Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K4140000"
Ahmed Mattar (Talk | contribs) |
Ahmed Mattar (Talk | contribs) |
||
| (23 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Part Description== | ==Part Description== | ||
| − | T7 promoter is a | + | T7 promoter is a DNA sequence that can be recognized by T7 RNA polymerase and is mainly used to regulate gene expression of recombinant proteins, all of which allow it to be used in downstream research approaches. It is considered to be a constitutive promoter with high levels of transcription and expression in the presence of T7 RNAP and minimal interaction with bacterial RNAP. |
==Usage== | ==Usage== | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | <br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
| + | ==Experimental Characterization== | ||
| + | [[File:capture7.png|right|]] | ||
| + | <br><br><br><br><br> | ||
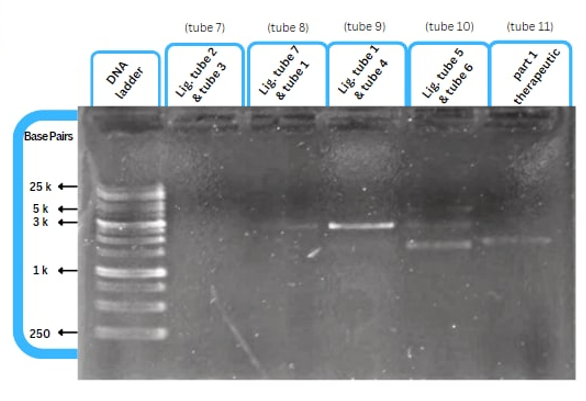
| + | This figure shows an experimental characterization of this part as it's validated through gel electrophoresis as it is in lane 6 (the last one). The running part (ordered from IDT) included T7P - TyrR RBS - TyrR - TyrPromoter. | ||
| + | <br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 11:03, 21 September 2023
T7 promoter
Part Description
T7 promoter is a DNA sequence that can be recognized by T7 RNA polymerase and is mainly used to regulate gene expression of recombinant proteins, all of which allow it to be used in downstream research approaches. It is considered to be a constitutive promoter with high levels of transcription and expression in the presence of T7 RNAP and minimal interaction with bacterial RNAP.
Usage
Because they are not recognized by E. coli RNAP, T7 promoters can generate considerable levels of transcription in E. coli and have the capacity to regulate themselves independently of E. coli promoters. We employ it to regulate TyrR protein expression constitutively in high levels as shown in figure 1.
Literature Characterization
In this study, in comparison to the cytoplasmically-expressing strain, the periplasmic-secreting strain showed faster organophosphorus OPH biocatalytic reaction rates. Additionally, the bacteria under T7 promoter regulation showed faster biocatalytic reaction rates than the strains under Trc promoter regulation, irrespective of the location of OPH inside the cell. The periplasmic-secreting strain's biocatalytic rate was substantially higher with substrate concentrations than the cytoplasmic-expressing strain and showed a 2-fold better conversion rate with 1 mM Paraoxon as shown in figure 2.
Experimental Characterization
This figure shows an experimental characterization of this part as it's validated through gel electrophoresis as it is in lane 6 (the last one). The running part (ordered from IDT) included T7P - TyrR RBS - TyrR - TyrPromoter.
References
1. Kang, D. G., Seo, S. H., Choi, S. S., & Cha, H. J. (2006). Comparison of whole cell biocatalytic reaction kinetics for recombinant Escherichia coli with periplasmic-secreting or cytoplasmic-expressing organophosphorus hydrolase. Studies in surface science and catalysis, 173-176. Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]