Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K4437503"
Mariangrell (Talk | contribs) |
Mariangrell (Talk | contribs) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
<p> The original B0034-FLAG-phasin-HlyA part (BBa_K2260002) was used as a template for this design, and unlike other parts in this collection, the B0034 (BBa_B0034) RBS was also conserved. The restriction enzyme cut sites for BstAPI and BstBI were added at both ends of the part, respectively, making the part compatible for digestion and ligation into the Tokyo Tech 2012 team’s BBa_K934001 plasmid for PHB expression.</p> | <p> The original B0034-FLAG-phasin-HlyA part (BBa_K2260002) was used as a template for this design, and unlike other parts in this collection, the B0034 (BBa_B0034) RBS was also conserved. The restriction enzyme cut sites for BstAPI and BstBI were added at both ends of the part, respectively, making the part compatible for digestion and ligation into the Tokyo Tech 2012 team’s BBa_K934001 plasmid for PHB expression.</p> | ||
| + | [[Image:03constructmap.png|700px|thumb|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <p><i>Figure 1. </i> An overview of the BBa_K4437503 construct map. | ||
| Line 29: | Line 34: | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:figure2gel.png|700px|thumb|center]] |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | <p> <i>Figure | + | <p> <i>Figure 2.</i> Agarose electrophoresis of purified DNA. Lane 1 contains a 2log 1000bp ladder. Lanes 9-13 contain the B0035-FLAG-phasin-HlyA insert in the BBa_K934001 plasmid, transformed in and purified from BL21 <i>E. coli</i>. Lanes 10, 11 and 12 indicate banding at the anticipated range of approximately 7100bp, indicating the successful insertion and transformation of the BBa_K4437503 insert.</p> |
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:figure3sds.png|700px|thumb|center]] |
| Line 48: | Line 50: | ||
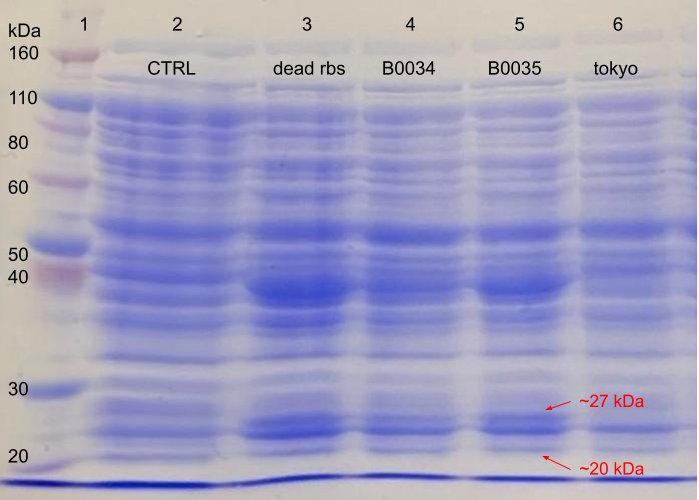
| − | <p><i>Figure | + | <p><i>Figure 3. </i>The expression of RBS-FLAG-phasin-hlyA with varying RBS strengths from the PHB construct (BBa_K934001) from BL21 (DE3) <i>E.coli</i> strain autoinduced for 24 hours. The process was visualised using 10% SDS-PAGE in 100V for 20 minutes and 180V for 40 minutes. The gel was stained with Coomassie blue. The gel was loaded as follows: (1) Ladder, (2) Lanmodulin positive control (BBa_K3945001), (3) Dead RBS upstream of phasin-Hlya in PHB construct (BBa_K4437501), (4) B0034 RBS upstream of phasin-Hlya in PHB construct (BBa_K226003), (5) B0035 upstream of phasin-Hlya in PHB construct (BBa_K4437502), (6) Tokyo 2012 PHB construct only (BBa_K934001). </p> |
| Line 55: | Line 57: | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:figure4absds.png|700px|thumb|center]] |
| Line 62: | Line 64: | ||
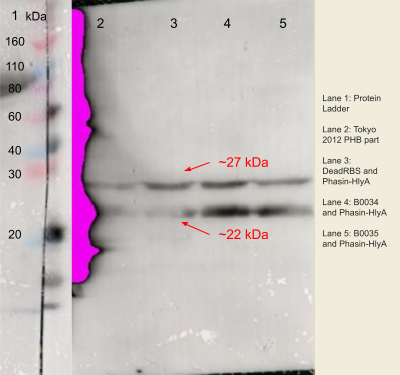
| − | <p><i>Figure | + | <p><i>Figure 4. </i>The expression of phasin-hlyA with varying RBS strengths from the PHB construct (BBa_K934001) from BL21 (DE3) E.coli strain autoinduced for 48 hours on an SDS page using Anti-FLAG antibodies and the complementary capture antibody. The process was visualised using 10% SDS-PAGE in 100V for 20 minutes and 180V for 40 minutes. The gel was loaded as follows: (1) Ladder; (2) Tokyo 2012 PHB construct only (BBa_K934001); (3) B0034 RBS upstream of phasin-HlyA in PHB plasmid (BBa_K4437500); (4)B0034 RBS upstream of phasin-HlyA in PHB construct (BBa_K226002); (5) B0035 upstream of phasin-Hlya in PHB construct (BBa_K4437504).</p> |
Latest revision as of 01:34, 14 October 2022
B0034-FLAG-phasin-HlyA (E. coli)
Usage and Biology
