Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1152007:Design"
m |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
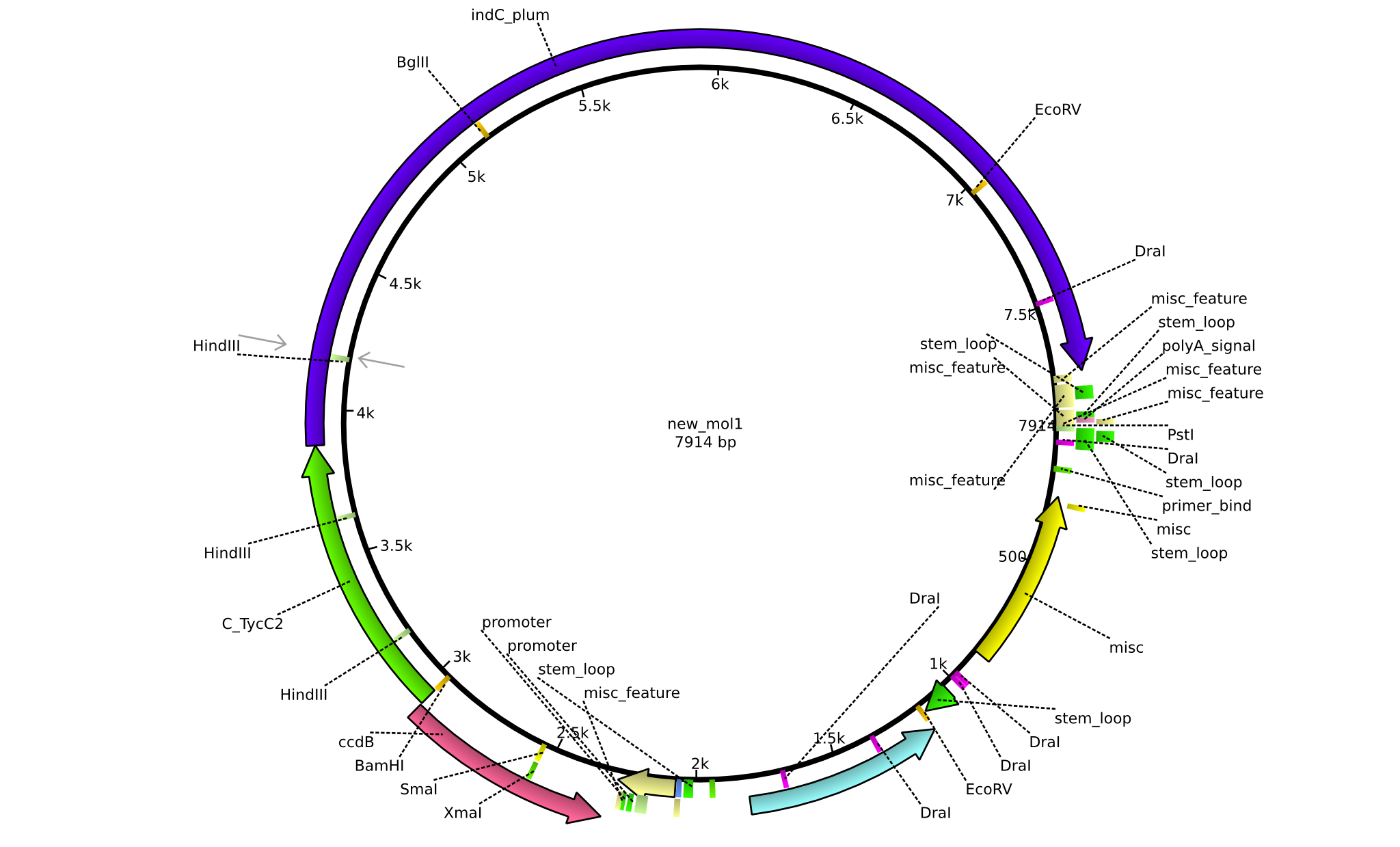
[[File:Heidelberg_Construct_ccdB.png|Plasmide map of the Helper construct for NRP-Indigoidine-tagging|700px|center]] | [[File:Heidelberg_Construct_ccdB.png|Plasmide map of the Helper construct for NRP-Indigoidine-tagging|700px|center]] | ||
| − | + | <div style="text-align:justify"> | |
===Design Notes=== | ===Design Notes=== | ||
BBa_K1152007 was assembled via Gibson Cloning out of four fragments. The modules that were required for the NRPS were amplified from ''B. parabrevis'', ''P. luminescens'' and the pDONR-vector. There were no illegal restriction sites, neither in ccdB, nor in the C-domain of TycC2. However, in indC, the gene that encodes for the Indigoidine synthetase, two illegal restriction sites (one for EcoRI, one for SpeI) had to be removed by mutagenesis. In order to change the Indigoidine-module from an initiation module to a subsequent module, it has to be put behind a C-domain. We selected the C-domain of TycC2-module, as it is specific for Glutamine, which is the substrate for Indigoidine. | BBa_K1152007 was assembled via Gibson Cloning out of four fragments. The modules that were required for the NRPS were amplified from ''B. parabrevis'', ''P. luminescens'' and the pDONR-vector. There were no illegal restriction sites, neither in ccdB, nor in the C-domain of TycC2. However, in indC, the gene that encodes for the Indigoidine synthetase, two illegal restriction sites (one for EcoRI, one for SpeI) had to be removed by mutagenesis. In order to change the Indigoidine-module from an initiation module to a subsequent module, it has to be put behind a C-domain. We selected the C-domain of TycC2-module, as it is specific for Glutamine, which is the substrate for Indigoidine. | ||
| + | ====indC==== | ||
| + | The native indC gene contains internal EcoRI and SpeI cutting sites. To avoid illegal restriction sites mutations were introduced (indicated with small letters) using a CPEC approach. IndC was amplified in three fragments from ''P. luminescens'' genomic DNA. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1. start codon to EcoRI cutting site | ||
| + | indC_fw: CATACTAGAG AAAGAGGAGAAA GGTACC ATGTTAGAAAATAATATTACACAATG | ||
| + | EcoRI_rv: CAATACCCACC GAAcTC TTTGAGCT AATTTCTGACAGACAATACC | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2. EcoRI cutting site to SpeI cutting site | ||
| + | EcoRI_fw: AGCTCAAA GAgTTC GGTGGGTATTG GGCTTTTTTGTGATC | ||
