Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1956014"
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K1956014 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K1956014 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | Noise in Device measurement | + | Noise in Device measurement 3 |
===Usage and Biology=== | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
[[File:Sp_growth.png|400px|right|Specific growth rates (ln) for Devices]] | [[File:Sp_growth.png|400px|right|Specific growth rates (ln) for Devices]] | ||
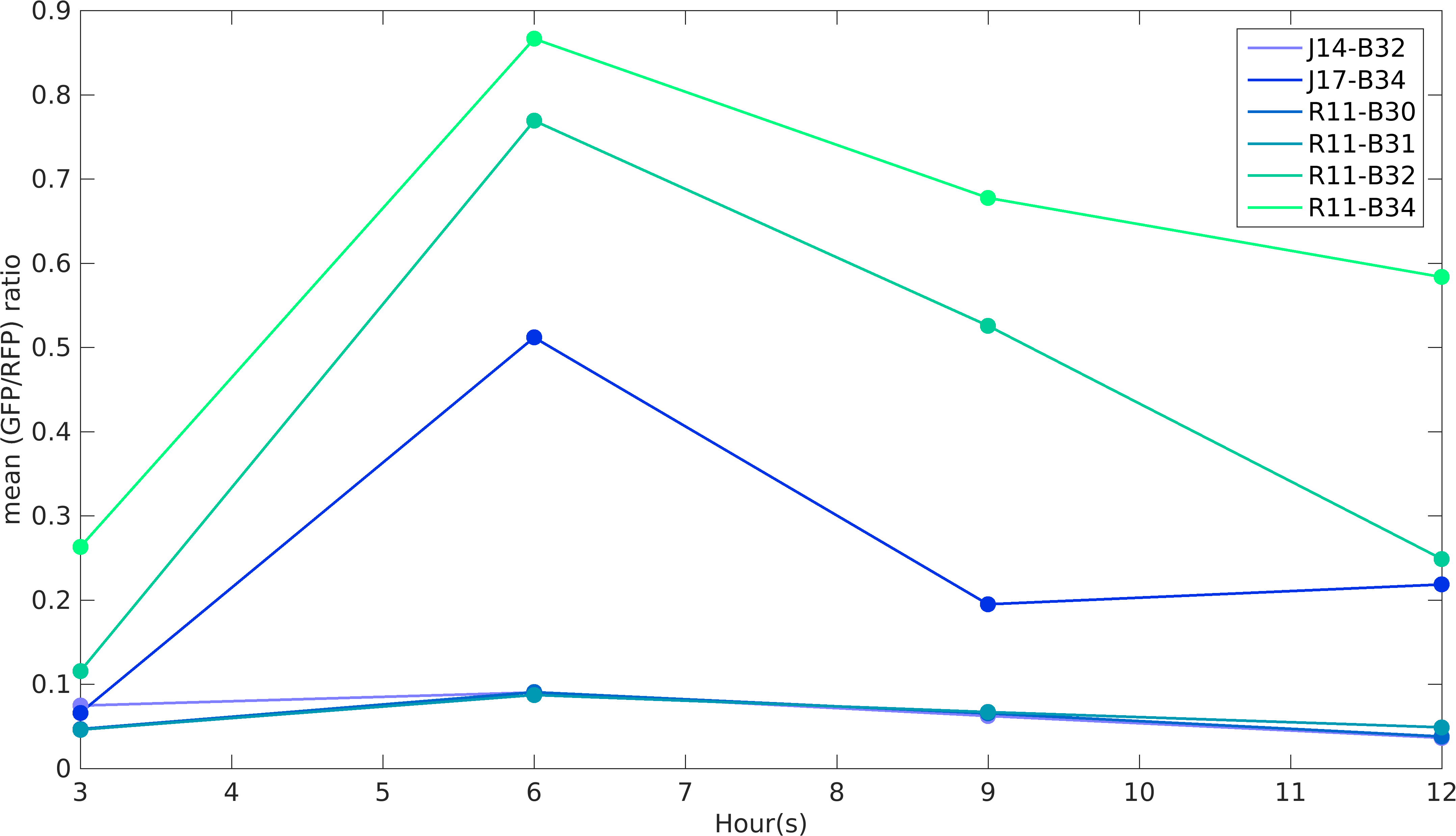
[[File:Gfpbyrfp_strength.png|400px|right|Relative strength of Devices]] | [[File:Gfpbyrfp_strength.png|400px|right|Relative strength of Devices]] | ||
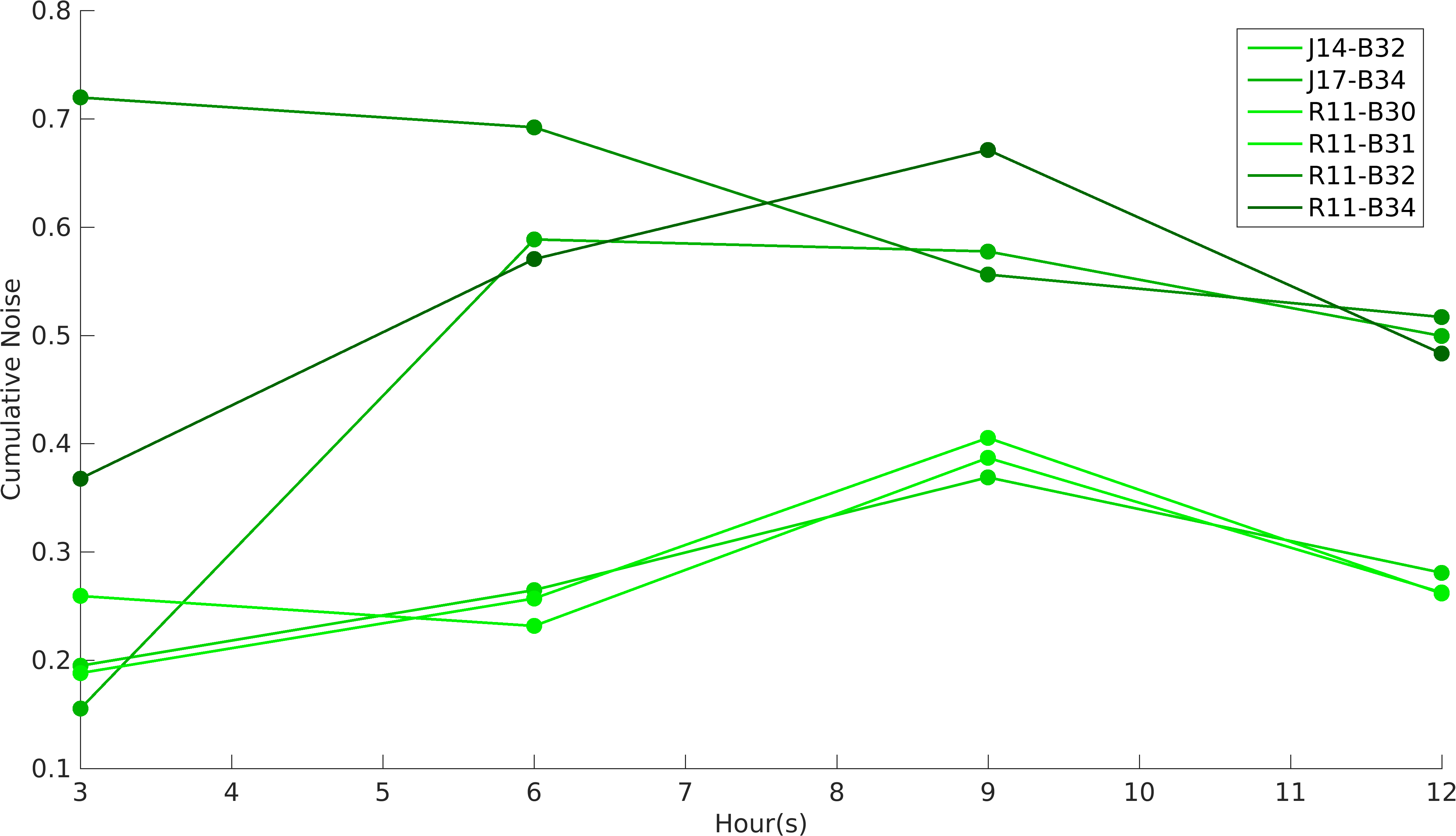
| + | [[File:Promoterrbs_noise.png|400px|right|Cumulative Intrinsic Noise of Devices]] | ||
== Experimentation == | == Experimentation == | ||
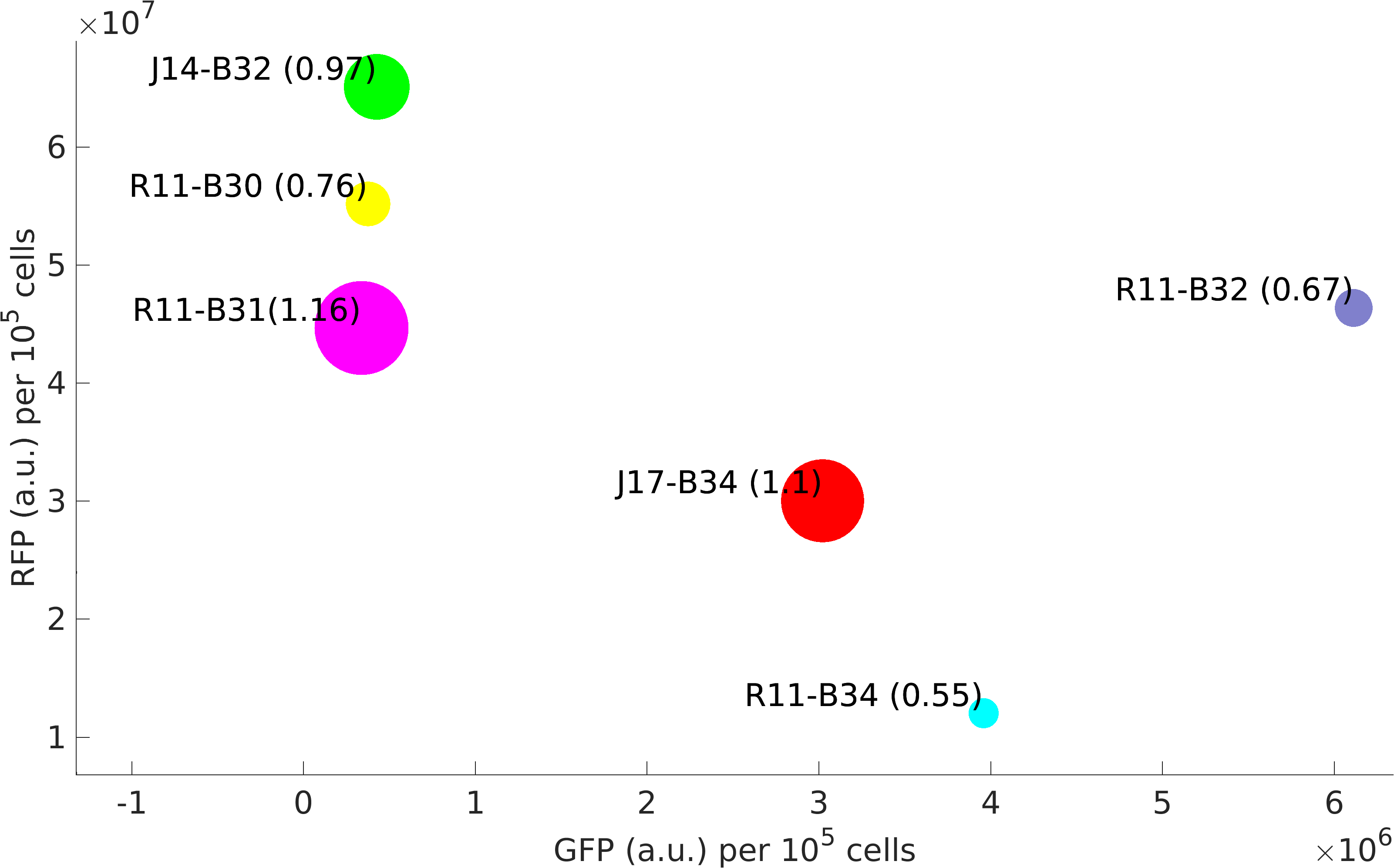
| − | This BioBrick was | + | <p>This BioBrick was made to understand the role of RBS and Promoter parts in giving rise to intrinsic noise in <i>E. coli</i> DH5alpha. Expression data for GFP and RFP proteins were obtained using flow cytometry (BD FACS Aria III) at 3hr, 