGCATCAGTTCGAGTGGCTCTACATGCAAGAATGGTACGAGAGCTGCGGCATCGAGGAATTCGGGATAAGCAGAAAGGACC
TTCTGCTTTCCTATTTCTTGGCGACCGCGAGCATCTTCGAGCTCGAGAGGACCAACGAGCGAATCGCGTGGGCCAAATCGCAGATCATCGCTAAGATGAT
CACTTCTTTCTTCAACAAGGAAACTACGTCGGAGGAGGACAAGCGAGCTCTTTTGAACGAGCTCGGAAACATTAATGGCCTCAACGACACAAACGGCGCA
GGGAGAGAAGGTGGGGCCGGTAGCATTGCGCTAGCGACCCTCACTCAGTTCCTCGAGGGATTCGACAGATACACCAGACACCAGCTGAAAAATGCTTGGA
GCGTATGGCTGACGCAGCTGCAACATGGCGAAGCAGACGACGCAGAGCTCCTAACCAACACGTTGAACATCTGCGCCGGCCACATCGCCTTCAGGGAAGA
AATACTGGCGCACAACGAGTACAAAACTCTCTCCAACCTAACCAGCAAAATCTGTCGGCAACTTTCTTTCATTCAAAGCGAAAAGGAGATGGGAGTAGAGGG
CGAGATCGCAGCGAAATCGAGCATAAAAAACAAGGAACTCGAAGAAGACATGCAAATGTTGGTGAAGTTGGTGCTTGAGAAATATGGGGGCATAGATAGAAA
TATAAAGAAAGCGTTTTTGGCAGTTGCGAAGACTTATTATTACAGAGCGTATCATGCCGCCGACACCATAGACACACACATGTTTAAAGTGCTTTTCGAGCCAG
TCGCGTGA
After Site-directed mutagenesis:
ATGGCCTCCTTATCCTCTACAATCCTCAGCCGCTCTCCGGCGGCCCGCCGCAGAATTACGCCGGCATCGGCTAAGCTTCACCTGCCGGAATGT
TTCGCCATCAGTGCATGGATGGGCAGCAGCACTAAAAACCTTTCTCTCAGCTACCAACTTAATCACAAGAAAATATCAGTTGCCACAGTAGATGC
GCCGCAGGTGCATGACCACGACGGCACTACCGTTCATCAAGGCCATGATGCGGTGAAGAATATTGAGGATCCCATTGAATACATCAGGACGTTG
TTGAGGACGACGGGGGACGGGAGAATAAGCGTGTCGCCGTACGACACGGCGTGGGTGGCGATGATCAAGGACGTGGAGGGGCGGGACGGGC
CCCAGTTCCCCTCCAGCCTCGAGTGGATCGTGCAGAATCAACTCGAGGATGGATCGTGGGGCGATCAGAAGCTTTTCTGCGTCTACGATCGCC
TCGTCAATACCATCGCGTGCGTGGTAGCCTTGAGATCGTGGAATGTTCATGCTCACAAGGTCAAAAGAGGAGTGACGTACATCAAGGAAAATGT
GGATAAACTTATGGAGGGAAATGAGGAGCACATGACTTGTGGGTTCGAAGTGGTGTTTCCGGCGCTTCTACAAAAAGCGAAAAGCTTAGGCATC
GAAGATCTTCCTTACGATTCTCCGGCGGTGCAGGAGGTTTATCATGTCAGGGAACAAAAGTTGAAAAGGATTCCACTGGAGATTATGCACAAAA
TACCGACATCATTATTATTTAGTTTGGAAGGGCTCGAAAATTTGGATTGGGACAAACTTTTGAAACTCCAGTCAGCCGACGGTTCCTTCCTCACC
TCTCCCTCCTCCACCGCCTTCGCGTTCATGCAAACCAAGGATGAAAAATGCTACCAATTCATCAAGAACACGATAGACACTTTCAACGGAGGAG
CGCCACACACTTATCCCGTCGACGTGTTTGGAAGGCTCTGGGCGATCGACCGGCTCCAGCGCCTCGGAATTTCCCGCTTTTTTGAGCCGGAG
ATTGCTGATTGCTTAAGCCACATCCACAAATTTTGGACGGATAAGGGAGTTTTCAGTGGGAGAGAATCGGAGTTTTGCGACATTGACGATACAT
CCATGGGAATGAGGCTTATGAGGATGCATGGATATGATGTTGATCCAAATGTGCTGAGGAATTTCAAGCAGAAAGATGGTAAATTCTCTTGCTACG
GCGGGCAGATGATCGAGTCGCCTTCTCCGATATACAATCTTTACAGAGCTTCTCAGCTCCGATTTCCCGGCGAGGAAATCCTCGAAGATGCGAA
GAAATTCGCCTACGATTTCTTGAAAGAAAAACTAGCCAACAATCAGATTCTGGATAAATGGGTTATTTCTAAGCACTTGCCTGATGAGATCAAGCTC
GGGCTAGAGATGCCGTGGCTCGCCACCCTACCCCGCGTCGAGGCGAAGTACTACATCCAGTACTACGCCGGCTCCGGCGACGTGTGGATCGGG
AAGACGCTGTACAGGATGCCGGAGATCAGCAACGACACGTACCACGACCTAGCCAAGACGGATTTCAAGAGATGCCAAGCGAAGCATCAGTTCG
AGTGGCTCTACATGCAAGAATGGTACGAGAGCTGCGGCATCGAGGAGTTCGGGATAAGCAGAAAGGACCTTCTGCTTTCCTATTTCTTGGCGACC
GCGAGCATCTTCGAGCTCGAGAGGACCAACGAGCGAATCGCGTGGGCCAAATCGCAGATCATCGCTAAGATGATCACTTCTTTCTTCAACAAGGA
AACTACGTCGGAGGAGGACAAGCGAGCTCTTTTGAACGAGCTCGGAAACATTAATGGCCTCAACGACACAAACGGCGCAGGGAGAGAAGGTGGG
GCCGGTAGCATTGCGCTAGCGACCCTCACTCAGTTCCTCGAGGGATTCGACAGATACACCAGACACCAGCTGAAAAATGCTTGGAGCGTATGGC
TGACGCAGCTGCAACATGGCGAAGCAGACGACGCAGAGCTCCTAACCAACACGTTGAACATCTGCGCCGGCCACATCGCCTTCAGGGAAGAAAT
ACTGGCGCACAACGAGTACAAAACTCTCTCCAACCTAACCAGCAAAATCTGTCGGCAACTTTCTTTCATTCAAAGCGAAAAGGAGATGGGAGTAGA
GGGCGAGATCGCAGCGAAATCGAGCATAAAAAACAAGGAACTCGAAGAAGACATGCAAATGTTGGTGAAGTTGGTGCTTGAGAAATATGGGGGCA
TAGATAGAAATATAAAGAAAGCGTTTTTGGCAGTTGCGAAGACTTATTATTACAGAGCGTATCATGCCGCCGACACCATAGACACACACATGTTTAAA
GTGCTTTTCGAGCCAGTCGCGTGA
Three Site-directed mutagenesis:
Usage and Biology
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 747
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal SapI.rc site found at 159