| + | SpeI_rv: ATAAGCCAG ACTcGT GGGTTTAGGAACTTG GAACTTGAACTGTG | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | 3. Spe cutting site to stop codon | ||
| + | SpeI_fw: CAAGTTCCTAAACCC ACgAGT CTGGCTTAT ATTATTTATACCTCTGGTAGCAC | ||
| + | indC_rv: CAGCGTTATTA GCTAGC TCA TTAGATTATTTTCTCAATCTCAG | ||
| + | </div> | ||
===Source=== | ===Source=== | ||
Coding regions were amplified from genomes of ''Brevibacillus parabrevis'' ATCC8185 that was sent to us by the lab of Prof. Marahiel from Marburg and ''Photorhabdus luminescens'' subsp. ''laumondii'' TT01 (DSM15139) obtained from DSMZ. ccdB was amplified from pDONR-vector from Invitrogen. | Coding regions were amplified from genomes of ''Brevibacillus parabrevis'' ATCC8185 that was sent to us by the lab of Prof. Marahiel from Marburg and ''Photorhabdus luminescens'' subsp. ''laumondii'' TT01 (DSM15139) obtained from DSMZ. ccdB was amplified from pDONR-vector from Invitrogen. | ||
| Line 14: | Line 30: | ||
===References=== | ===References=== | ||
| − | + | # Marahiel MA, Stachelhaus T, Mootz HD (1997) Modular Peptide Synthetases Involved in Nonribosomal Peptide Synthesis. Chem Rev 97:2651–2674.<br/> | |
| − | + | # Mootz HD, Schwarzer D, Marahiel MA (2000) Construction of hybrid peptide synthetases by module and domain fusions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 5848–5853.<br/> | |
| − | + | # Mootz HD, Marahiel MA (1997) The tyrocidine biosynthesis operon of Bacillus brevis: complete nucleotide sequence and biochemical characterization of functional internal adenylation domains. JBacteriol 179: 6843–6850.<br/> | |
| − | + | # Finking R, Marahiel MA (2004) Biosynthesis of nonribosomal peptides. Annu Rev Microbiol 58: 453–488. | |
| + | #Brachmann AO, Kirchner F, Kegler C, Kinski SC, Schmitt I, Bode HB (2012) Triggering the production of the cryptic blue pigment indigoidine from Photorhabdus luminescens. J Biotechnol 157: 96-99. | ||
| + | #Quan J, Tian J (2009) Circular polymerase extension cloning of complex gene libraries and pathways. PLoS One 4: e6441. | ||
Latest revision as of 03:01, 29 October 2013
Helper construct for NRP-Indigoidine-tagging
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 3061
Illegal BamHI site found at 891 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 341
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 4324
Design Notes
