Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K808030"
(→Visualization) |
(→Composition) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
====Composition==== | ====Composition==== | ||
| − | Our fusion protein BBa_K808030 is highly chimeric. It consists of parts from three different bacteria, which are the following (starting from N-terminus to C-terminus): | + | Our fusion protein BBa_K808030 (Figure 1) is highly chimeric. It consists of parts from three different bacteria, which are the following (starting from N-terminus to C-terminus): |
* [https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K808028 PhoA] (BBa_K808028) is responsible for the peri plasmatic expression of our chimeric protein. This is highly important because once expressed into peri plasma, our construct will self-install into the outer membrane. PhoA is native to ''E.coli'' | * [https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K808028 PhoA] (BBa_K808028) is responsible for the peri plasmatic expression of our chimeric protein. This is highly important because once expressed into peri plasma, our construct will self-install into the outer membrane. PhoA is native to ''E.coli'' | ||
* [https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K808026 pNB-Esterase 13] (BBa_K808026) is the the catalytical domain of BBa_K808030. It derives from an esterase of ''Bacillus licheniformis''. | * [https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K808026 pNB-Esterase 13] (BBa_K808026) is the the catalytical domain of BBa_K808030. It derives from an esterase of ''Bacillus licheniformis''. | ||
* [https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K808027 EstA] (BBa_K808027) serves as a membrane anchor but is an inactive and membrane bound esterase mutant deriving from ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' | * [https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K808027 EstA] (BBa_K808027) serves as a membrane anchor but is an inactive and membrane bound esterase mutant deriving from ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:bba_k808032_schema.png|600px|center|thumb|Figure 1: schematic graphic of BBa_K808030, integrated into an biological membrane. The C-terminal[https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K808027 EstA] (BBa_K808027) consists of a C-terminal ß-Barrel froming the membrane anchor, and a N-terminal inactive esterase domain, carrying the passenger enzyme. In this case the passenger Enzyme is [https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K808026 pNB-Esterase 13] (BBa_K808026).]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Once this Biobrick is expressed it will develope hydrolytic activities due to its catalytical domain, the [https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K808026 pNB-Esterase 13] (BBa_K808026). Our characerisation of this chimeric protein was performed with the arabinose inducible operon [https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K808032 BBa_K808032] | ||
====Visualization==== | ====Visualization==== | ||
| − | With special regards to our [http://2012.igem.org/Team:TU_Darmstadt/Project/Simulation Simulation lab] we show you the result of great computional work. Our dry lab made some homologies and edited these beautiful graphics of our chimeric protein. (Figure | + | With special regards to our [http://2012.igem.org/Team:TU_Darmstadt/Project/Simulation Simulation lab] we show you the result of great computional work. Our dry lab made some homologies and edited these beautiful graphics of our chimeric protein. (Figure 2 & 3) |
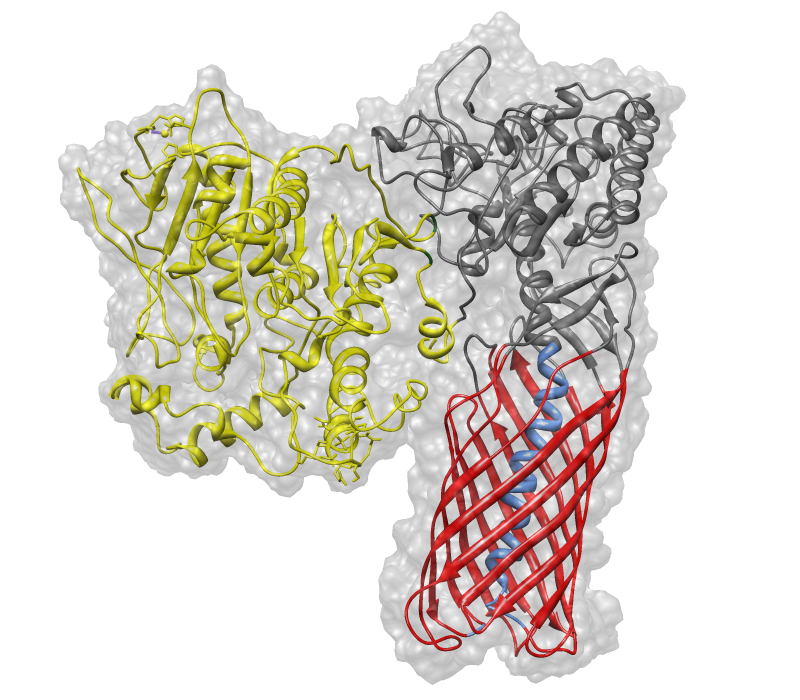
| − | [[Image:pnb_EstA_ohne_mem.png|500px|center|thumb|Figure | + | [[Image:pnb_EstA_ohne_mem.png|500px|center|thumb|Figure 2: The composition and folding of BBa_K808030. Yellow:[https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K808026 pNB-Esterase 13] (BBa_K808026)after the N-terminal cut-off of PhoA. Gray: inactive catalytical part of [https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K808027 EstA] (BBa_K808027). Blue: Transmembrane helix of EstA, connecting its inactive catalytical domain and membrane anchor. Red: Anchor domain of [https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K808027 EstA] (BBa_K808027)]] |
| Line 26: | Line 31: | ||
| − | [[Image:pnb_EstA.png|500px|center|thumb|Figure | + | [[Image:pnb_EstA.png|500px|center|thumb|Figure 3: The composition and folding of BBa_K808030 when integrated into a biological membrane]] |
Latest revision as of 21:15, 25 September 2012
RBS-PhoA-His6tag-pNBEst13-Myctag-EstA
RBS-PhoA-His6tag-pNBEst13-Myctag-EstA is a long name for a long protein construct. It is a fusion protein which is secreted into the peri plasma in order to be integrated into the outer membran. When the phoA signal sequence is cut off, the N-terminus is formed by our pNB-Est13. This esterase shows actitivty towards PET and is anchored onto the cell by its inactive EstA membrane anchor.
Annotation: This site is about the construct and composition of our chimeric protein BBa_K808030. For any information about its expression rate or enzyme activity please visit BBa_K808032
Usage and Biology
Composition
Our fusion protein BBa_K808030 (Figure 1) is highly chimeric. It consists of parts from three different bacteria, which are the following (starting from N-terminus to C-terminus):
- PhoA (BBa_K808028) is responsible for the peri plasmatic expression of our chimeric protein. This is highly important because once expressed into peri plasma, our construct will self-install into the outer membrane. PhoA is native to E.coli
- pNB-Esterase 13 (BBa_K808026) is the the catalytical domain of BBa_K808030. It derives from an esterase of Bacillus licheniformis.
- EstA (BBa_K808027) serves as a membrane anchor but is an inactive and membrane bound esterase mutant deriving from Pseudomonas aeruginosa

Once this Biobrick is expressed it will develope hydrolytic activities due to its catalytical domain, the pNB-Esterase 13 (BBa_K808026). Our characerisation of this chimeric protein was performed with the arabinose inducible operon BBa_K808032
Visualization
With special regards to our [http://2012.igem.org/Team:TU_Darmstadt/Project/Simulation Simulation lab] we show you the result of great computional work. Our dry lab made some homologies and edited these beautiful graphics of our chimeric protein. (Figure 2 & 3)
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 1174
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 1700
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 1838
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 2378
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 2747
Illegal AgeI site found at 1245 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]