6hr, 9hr and 12hr stage of growth along with cells expressing only GFP, only RFP and none. Cumulative intrinsic and extrinsic noise were measured using modified [http://2016.igem.org/Team:IIT-Madras/Model#Noise_in_Devices| Elowitz formula]. OD600 values for specific growth rate estimation were obtained using Spectrophotometer over an interval of an hour for 12 hours. Given specific growth rates are in it's logarithmic values. This BioBrick can be used to characterize noise and strength of complex devices by cloning this device with given device, which produces a different reporter protein. In graphs, we have [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1956014 R11-B32], [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1956015 R11-B34], [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1956017 J14-B3], [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1956018 J17-B34], [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1956022 R11-B30] and [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1956023 R11-B31]. </p> |
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
<span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | <span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | ||
Latest revision as of 19:31, 22 October 2016
Noise in Device measurement
Noise in Device measurement 3
Usage and Biology
IIT Madras 2016's Characterization
Experimentation
This BioBrick was made to understand the role of RBS and Promoter parts in giving rise to intrinsic noise in E. coli DH5alpha. Expression data for GFP and RFP proteins were obtained using flow cytometry (BD FACS Aria III) at 3hr, 6hr, 9hr and 12hr stage of growth along with cells expressing only GFP, only RFP and none. Cumulative intrinsic and extrinsic noise were measured using modified [http://2016.igem.org/Team:IIT-Madras/Model#Noise_in_Devices| Elowitz formula]. OD600 values for specific growth rate estimation were obtained using Spectrophotometer over an interval of an hour for 12 hours. Given specific growth rates are in it's logarithmic values. This BioBrick can be used to characterize noise and strength of complex devices by cloning this device with given device, which produces a different reporter protein. In graphs, we have R11-B32, R11-B34, J14-B3, J17-B34, R11-B30 and R11-B31.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 1728
Illegal AgeI site found at 1840 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 726