Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3257003"
| (3 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K3257003 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K3257003 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | This part is lacIq promoter and it can be used to initiate the expression of lacI protein. | + | This part is lacIq promoter and it can be used to initiate the expression of lacI protein. In the lacIq allele, a single base change in the promoter boosts expression of the lacI gene about 10-fold. |
| + | |||
| + | '''Biology''' | ||
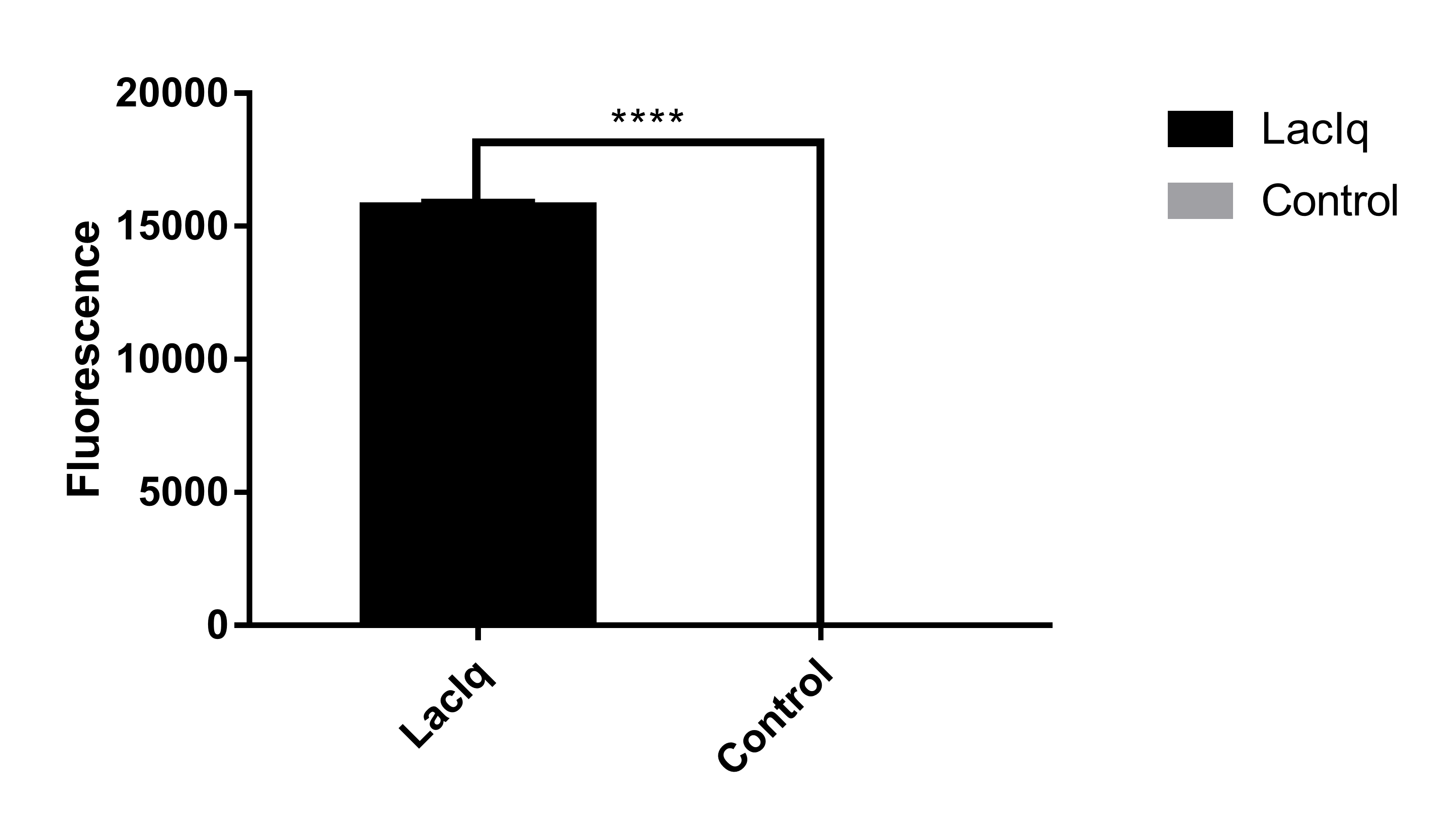
| + | [[File:EGFP with lacIq.tiff|center|400px|thumb|'''Figure 1. The relative fluorescence intensity of EGFP with lacIq promoter measured by 96-well plate reader''' EGFP represents the relative fluorescence intensity of BL21(DE3) transformed with plasmid encoding EGFP protein. The Negative represents the relative fluorescence intensity of BL21(DE3) transformed with plasmid encoding nonsense mutated EGFP protein. Significant difference between them shows that EGFP can be expressed and function well inside E.coli cells.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Contributed Information=== | ||
| + | <p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <strong>Laciq Mutation Outcome:</strong> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | The presence of the lacIq mutation leads to an elevated production of lac repressor compared to the wild-type strain. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | The Iac repressor is a protein that stops the coding of proteins necessary for lactose metabolism. In E Coli, this lactose metabolism is necessary for survival should a more efficient sugar like glucose not be available. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <strong>LacIq Mutation Overview:</strong> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Characterised by a 15 base pair deletion within the lacIq promoter region. | ||
| + | A deletion is a mutation involving the loss of one (or more) nucleotides from a segment of DNA. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Interestingly, it replaces the suboptimal -35 region of the wild-type promoter with a sequence perfectly matching the consensus sequence for the six most crucial base pairs in the -35 region. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <strong>Transcriptional Impact of LacIq Mutation:</strong> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Facilitates an augmented transcription of I mRNA. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Leads to a subsequent increase in the quantity of lac repressor in lacIq strains. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <strong>Induction and Origin of LacIq Mutation:</strong> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | LacIq mutation may have been induced by the usage of nitrosoguanidine, an alkylating agent that acts as a mutagen. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Alternatively, it may have emerged spontaneously during the selection process aimed at enhancing lacI expression. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <strong>Comparison with Wild-Type LacI Promoter:</strong> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Wild-type lacI promoter exhibits a relatively low level of transcription. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | This is due to high levels of guanine-cytosine and the presence of a deficient -35 region that differs from other promoters. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <strong>Effect on Repressor Synthesis:</strong> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | LacIq mutation results in a tenfold elevation in the level of repressor synthesis compared to the wild-type strain. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <strong>U J177 Mutation Impact:</strong> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | U J177 mutation completely terminates the activity of the promoter. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Achieved by removing four base pairs, destroying the homology region at the -10 position. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Aoyama, T., Mituru Takanami, Eiko Ohtsuka, Yoshio Taniyama, Marumoto, R., Sato, H., & Ikehara, M. (1983). Essential structure ofE. colipromoter effect of spacer length between the two consensus sequences on promoter function. Nucleic Acids Research, 11(17), 5855–5864. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/11.17.5855 | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Calos, M. P., & Miller, J. H. (1981). The DNA sequence change resulting from the I Q1mutation, which greatly increases promoter strength. Molecular and General Genetics MGG, 183(3), 559–560. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00268783 | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| − | < | + | </p> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | <span class='h3bb'>'''Sequence and Features'''</span> | |
| − | <span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | + | |
<partinfo>BBa_K3257003 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K3257003 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | ||
Latest revision as of 11:36, 11 October 2023
lacIq Promoter
This part is lacIq promoter and it can be used to initiate the expression of lacI protein. In the lacIq allele, a single base change in the promoter boosts expression of the lacI gene about 10-fold.
Biology
Contributed Information
Laciq Mutation Outcome:
The presence of the lacIq mutation leads to an elevated production of lac repressor compared to the wild-type strain.
The Iac repressor is a protein that stops the coding of proteins necessary for lactose metabolism. In E Coli, this lactose metabolism is necessary for survival should a more efficient sugar like glucose not be available.
LacIq Mutation Overview:
Characterised by a 15 base pair deletion within the lacIq promoter region.
A deletion is a mutation involving the loss of one (or more) nucleotides from a segment of DNA.
Interestingly, it replaces the suboptimal -35 region of the wild-type promoter with a sequence perfectly matching the consensus sequence for the six most crucial base pairs in the -35 region.
Transcriptional Impact of LacIq Mutation:
Facilitates an augmented transcription of I mRNA.
Leads to a subsequent increase in the quantity of lac repressor in lacIq strains.
Induction and Origin of LacIq Mutation:
LacIq mutation may have been induced by the usage of nitrosoguanidine, an alkylating agent that acts as a mutagen.
Alternatively, it may have emerged spontaneously during the selection process aimed at enhancing lacI expression.
Comparison with Wild-Type LacI Promoter:
Wild-type lacI promoter exhibits a relatively low level of transcription.
This is due to high levels of guanine-cytosine and the presence of a deficient -35 region that differs from other promoters.
Effect on Repressor Synthesis:
LacIq mutation results in a tenfold elevation in the level of repressor synthesis compared to the wild-type strain.
U J177 Mutation Impact:
U J177 mutation completely terminates the activity of the promoter.
Achieved by removing four base pairs, destroying the homology region at the -10 position.
Aoyama, T., Mituru Takanami, Eiko Ohtsuka, Yoshio Taniyama, Marumoto, R., Sato, H., & Ikehara, M. (1983). Essential structure ofE. colipromoter effect of spacer length between the two consensus sequences on promoter function. Nucleic Acids Research, 11(17), 5855–5864. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/11.17.5855
Calos, M. P., & Miller, J. H. (1981). The DNA sequence change resulting from the I Q1mutation, which greatly increases promoter strength. Molecular and General Genetics MGG, 183(3), 559–560. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00268783
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
