Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K733002"
Feisun0718 (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
| − | + | The xylose inducible promoter used to construct this part is amplified from the integration plasmid pAX01. (Zeigler 2002)This plasmid contains a xylose inducible promoter which is originated from ''Bacillis megaterium''. | |
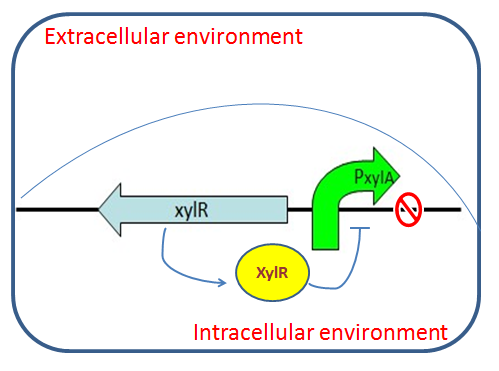
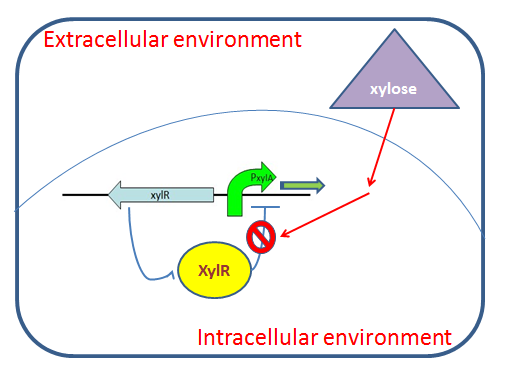
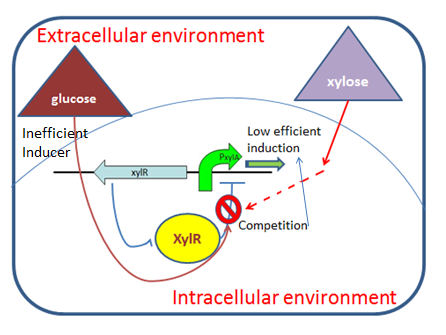
| + | The xylose inducible promoter we constructed contains promoter <i>PxylA</i> which located within xylose operon, originally to drive the expression of ''<i>xylA</i>'' (xylose isomerase coding gene) and'' <i>xylB</i>'' (xylulose kinase). ''<i>xylR</i>'' with its promoter located at upstream of xylose operon is also included in our parts. It encodes ''xyl'' repressor which binds to'' xyl'' operator in the absence of xylose, repressing transcription event. In the presence of glucose, glucose-6-phosphate metabolized from glucose can compete with xylose in the binding site of xylose on XylR. In addition, glucose itself is also supposed to be a low efficiency inducer for XylR. (DAHL, 1997) Therefore while xylose induces the transcription, the existence of glucose, to some extent, represses gene transcription. | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:Pxyl1.png]] [[Image:Pxyl2.png]] | [[Image:Pxyl1.png]] [[Image:Pxyl2.png]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Pxyl3.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | For the characterization of <i>xylR</i>+<i>PxylA</i>, please refer to: [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K733018 BBa_K733018] | ||
| Line 26: | Line 31: | ||
== Reference == | == Reference == | ||
| − | Zeigler, D. (2002). ''Integration Vectors for Gram-Positive Bacteria'' (7 ed.). Columbus: The Bacillus Genetic Stock Center. | + | Zeigler, D. (2002). ''Integration Vectors for Gram-Positive Bacteria'' (7 ed.). Columbus: The <i>Bacillus</i> Genetic Stock Center. |
| − | + | Dahl, M. K., D. Schmiedel, and W. Hillen. 1995. Glucose and glucose-6-phosphate interaction with Xyl repressor proteins from Bacillus spp. May contribute to regulation of xylose utilization. ''J. Bacteriol.'' 177:5467–5472. | |
Latest revision as of 03:50, 27 September 2012
xylR+PxylA: A xylose inducible promoter with its transcriptional regulator.
The xylose inducible promoter used to construct this part is amplified from the integration plasmid pAX01. (Zeigler 2002)This plasmid contains a xylose inducible promoter which is originated from Bacillis megaterium.
The xylose inducible promoter we constructed contains promoter PxylA which located within xylose operon, originally to drive the expression of xylA (xylose isomerase coding gene) and xylB (xylulose kinase). xylR with its promoter located at upstream of xylose operon is also included in our parts. It encodes xyl repressor which binds to xyl operator in the absence of xylose, repressing transcription event. In the presence of glucose, glucose-6-phosphate metabolized from glucose can compete with xylose in the binding site of xylose on XylR. In addition, glucose itself is also supposed to be a low efficiency inducer for XylR. (DAHL, 1997) Therefore while xylose induces the transcription, the existence of glucose, to some extent, represses gene transcription.
For the characterization of xylR+PxylA, please refer to: BBa_K733018
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal XhoI site found at 847
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Reference
Zeigler, D. (2002). Integration Vectors for Gram-Positive Bacteria (7 ed.). Columbus: The Bacillus Genetic Stock Center.
Dahl, M. K., D. Schmiedel, and W. Hillen. 1995. Glucose and glucose-6-phosphate interaction with Xyl repressor proteins from Bacillus spp. May contribute to regulation of xylose utilization. J. Bacteriol. 177:5467–5472.