Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K346005:Design"
JjunyiJiao (Talk | contribs) (→Design Notes) |
Spring zhq (Talk | contribs) (→Design Notes) |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
| + | |||
<partinfo>BBa_K346005 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K346005 short</partinfo> | ||
| Line 7: | Line 8: | ||
===Design Notes=== | ===Design Notes=== | ||
| − | + | This part was designed to combine three subparts together, in order to implement a mercury binding device. | |
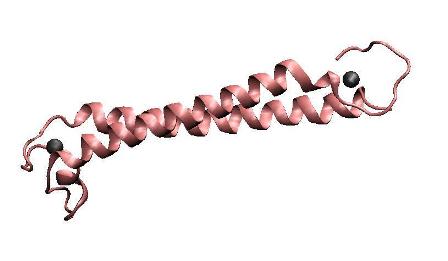
| − | '''Metal binding | + | '''Metal binding peptide(MBP)''' |
| − | To achieve the goal of making a high performance MBP, we constructed a single polypeptide consisting of two dimerization | + | To achieve the goal of making a high performance MBP, we constructed a single-chained polypeptide consisting of two dimerization helices and metal binding loops of MerR, to form an antiparallel coiled coil MBP mimicking the dimerized metal binding domains of the wild-type MerR. We amplified the N-terminal and C-terminal of MBP directly from full length MerR by PCR, and then cloned them into the backbone together by one step. After that, RBS, T7 promoter and terminator are prefixed and suffixed, respectively. |
[[Image:mbp2.jpg]] [[Image:mbp3.jpg]] | [[Image:mbp2.jpg]] [[Image:mbp3.jpg]] | ||
| Line 18: | Line 19: | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''DsbA-MBP''' |
| − | + | DsbA-MBP is a fusion protein aiming to translocate the MBP to the periplasm. | |
[[Image:dsba-mbp.jpg]] | [[Image:dsba-mbp.jpg]] | ||
| Line 33: | Line 34: | ||
[[Image:lom.jpg]] | [[Image:lom.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Assembly''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:DML.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | For the Lpp-OmpA-MBP which is displayed on the surface, previous work showed that over 20000 copies of MBPs are expressed on the membrane per cell, with metal stoichiometries of ~1.0 Hg(II) per MBP monomer. But at the same time, the membrane protein consumes more energy. In contrast, the copy number of cytoplasmic MBP is 560000~800000 per cell, with a stoichiometries of ~0.455Hg(II) per MBP monomer at low concentration of Hg(II) and ~1.12±0.18 Hg(II) per MBP monomer at high concentration of Hg(II) and the energy needed to express the protein is less than the membrane protein. The data for DsbA-MBP, which is expressed in the periplasmic space is between MBP and Lpp-OmpA-MBP. However, given that our bioabsorbent is aimed to tackle the water with trace of Hg(II), we find us are trapped in the dilemma due to the contradiction between copy number of proteins and the absorption capacity if only one type of MBP is chosen. To make full advantage of the space in the cell and reduce the energy-assumption to the least, we assembled these three parts together, expecting MBP to express and play roles in cytoplasm, periplasm space and on the membrane simultaneously. | ||
===Source=== | ===Source=== | ||
| Line 38: | Line 46: | ||
MerR is from plasmid NR1 | MerR is from plasmid NR1 | ||
| − | lpp-ompa-mbp is from plasmid | + | lpp-ompa-mbp is from plasmid PSD-MBD |
both these two plasmids are offered by Anne O. Summers. | both these two plasmids are offered by Anne O. Summers. | ||
| Line 54: | Line 62: | ||
[6]Jie Qin,Lingyun Song,Hassan Brim, Michael J. Daly and Anne O. Summers(2006) Hg(II) sequestration and protection by the MerR metal-binding domain(MBD).Microbiology 15, 709–719 | [6]Jie Qin,Lingyun Song,Hassan Brim, Michael J. Daly and Anne O. Summers(2006) Hg(II) sequestration and protection by the MerR metal-binding domain(MBD).Microbiology 15, 709–719 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Mulligan, C. N., Yong, R. N. & Gibbs, B. F. Remediation technologies for metal-contaminated soils and groundwater: an evaluation. Eng. Geol. 60, 193-207 (2000). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Matlock, M. M., Henke, K. R. & Atwood, D. A. Effectiveness of commercial reagents for heavy metal removal from water with new insights for future chelate designs. J. Hazard Mater. B92, 129-142 (2002). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Gavrilescu, M. Removal of Heavy metals from the Environment by Biosorption. Eng. Life Sci. 4, 219-232 (2004). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Mejare, M. & Bulow, L. Metal-binding proteins and peptides in bioremediation and phytoremediation of heavy metals. Trends in biotechnol. 19, 67-73(2001). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Brown, N. L., Stoyanov, J. V. & Kidd, S. P. & Hobman, J. L. The MerR family of transcriptional regulators. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 27, 145-163 (2003). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Shewchuk, L. M., Verdine, G. L., Nash, H. & Walsh, C.T. Mutagenesis of the cysteines in the metalloregulatory protein MerR indicates that a metal-bridged dimer activates transcription. Biochemistry 28, 6140-6145 (1989). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Changela, A., Chen, K., Xue, Y., Holschen, J., Outten, C. E., Halloran, T. V. & Mondrago, A. Molecular Basis of Metal-Ion Selectivity and Zeptomolar Sensitivity by CueR. Science 301, 1383-1387 (2003). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Song, L., Caguiat, J., Li, Z., Shokes, J., Scott, R. A., Olliff, L. & Summers, A. O. Engineered Single-Chain, Antiparallel, Coiled Coil Mimics the MerR Metal Binding Site. J. Bacteriol. 186, 1861–1868 (2004). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Silver, S. & Phung, L. T. A bacterial view of the periodic table: genes and proteins for toxic inorganic ions. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 32, 587-605 (2005). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Barkay, T., Miller, S. M. & Summers, A. O. Bacterial mercury resistance from atoms to ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 27, 355-384 (2003). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Woude, M. W. & Henderson, I. R. Regulation and Function of Ag43 (Flu). Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 62, 153-169 (2008). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Jingping Wang, Zhongming Wu. Simultaneous titration determination of mercury and lead with 1-(2-Pyridylazo)-2-naphthol sulphonic acid as a complexometric indicator. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, Vol. 23. No. 2, 2004, p60-62. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Min Li, Guojun Lian. The effect of TritonX-100-PAN-S as a complexometric titration indicator in determining copper. Guangdong Trace Element Science, Vol.11. No.2, 2004, 56-58. | ||
Latest revision as of 04:28, 28 October 2010
Mercury (II) ions absorption device
- 10INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]Illegal PstI site found at 529
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal PstI site found at 529
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 317
Illegal BamHI site found at 1148
Illegal BamHI site found at 2111 - 23INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]Illegal PstI site found at 529
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal PstI site found at 529
Illegal AgeI site found at 149 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Design Notes
This part was designed to combine three subparts together, in order to implement a mercury binding device.
Metal binding peptide(MBP)
To achieve the goal of making a high performance MBP, we constructed a single-chained polypeptide consisting of two dimerization helices and metal binding loops of MerR, to form an antiparallel coiled coil MBP mimicking the dimerized metal binding domains of the wild-type MerR. We amplified the N-terminal and C-terminal of MBP directly from full length MerR by PCR, and then cloned them into the backbone together by one step. After that, RBS, T7 promoter and terminator are prefixed and suffixed, respectively.
DsbA-MBP
DsbA-MBP is a fusion protein aiming to translocate the MBP to the periplasm.
LPP-OmpA-MBP
LPP-OmpA-MBP is designed as a fusion protein consisting of the signal sequence and first 9 amino acid of Lpp, residue 46~159 of OmpA and the metal binding peptide(MBP). The signal peptide of the N-termini of this fusion protein targets the protein on the membrane while the trans-membrane domain of Ompa serves as an anchor. MBP is on the externally exposed loops of OmpA, which can be anchored to the outer membrane.
Assembly
For the Lpp-OmpA-MBP which is displayed on the surface, previous work showed that over 20000 copies of MBPs are expressed on the membrane per cell, with metal stoichiometries of ~1.0 Hg(II) per MBP monomer. But at the same time, the membrane protein consumes more energy. In contrast, the copy number of cytoplasmic MBP is 560000~800000 per cell, with a stoichiometries of ~0.455Hg(II) per MBP monomer at low concentration of Hg(II) and ~1.12±0.18 Hg(II) per MBP monomer at high concentration of Hg(II) and the energy needed to express the protein is less than the membrane protein. The data for DsbA-MBP, which is expressed in the periplasmic space is between MBP and Lpp-OmpA-MBP. However, given that our bioabsorbent is aimed to tackle the water with trace of Hg(II), we find us are trapped in the dilemma due to the contradiction between copy number of proteins and the absorption capacity if only one type of MBP is chosen. To make full advantage of the space in the cell and reduce the energy-assumption to the least, we assembled these three parts together, expecting MBP to express and play roles in cytoplasm, periplasm space and on the membrane simultaneously.
