Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1321342"
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K1321342 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K1321342 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | + | sfGFP fused N-terminally to CBDcex (a cellulose-binding domain). | |
This construct is part of a library of Super-folder GFP fusions with cellulose binding domains, which we used to assay the CBD binding affinity. Please see our [http://2014.igem.org/Team:Imperial/Functionalisation project page] for more information. The collection of sfGFP-CBD fusion parts can be seen in the table below: [[File:IC14-sfGFP-part-table.PNG]] | This construct is part of a library of Super-folder GFP fusions with cellulose binding domains, which we used to assay the CBD binding affinity. Please see our [http://2014.igem.org/Team:Imperial/Functionalisation project page] for more information. The collection of sfGFP-CBD fusion parts can be seen in the table below: [[File:IC14-sfGFP-part-table.PNG]] | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
Note that the start and stop codon, plus 6 bp either side of the sequence, are included the RFC25 prefix and suffix which is not shown. | Note that the start and stop codon, plus 6 bp either side of the sequence, are included the RFC25 prefix and suffix which is not shown. | ||
| − | + | ||
===Usage and Biology=== | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
| + | |||
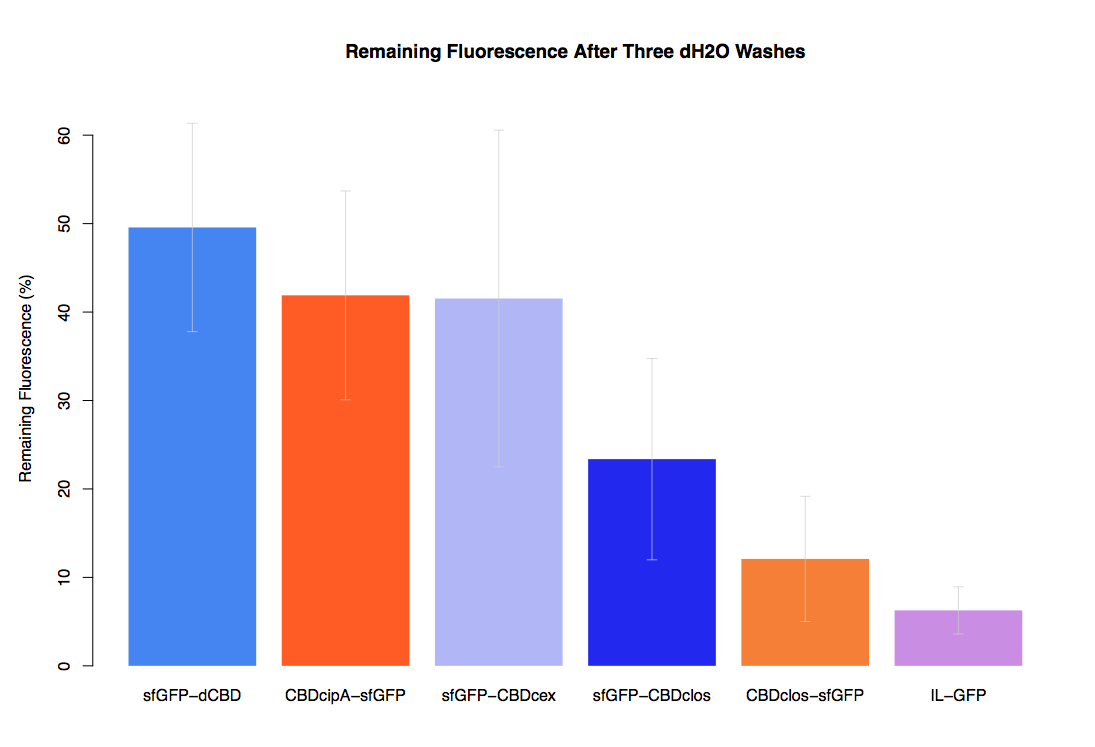
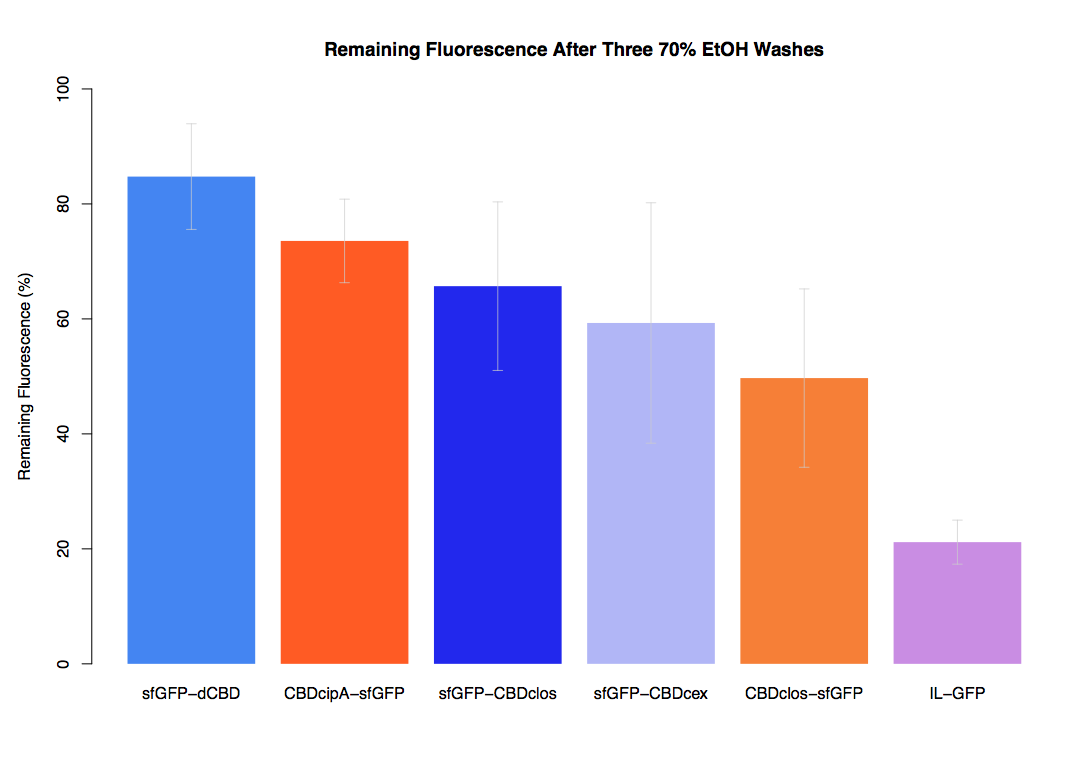
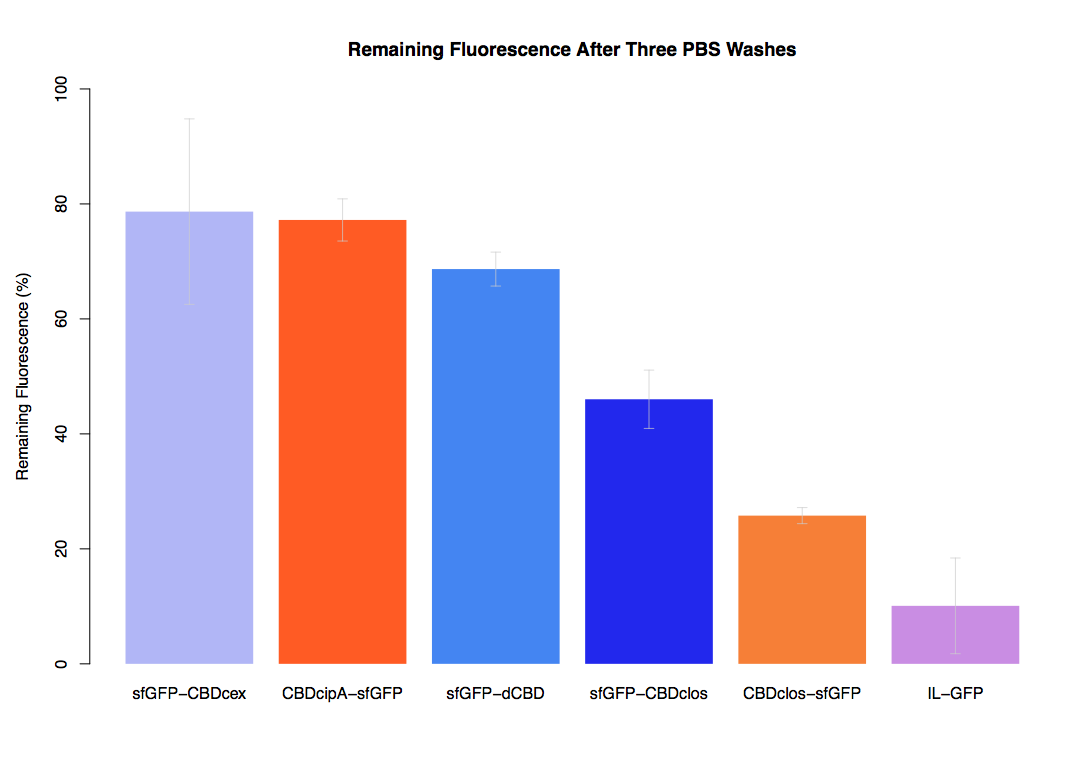
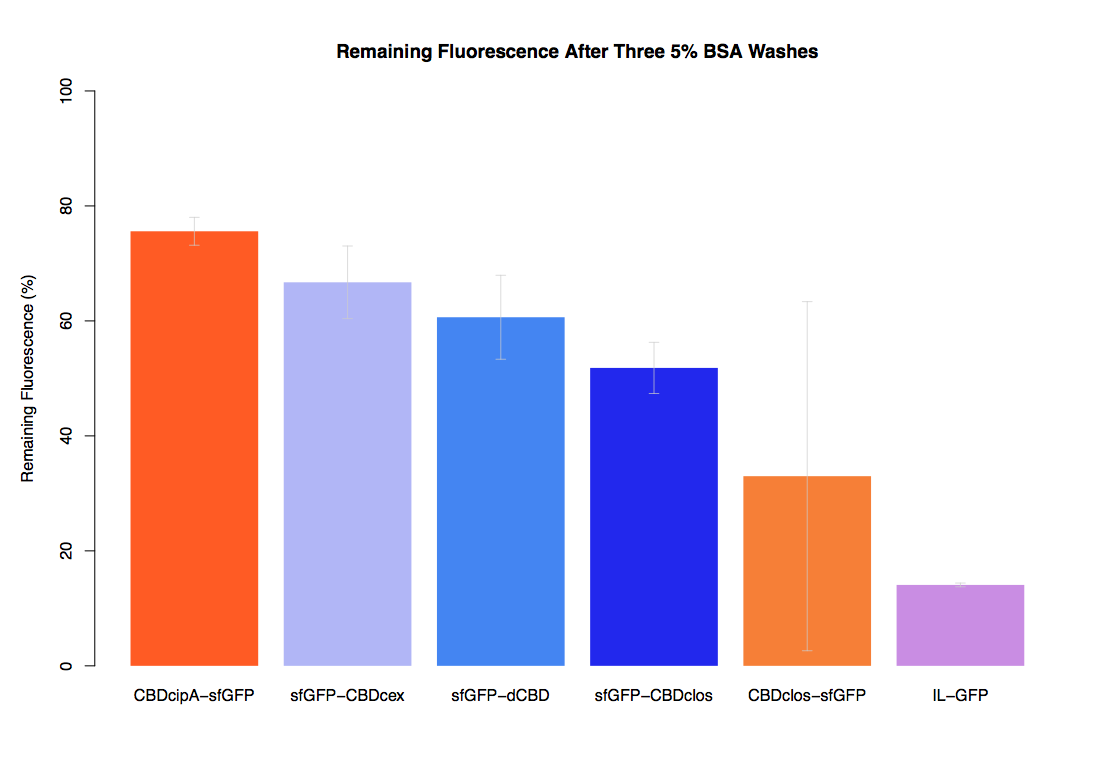
| + | The binding ability of this CBD to bacterial cellulose was characterised when fused to [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1321337 sfGFP], relative to other CBDs fused to [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1321337 sfGFP]. The binding ability was represented by the percentage fluorescence remaining from the sfGFP-CBD fusions bound to bacterial cellulose discs, when subjected to various washes (protocol [http://2014.igem.org/Team:Imperial/Protocols here]). When washed with PBS, sfGFP-CBDcex fusions performed the best out of all the CBDs tested (third graph) followed by washes with 5% BSA (fourth graph), dH20 (first graph) and 70% EtOH (second graph). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:IC14_-_dH2Obplot1.png|700px|left|]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:IC14-EtOHbplot1.png|700px|left|]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:IC14-PBSbplot1.png|700px|left|]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:IC14-BSAbplot1.png|700px|left|]] | ||
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
| − | + | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K1321342 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K1321342 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | ||
Latest revision as of 04:37, 2 November 2014
sfGFP fused to CBDcex in RFC 25
sfGFP fused N-terminally to CBDcex (a cellulose-binding domain).
This construct is part of a library of Super-folder GFP fusions with cellulose binding domains, which we used to assay the CBD binding affinity. Please see our [http://2014.igem.org/Team:Imperial/Functionalisation project page] for more information. The collection of sfGFP-CBD fusion parts can be seen in the table below: 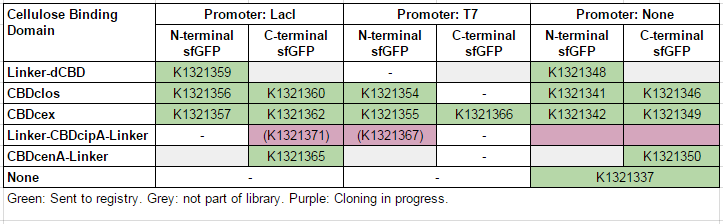
Note that the start and stop codon, plus 6 bp either side of the sequence, are included the RFC25 prefix and suffix which is not shown.
Usage and Biology
The binding ability of this CBD to bacterial cellulose was characterised when fused to sfGFP, relative to other CBDs fused to sfGFP. The binding ability was represented by the percentage fluorescence remaining from the sfGFP-CBD fusions bound to bacterial cellulose discs, when subjected to various washes (protocol [http://2014.igem.org/Team:Imperial/Protocols here]). When washed with PBS, sfGFP-CBDcex fusions performed the best out of all the CBDs tested (third graph) followed by washes with 5% BSA (fourth graph), dH20 (first graph) and 70% EtOH (second graph).
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal SapI.rc site found at 10