Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K525720"
| (3 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K525720 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K525720 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | + | NAD<sup>+</sup>-dependent DNA ligase from ''E. coli'' in Freiburg BioBrick Assembly Standard (RFC 25) | |
| − | |||
===Usage and Biology=== | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
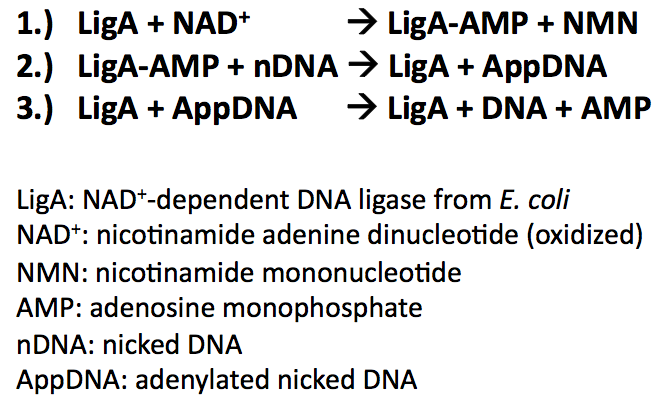
| − | < | + | Bacterial DNA ligases are important enzymes for DNA repair and replication. They use NAD<sup>+</sup> as a cofactor to bind hydrolysed AMP to the active site lysine under release of NMN. AMP is used to catalyse the formation of a phosphodiester bond in nicked DNA by transferring AMP to the 5'-phosphate group. This results in an attack of the nick 3'-OH on the 5'-phosphoanhydride linkage and release of free AMP: |
| − | < | + | |
| + | [[Image:Bielefeld-Germany-2011_LigA_reactionmechanism.png|350px|centre]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | During the reaction mechanism the DNA ligases functional domains undergo conformational changes promoting intra- and intermolecular interactions. The domains are highly conserved throughout the bacterial kingdom and categorized in the following way: | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | *Domain 1: Ia, Ib (NTase)<br> | ||
| + | *Domain 2: Oligomer-binding (OB) beta-barrel<br> | ||
| + | *Domain 3: Zinc (Zn)-finger, helix-hairpin-helix motif (HhH)<br> | ||
| + | *Domain 4: BRCT domain <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The NAD<sup>+</sup>-dependent DNA ligase from ''E. coli'' (LigA) can be applied to biochemical studies ranging from cloning procedures and enzymatic assays to biomedical investigations. For instance, the purified enzyme can contribute to ''in vitro'' experiments dealing with antibiotic drug design because bacterial DNA ligases are essential for fundamental life-sustaining processes and differentiate from eukaryotic DNA ligases due to their specifity for NAD<sup>+</sup> as a cofactor. | ||
| + | <br style="clear: both" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Sequence and Features=== | ||
| + | |||
<partinfo>BBa_K525720 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K525720 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | ||
| + | <br style="clear: both" /> | ||
| + | ===Characterization=== | ||
| + | Detailed information about the characteristics can be found for the PT7 promoter, RBS and His-tag equipped form of LigA <partinfo>BBa_K525710</partinfo>. | ||
| + | <br style="clear: both" /> | ||
<!-- Uncomment this to enable Functional Parameter display | <!-- Uncomment this to enable Functional Parameter display | ||
Latest revision as of 17:48, 21 September 2011
DNA ligase from Escherichia coli (LigA)
NAD+-dependent DNA ligase from E. coli in Freiburg BioBrick Assembly Standard (RFC 25)
Usage and Biology
Bacterial DNA ligases are important enzymes for DNA repair and replication. They use NAD+ as a cofactor to bind hydrolysed AMP to the active site lysine under release of NMN. AMP is used to catalyse the formation of a phosphodiester bond in nicked DNA by transferring AMP to the 5'-phosphate group. This results in an attack of the nick 3'-OH on the 5'-phosphoanhydride linkage and release of free AMP:
During the reaction mechanism the DNA ligases functional domains undergo conformational changes promoting intra- and intermolecular interactions. The domains are highly conserved throughout the bacterial kingdom and categorized in the following way:
- Domain 1: Ia, Ib (NTase)
- Domain 2: Oligomer-binding (OB) beta-barrel
- Domain 3: Zinc (Zn)-finger, helix-hairpin-helix motif (HhH)
- Domain 4: BRCT domain
The NAD+-dependent DNA ligase from E. coli (LigA) can be applied to biochemical studies ranging from cloning procedures and enzymatic assays to biomedical investigations. For instance, the purified enzyme can contribute to in vitro experiments dealing with antibiotic drug design because bacterial DNA ligases are essential for fundamental life-sustaining processes and differentiate from eukaryotic DNA ligases due to their specifity for NAD+ as a cofactor.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 1422
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 4
Illegal AgeI site found at 2020 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal SapI.rc site found at 1636
Characterization
Detailed information about the characteristics can be found for the PT7 promoter, RBS and His-tag equipped form of LigA BBa_K525710.