BBa_K1152007 was assembled via Gibson Cloning out of four fragments. The modules that were required for the NRPS were amplified from B. parabrevis, P. luminescens and the pDONR-vector. There were no illegal restriction sites, neither in ccdB, nor in the C-domain of TycC2. However, in indC, the gene that encodes for the Indigoidine synthetase, two illegal restriction sites (one for EcoRI, one for SpeI) had to be removed by mutagenesis. In order to change the Indigoidine-module from an initiation module to a subsequent module, it has to be put behind a C-domain. We selected the C-domain of TycC2-module, as it is specific for Glutamine, which is the substrate for Indigoidine.
indC
The native indC gene contains internal EcoRI and SpeI cutting sites. To avoid illegal restriction sites mutations were introduced (indicated with small letters) using a CPEC approach. IndC was amplified in three fragments from P. luminescens genomic DNA.
1. start codon to EcoRI cutting site
indC_fw: CATACTAGAG AAAGAGGAGAAA GGTACC ATGTTAGAAAATAATATTACACAATG EcoRI_rv: CAATACCCACC GAAcTC TTTGAGCT AATTTCTGACAGACAATACC
2. EcoRI cutting site to SpeI cutting site
EcoRI_fw: AGCTCAAA GAgTTC GGTGGGTATTG GGCTTTTTTGTGATC SpeI_rv: ATAAGCCAG ACTcGT GGGTTTAGGAACTTG GAACTTGAACTGTG
3. Spe cutting site to stop codon
SpeI_fw: CAAGTTCCTAAACCC ACgAGT CTGGCTTAT ATTATTTATACCTCTGGTAGCAC indC_rv: CAGCGTTATTA GCTAGC TCA TTAGATTATTTTCTCAATCTCAG
Source
Coding regions were amplified from genomes of Brevibacillus parabrevis ATCC8185 that was sent to us by the lab of Prof. Marahiel from Marburg and Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. laumondii TT01 (DSM15139) obtained from DSMZ. ccdB was amplified from pDONR-vector from Invitrogen.
References
- Marahiel MA, Stachelhaus T, Mootz HD (1997) Modular Peptide Synthetases Involved in Nonribosomal Peptide Synthesis. Chem Rev 97:2651–2674.
- Mootz HD, Schwarzer D, Marahiel MA (2000) Construction of hybrid peptide synthetases by module and domain fusions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 5848–5853.
- Mootz HD, Marahiel MA (1997) The tyrocidine biosynthesis operon of Bacillus brevis: complete nucleotide sequence and biochemical characterization of functional internal adenylation domains. JBacteriol 179: 6843–6850.
- Finking R, Marahiel MA (2004) Biosynthesis of nonribosomal peptides. Annu Rev Microbiol 58: 453–488.
- Brachmann AO, Kirchner F, Kegler C, Kinski SC, Schmitt I, Bode HB (2012) Triggering the production of the cryptic blue pigment indigoidine from Photorhabdus luminescens. J Biotechnol 157: 96-99.
- Quan J, Tian J (2009) Circular polymerase extension cloning of complex gene libraries and pathways. PLoS One 4: e6441.