Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1152007"
m |
|||
| (37 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K1152007 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K1152007 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | + | {{Curation/ccdb}} | |
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:justify"> | ||
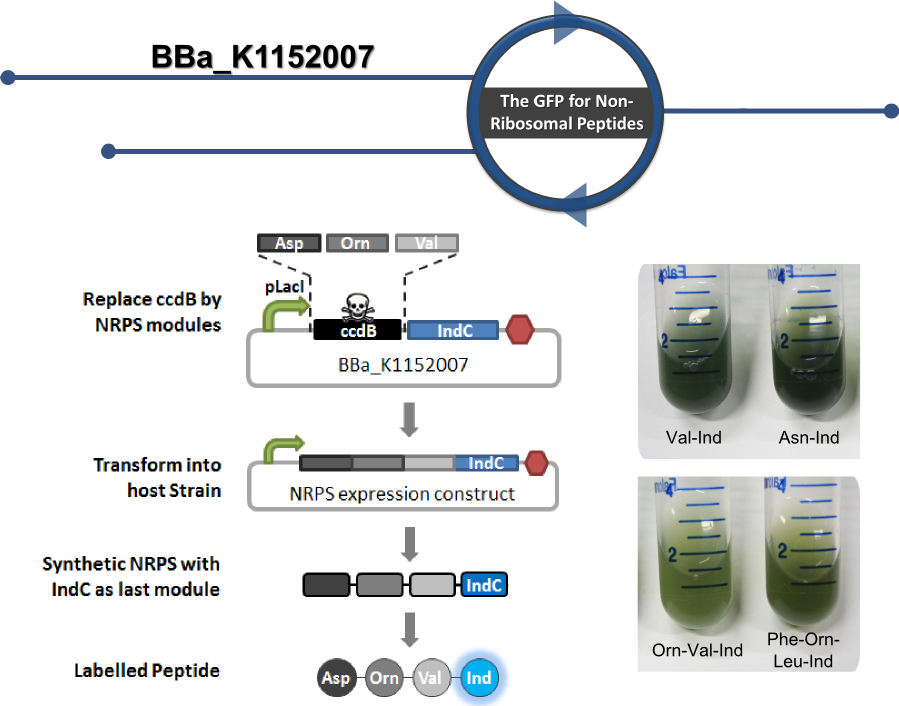
| + | This part serves as helper plasmid for efficient cloning of custom [http://2013.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Project non-ribosomal peptide synthetases] (NRPSs) that enable labeling of the synthesized non-ribosomal peptides with the blue pigment indigoidine <em>in-vivo</em>. Peptides labelled this way can easily be purified and characterized by analytical means, since peptide production can be observed with the naked eye or quantified photometrically. | ||
| + | Therefore, the helper-construct can be applied for high-throughput cloning of custom NRPSs for production of synthetic peptides ([http://2013.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/RFCs RFC 100] for details). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | NRPS modules can be introduced by Gibson ([http://www.synbio.org.uk/gibson/downloads/files/RFC57.pdf RFC 57]) or CPEC cloning ([http://2013.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/RFCs#rfc99 RFC 99]) in any desired order. NRPS modules of choice are introduced in front of an engineered IndC module containing an additional C-domain for communication with the previous module. When inserted, they are replacing the ccdB suicide gene located in front of the indigoidine module. The ccdB gene acts as a negative selection marker (death cassette) and is lost in recombined (with insert) form. During cloning the gene is replaced with an cloning efficiency close to 100 %. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Heidelberg_Registry_2007_main_fig1.png|700px|center|'''Figure 1''':]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><div style="width:700px; text-align:justify"><b>Figure 1: BBa_K1152007. Functionality of the ccdB-helper construct for tagging.</b> BBa_1152007 enables labeling of custom non-ribosomal peptides with the blue pigment indigoidine ''in vivo''. NRPS modules of choice can be introduced in front of an engineered IndC module containing an additional C-domain for communication with the previous module. During cloning, ccdB is replaced which leads to close to 100 % cloning efficiency. By the tag, peptide production can be seen with the naked eye and quantified photometrically. Labelled peptides can easily be purified and characterized by thin-layer chromatography.</div></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Note''': as ccdB is replaced during cloning, only constructs bearing the desired custom NRPS sequences are successfully propagated in ''E. coli'' strains such as Top10 or DH5alpha. Thereby, false-positive-rate of clones is reduced to almost to 0 %. | ||
| + | <br>Expression is under control of a lac-inducible promoter. Since the blue pigment indigoidine can be seen after induction with Isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranosid (IPTG) by the naked eye, analytical procedures can be facilitated. Blue colonies indicate synthesis of the synthetic peptide fused to Indigoidine. A thin-layer chromatography ([[Part:BBa_K1152007:Experience#Valine-Indigoidine_.28pPW05.29 |TLC]]) can be easily applied to confirm those observations. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | To verify the sequence of our construct, colony PCRs, and analytical restriction digests with Pst1 and EcoRI were usually performed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''We characterized this construct by cloning different NRPS module compositions into this helper construct, leading to the production of different peptides bearing the indigoidine tag. Please refer to [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1152007:Experience the experience page] for charaterization of this part. Also refer to [http://2013.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/RFCs RFC 100] for further details on how to engineer synthetic NRPSs.''' | ||
<!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | <!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | ||
===Usage and Biology=== | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
| − | |||
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
<span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | <span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | ||
| Line 16: | Line 35: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K1152007 parameters</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K1152007 parameters</partinfo> | ||
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===IndC Indigoidine Synthetase (cds)=== | ||
| + | The single module NRPS IndC (Indigoidine Synthetase) from Photorhabdus luminescens laumondii TT01 is a nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) which produces the blue pigment indigoidine. It consists of an Adenylation domain, which contains an internal oxidation domain, a Thiolation- and a Thioesterase-domain. Indigoidine itself is composed of two cyclic glutamine molecules. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The open reading frame of the native indigoidine synthetase indC was amplified from genomic DNA of P. lumninescens laumondii TT01 and cloned into the helper plasmide for NRP-Indigoidine-tagging. Host strains as for instance E. coli BAP1 or TOP10 express endogenous PPTases, which are capable of transferring 4'-phosphopantetheine residues from coenzyme A to the T-domain of modules and therefore needed for properly working NRPS. For cells transformed with the plasmide decelerated growth and smaller colonies were observed in comparison to negative controls. | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | ===Source=== | ||