Phasin is an intracellular protein native to PHB-producing bacteria, which coats and stabilises polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) granules in the bacterial cytoplasm, preventing the aggregation of the newly formed polymer [1]. By adding the C-terminus of the HlyA gene to the end of the phasin molecule, the resulting HlyA-tagged phasin molecule -- and the PHB granules to which it is bound -- can be secreted via the single-step Type I secretion system (TISS) in gram-negative bacteria [2]. This part is based directly on the University of Calgary 2017 team’s BBa_K2260002 part, and has been designed to preserve the original RBS (BBa_B0034) as a positive control for experiments comparing the strength of the RBS upstream of the FLAG-phasin-HlyA sequence and resulting phasin-HlyA expression, as well as the subsequent yield of secreted PHB. This positive control provides an important experimental "baseline" against which to compare the yields resulting from other RBS types, and any proposed improvement.
Design
The original B0034-FLAG-phasin-HlyA part (BBa_K2260002) was used as a template for this design, and unlike other parts in this collection, the B0034 (BBa_B0034) RBS was also conserved. The restriction enzyme cut sites for BstAPI and BstBI were added at both ends of the part, respectively, making the part compatible for digestion and ligation into the Tokyo Tech 2012 team’s BBa_K934001 plasmid for PHB expression.
Figure 1. An overview of the BBa_K4437503 construct map.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Characterization
<p> We have successfully amplified the B0034-FLAG-phasin-HlyA part and ligated it into the PHB (BBa_K934001) plasmid. These preliminary confirmations were performed with restriction digests and diagnostic gel electrophoresis. Future directions for the charcterization of this part include its transformation into the BL21 E. coli expression vector, and a subsequent SDS-PAGE and Western blot to confirm the production of phasin. These results will be compared to the phasin expression levels of versions of the part outfitted with weaker RBS types. Finally, in-vitro PHB production assays will be used to quantify resulting yields of secreted PHB.
Figure 2. Agarose electrophoresis of purified DNA. Lane 1 contains a 2log 1000bp ladder. Lanes 9-13 contain the B0035-FLAG-phasin-HlyA insert in the BBa_K934001 plasmid, transformed in and purified from BL21 E. coli. Lanes 10, 11 and 12 indicate banding at the anticipated range of approximately 7100bp, indicating the successful insertion and transformation of the BBa_K4437503 insert.
Figure 3. The expression of RBS-FLAG-phasin-hlyA with varying RBS strengths from the PHB construct (BBa_K934001) from BL21 (DE3) E.coli strain autoinduced for 24 hours. The process was visualised using 10% SDS-PAGE in 100V for 20 minutes and 180V for 40 minutes. The gel was stained with Coomassie blue. The gel was loaded as follows: (1) Ladder, (2) Lanmodulin positive control (BBa_K3945001), (3) Dead RBS upstream of phasin-Hlya in PHB construct (BBa_K4437501), (4) B0034 RBS upstream of phasin-Hlya in PHB construct (BBa_K226003), (5) B0035 upstream of phasin-Hlya in PHB construct (BBa_K4437502), (6) Tokyo 2012 PHB construct only (BBa_K934001).
Figure 4. The expression of phasin-hlyA with varying RBS strengths from the PHB construct (BBa_K934001) from BL21 (DE3) E.coli strain autoinduced for 48 hours on an SDS page using Anti-FLAG antibodies and the complementary capture antibody. The process was visualised using 10% SDS-PAGE in 100V for 20 minutes and 180V for 40 minutes. The gel was loaded as follows: (1) Ladder; (2) Tokyo 2012 PHB construct only (BBa_K934001); (3) B0034 RBS upstream of phasin-HlyA in PHB plasmid (BBa_K4437500); (4)B0034 RBS upstream of phasin-HlyA in PHB construct (BBa_K226002); (5) B0035 upstream of phasin-Hlya in PHB construct (BBa_K4437504).
References
1. Brown B, Immethun C, Wilkins M, Saha R. Biotechnical applications of phasins: Small proteins with large potential. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 2022 Apr 1;158:112129.
2. Thomas S, Holland IB, Schmitt L. The Type 1 secretion pathway — The hemolysin system and beyond. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research. 2014 Aug 1;1843(8):1629–41.