Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K206000:Characterization"
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==Transfer Function== | ==Transfer Function== | ||
We attempted to find the transfer function relating input concentration of arabinose to PoPS by measuring RFP production in response to varying arabinose concentration. | We attempted to find the transfer function relating input concentration of arabinose to PoPS by measuring RFP production in response to varying arabinose concentration. | ||
| − | [[Image:PBAD strong - Transfer Function. | + | [[Image:PBAD strong - Transfer Function.png|center|frame|Figure 1. Transfer function of <partinfo>K206000</partinfo>. Points represent individual measurements. The line is of a Hill equation fitted to our data.]] |
We fit a Hill equation to the data from our experiment and used it to determine the values listed in our [[#Summary Datasheet|datasheet]]. | We fit a Hill equation to the data from our experiment and used it to determine the values listed in our [[#Summary Datasheet|datasheet]]. | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
==Expression Rate== | ==Expression Rate== | ||
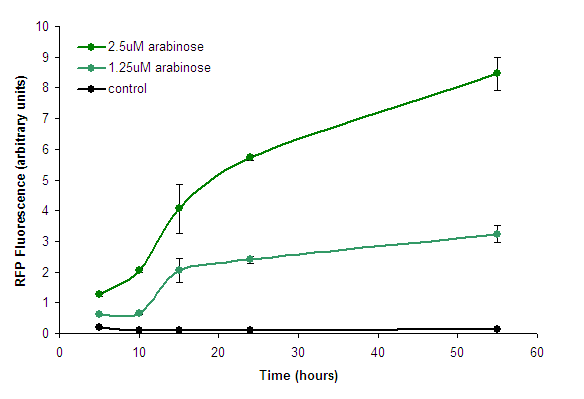
We measured the development of RFP over time, in response to intermediate concentrations of arabinose. | We measured the development of RFP over time, in response to intermediate concentrations of arabinose. | ||
| − | [[Image:PBAD strong - Timecourse. | + | [[Image:PBAD strong - Timecourse.png|center|frame|Figure 2. Fluorescence development after induction with arabinose. Points represent means of 3 separate measurements. Error bars represent the standard deviation. Control measurements were of BW27783 cells lacking the construct.]] |
==Specificity== | ==Specificity== | ||
We investigated the specificity of <partinfo>K206000</partinfo> for its ligand, arabinose, by testing it against several other aldopentoses (except rhamnose, a methyl-pentose). | We investigated the specificity of <partinfo>K206000</partinfo> for its ligand, arabinose, by testing it against several other aldopentoses (except rhamnose, a methyl-pentose). | ||
| − | [[Image:PBAD strong - Specificity. | + | [[Image:PBAD strong - Specificity.png|center|frame|Figure 3. Sugar specificity of <partinfo>K206000</partinfo>. Bars represent individual measurements. Sugars were present at 0.05% w/v except for lyxose which was 0.01% w/v.]] |
==Summary Datasheet== | ==Summary Datasheet== | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
|rowspan="2"|[[#Transfer Function|'''Transfer Function''']] | |rowspan="2"|[[#Transfer Function|'''Transfer Function''']] | ||
|''Hill coefficient'' | |''Hill coefficient'' | ||
| − | |2. | + | |2.26 |
|- | |- | ||
|''Switch Point'' | |''Switch Point'' | ||
| − | |3. | + | |3.14E-6 M L-arabinose, exogenous |
|- | |- | ||
|[[#Expression Rate|'''Rate of Expression''']] | |[[#Expression Rate|'''Rate of Expression''']] | ||
Latest revision as of 03:25, 22 October 2009
All characterization of BBa_K206000 was done using BW27783 cells carrying the construct BBa_K206002. Transfer FunctionWe attempted to find the transfer function relating input concentration of arabinose to PoPS by measuring RFP production in response to varying arabinose concentration. 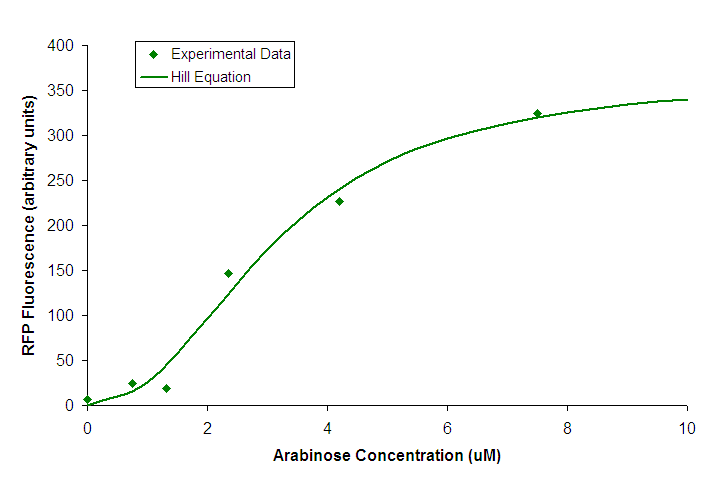 Figure 1. Transfer function of BBa_K206000. Points represent individual measurements. The line is of a Hill equation fitted to our data. We fit a Hill equation to the data from our experiment and used it to determine the values listed in our datasheet.
Expression RateWe measured the development of RFP over time, in response to intermediate concentrations of arabinose. SpecificityWe investigated the specificity of BBa_K206000 for its ligand, arabinose, by testing it against several other aldopentoses (except rhamnose, a methyl-pentose). 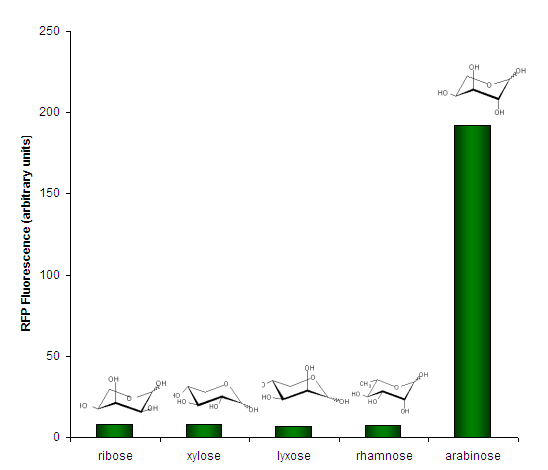 Figure 3. Sugar specificity of BBa_K206000. Bars represent individual measurements. Sugars were present at 0.05% w/v except for lyxose which was 0.01% w/v. Summary Datasheet
1Measured by the UBC iGEM Team 2009 General Characterization Protocols
Sugars were made up to 10% w/v or 500uM stock solutions in water and filter sterilized with a 0.45um filter. RFP fluorescence was measured by pelleting 500uL of cells and resuspending in PBS, then collecting 50000 events on a Becton-Dickinson Influx flow cytometer. Fluorescence was calculated by finding the mean of the RFP histogram for each sample, normalized to OD600 (when possible). |