| + | * IndC was amplified from P. luminescens laumondii TT01 (DSM15139) genomic DNA. | ||
| + | * C-domain of TycC2 was amplified from the tyrocidine gene cluster of ''Brevibacillus Parabrevis''. Genebank File taken from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/af004835 | ||
| + | * ccdB gene was amplified from Gateway pDONR vector (bacterial plasmide) | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | #Duchaud, E. et. al., Nat. Biotechnol. 21 (11), 1307-1313 (2003): The genome sequence of the entomopathogenic bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens | ||
| + | #Brachmann AO et. al. (2012) Triggering the production of the cryptic blue pigment indigoidine from Photorhabdus luminescens. J Biotechnol 157: 96-99. | ||
| + | #Lambalot RH, Gehring AM, Flugel RS, Zuber P, LaCelle M, Marahiel MA, Reid R, Khosla C, Walsh CT (1996) A new enzyme superfamily - the phosphopantetheinyl transferases. Chem Biol 3: 923-936. | ||
Latest revision as of 17:48, 9 July 2015
Helper construct for NRP-Indigoidine-tagging
This part serves as helper plasmid for efficient cloning of custom [http://2013.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Project non-ribosomal peptide synthetases] (NRPSs) that enable labeling of the synthesized non-ribosomal peptides with the blue pigment indigoidine in-vivo. Peptides labelled this way can easily be purified and characterized by analytical means, since peptide production can be observed with the naked eye or quantified photometrically. Therefore, the helper-construct can be applied for high-throughput cloning of custom NRPSs for production of synthetic peptides ([http://2013.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/RFCs RFC 100] for details).
NRPS modules can be introduced by Gibson ([http://www.synbio.org.uk/gibson/downloads/files/RFC57.pdf RFC 57]) or CPEC cloning ([http://2013.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/RFCs#rfc99 RFC 99]) in any desired order. NRPS modules of choice are introduced in front of an engineered IndC module containing an additional C-domain for communication with the previous module. When inserted, they are replacing the ccdB suicide gene located in front of the indigoidine module. The ccdB gene acts as a negative selection marker (death cassette) and is lost in recombined (with insert) form. During cloning the gene is replaced with an cloning efficiency close to 100 %.
Note: as ccdB is replaced during cloning, only constructs bearing the desired custom NRPS sequences are successfully propagated in E. coli strains such as Top10 or DH5alpha. Thereby, false-positive-rate of clones is reduced to almost to 0 %.
Expression is under control of a lac-inducible promoter. Since the blue pigment indigoidine can be seen after induction with Isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranosid (IPTG) by the naked eye, analytical procedures can be facilitated. Blue colonies indicate synthesis of the synthetic peptide fused to Indigoidine. A thin-layer chromatography (TLC) can be easily applied to confirm those observations.
To verify the sequence of our construct, colony PCRs, and analytical restriction digests with Pst1 and EcoRI were usually performed.
We characterized this construct by cloning different NRPS module compositions into this helper construct, leading to the production of different peptides bearing the indigoidine tag. Please refer to the experience page for charaterization of this part. Also refer to [http://2013.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/RFCs RFC 100] for further details on how to engineer synthetic NRPSs.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 3061
Illegal BamHI site found at 891 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 341
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 4324
IndC Indigoidine Synthetase (cds)
The single module NRPS IndC (Indigoidine Synthetase) from Photorhabdus luminescens laumondii TT01 is a nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) which produces the blue pigment indigoidine. It consists of an Adenylation domain, which contains an internal oxidation domain, a Thiolation- and a Thioesterase-domain. Indigoidine itself is composed of two cyclic glutamine molecules.
The open reading frame of the native indigoidine synthetase indC was amplified from genomic DNA of P. lumninescens laumondii TT01 and cloned into the helper plasmide for NRP-Indigoidine-tagging. Host strains as for instance E. coli BAP1 or TOP10 express endogenous PPTases, which are capable of transferring 4'-phosphopantetheine residues from coenzyme A to the T-domain of modules and therefore needed for properly working NRPS. For cells transformed with the plasmide decelerated growth and smaller colonies were observed in comparison to negative controls.
Source
- IndC was amplified from P. luminescens laumondii TT01 (DSM15139) genomic DNA.
- C-domain of TycC2 was amplified from the tyrocidine gene cluster of Brevibacillus Parabrevis. Genebank File taken from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/af004835
- ccdB gene was amplified from Gateway pDONR vector (bacterial plasmide)
References
- Duchaud, E. et. al., Nat. Biotechnol. 21 (11), 1307-1313 (2003): The genome sequence of the entomopathogenic bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens
- Brachmann AO et. al. (2012) Triggering the production of the cryptic blue pigment indigoidine from Photorhabdus luminescens. J Biotechnol 157: 96-99.
- Lambalot RH, Gehring AM, Flugel RS, Zuber P, LaCelle M, Marahiel MA, Reid R, Khosla C, Walsh CT (1996) A new enzyme superfamily - the phosphopantetheinyl transferases. Chem Biol 3: 923-936.