Source
MerR is from plasmid NR1 lpp-ompa-mbp is from plasmid PSD-MBD both these two plasmids are offered by Anne O. Summers.
References
[1]Yamaguchi, K., Yu, F. & Inouye, M. (1988) Cell 53, 423-432.
[2]Francisco, J. A., Earhart, C. F. & Georgiou, G. (1992). Transport and anchoring of beta-lactamase to the external surface of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89, 2713–2717.
[3]Francisco, J. A., Campbell, R., Iverson, B. L. & Georgiou, G. (1993). Production and fluorescence-activated cell sorting of Escherichia coli expressing a function antibody fragment on the external surface. ProcNatl Acad Sci U S A 90, 10444–10448
[4]Daugherty, P. S., Olsen, M. J., Iverson, B. L. & Georgiou, G. (1999).Development of an optimized expression system for the screening of antibody libraries displayed on the Escherichia coli surface. Protein Eng 12, 613–621.
[5]Song, L., Caguiat, J., Li, Z., Shokes, J., Scott, R. A., Olliff, L. &Summers, A. O. (2004). Engineered single-chain, antiparallel,coiled coil mimics the MerR metal binding site. J Bacteriol 186,1861–1868.
[6]Jie Qin,Lingyun Song,Hassan Brim, Michael J. Daly and Anne O. Summers(2006) Hg(II) sequestration and protection by the MerR metal-binding domain(MBD).Microbiology 15, 709–719
Mulligan, C. N., Yong, R. N. & Gibbs, B. F. Remediation technologies for metal-contaminated soils and groundwater: an evaluation. Eng. Geol. 60, 193-207 (2000).
Matlock, M. M., Henke, K. R. & Atwood, D. A. Effectiveness of commercial reagents for heavy metal removal from water with new insights for future chelate designs. J. Hazard Mater. B92, 129-142 (2002).
Gavrilescu, M. Removal of Heavy metals from the Environment by Biosorption. Eng. Life Sci. 4, 219-232 (2004).
Mejare, M. & Bulow, L. Metal-binding proteins and peptides in bioremediation and phytoremediation of heavy metals. Trends in biotechnol. 19, 67-73(2001).
Brown, N. L., Stoyanov, J. V. & Kidd, S. P. & Hobman, J. L. The MerR family of transcriptional regulators. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 27, 145-163 (2003).
Shewchuk, L. M., Verdine, G. L., Nash, H. & Walsh, C.T. Mutagenesis of the cysteines in the metalloregulatory protein MerR indicates that a metal-bridged dimer activates transcription. Biochemistry 28, 6140-6145 (1989).
Changela, A., Chen, K., Xue, Y., Holschen, J., Outten, C. E., Halloran, T. V. & Mondrago, A. Molecular Basis of Metal-Ion Selectivity and Zeptomolar Sensitivity by CueR. Science 301, 1383-1387 (2003).
Song, L., Caguiat, J., Li, Z., Shokes, J., Scott, R. A., Olliff, L. & Summers, A. O. Engineered Single-Chain, Antiparallel, Coiled Coil Mimics the MerR Metal Binding Site. J. Bacteriol. 186, 1861–1868 (2004).
Silver, S. & Phung, L. T. A bacterial view of the periodic table: genes and proteins for toxic inorganic ions. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 32, 587-605 (2005).
Barkay, T., Miller, S. M. & Summers, A. O. Bacterial mercury resistance from atoms to ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 27, 355-384 (2003).
Woude, M. W. & Henderson, I. R. Regulation and Function of Ag43 (Flu). Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 62, 153-169 (2008).
Jingping Wang, Zhongming Wu. Simultaneous titration determination of mercury and lead with 1-(2-Pyridylazo)-2-naphthol sulphonic acid as a complexometric indicator. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, Vol. 23. No. 2, 2004, p60-62.
Min Li, Guojun Lian. The effect of TritonX-100-PAN-S as a complexometric titration indicator in determining copper. Guangdong Trace Element Science, Vol.11. No.2, 2004, 56-58.