Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1028000"
(→Usage and Experimental Data) |
(→Introduction) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
| − | <img src="http://i276.photobucket.com/albums/kk29/JosephBeetBeet/ | + | <img src="http://i276.photobucket.com/albums/kk29/JosephBeetBeet/Si4bindingpeptide.jpg" style="width:350px;margin-left:160px" ></a> |
<p style="text-align:left"><b>Figure.1</b> Illustrated schematic of the Si4 Binding Peptide binding with a silica microsphere. | <p style="text-align:left"><b>Figure.1</b> Illustrated schematic of the Si4 Binding Peptide binding with a silica microsphere. | ||
</p></html> | </p></html> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | This part was originally designed by the Leeds 2013 iGEM team to bind with silica microspheres, designed to act as pathogen surrogates, when presented on the exterior of the plasma membrane via fusion with Ice Nucleation Protein. | + | This part was originally designed by the Leeds 2013 iGEM team to bind with silica microspheres, designed to act as pathogen surrogates, when presented on the exterior of the plasma membrane via fusion with Ice Nucleation Protein. |
=== '''Usage and Experimental Data''' === | === '''Usage and Experimental Data''' === | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | The experimental data acquired regarding this part is shown on the page for its sister part [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1028001#Introduction BBa_K1028001]. The Si4 Binding Peptide was tested in unison with INP as an INP.Si4 complex to allow expression in the extracellular space via the plasma membrane. | ||
Latest revision as of 16:17, 4 October 2013
Silica binding peptide
Introduction
This BioBrick is a short peptide of 15 amino acids designed to act as a tag binding with high affinity to silica and silica-like particles. As a tag it can easily be added to the C-terminus of proteins using molecular biology techniques allowing the peptide to assist with purification or to serve other experimental processes related to silica binding.
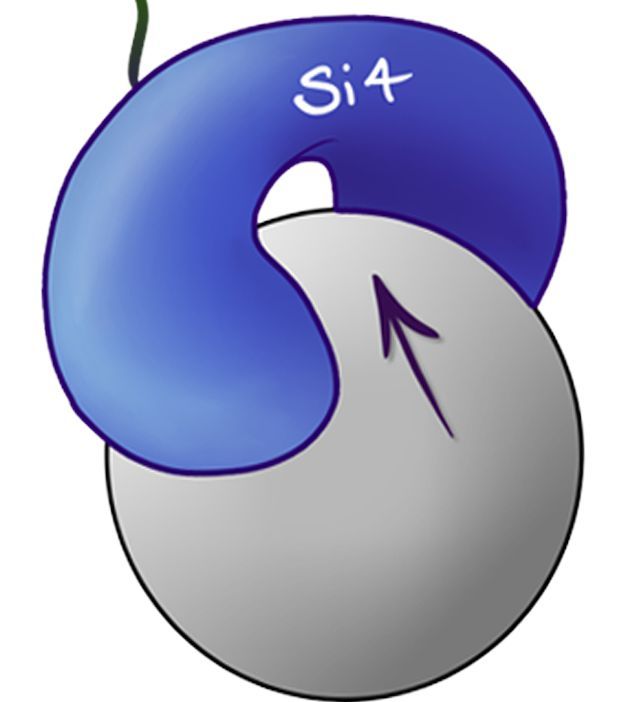
Figure.1 Illustrated schematic of the Si4 Binding Peptide binding with a silica microsphere.
This part was originally designed by the Leeds 2013 iGEM team to bind with silica microspheres, designed to act as pathogen surrogates, when presented on the exterior of the plasma membrane via fusion with Ice Nucleation Protein.
Usage and Experimental Data
The experimental data acquired regarding this part is shown on the page for its sister part BBa_K1028001. The Si4 Binding Peptide was tested in unison with INP as an INP.Si4 complex to allow expression in the extracellular space via the plasma membrane.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
