Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1675002"
(→Pasr-glsA (BBa_K4340603)pH maintenance functional test) |
(→genetic pH shooting system (BBa_K4340609) and pET11a empty vector pH maintenance functional test) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
=PuiChing_Macau 2022= | =PuiChing_Macau 2022= | ||
| − | == | + | ==genetic pH shooting system (BBa_K4340609) and pET11a empty vector pH maintenance functional test== |
| − | This | + | This year, PuiChing_Macau improved this part through design it with genetic pH shooting system. The system contains two circuits, an acid shooting circuit (ASC), which is the glsA part with Pasr promoter, and a base shooting circuit (BSC) including ldhA and P-atp2 alkaline promoter. This system improved the usage and efficiency of the original construct. |
| − | + | ===Experiment 1: pH change=== | |
| − | ===1 | + | |
| − | + | [[File:Compare ph glsa phs ph5.jpeg|400px|thumb|center|Figure 1. The pH change of genetic pH shooting system_pET11a and Pasr-glsA-pET11a against empty pET11a vector control in the pH 5 initial environment]] | |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:PHS-pH-6.png|400px|thumb|center|Figure 2. The pH change of genetic pH shooting system_pET11a in the pH 6 initial environment]] | |
| − | + | [[File:Compare ph glsa phs ph7.jpeg|400px|thumb|center|Figure 3. The pH change of genetic pH shooting system_pET11a and Pasr-glsA-pET11a against empty pET11a vector control in the pH 7 initial environment]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:PHS-pH-8.png|400px|thumb|center|Figure 4. The pH change of genetic pH shooting system_pET11a in the pH 8 initial environment]] | |
| − | + | [[File:Compare ph glsa phs ph9.jpeg|400px|thumb|center|Figure 5. The pH change of genetic pH shooting system_pET11a and Pasr-glsA-pET11a against empty pET11a vector control in the pH 9 initial environment]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:PHS 2.png|400px|thumb|center|Photo 1: The pH adjusted LB broth for pH changes test.]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | <p>The pH change of the genetic pH shooting system is larger than the control group (pET11a) in the initial pH 5 environment in the first 5 hours, indicating that the genetic pH shooting system worked to converge the pH to neutral pH level. However, compared with Pasr-glsA, this system has less efficiency in acidic environment adjusting.(Figure 1)</p> | |
| − | + | <p>In the initial pH 6 environment, the convergence of the genetic pH shooting system to neutral pH performed well in the 7th to 9th hours. In the following 15 hours, both the pH levels of the control and genetic pH shooting system group raised to pH 8 due to the possibility of the ammonia generated by the died E.coli. (Figure 2)</p> | |
| − | + | <p>In the initial pH 7 environment, the pH curve of both groups are relatively similar, showing that the system does not function in a pH 7 environment, which conforms to the promoter design (Pasr for acidic environment and P-atp2 for alkaline environment) (Figure 3) </p> | |
| + | |||
| + | <p>In both initial pH 8 and pH 9, the pH level of the genetic pH shooting system drops more than the control group (pET11a). This demonstrated that the base shooting circuit functioned to neutralize the alkaline environment. (Figure 4&5)</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>To sum up, the genetic pH shooting system worked and optimize the Pasr-glsA construct, with an alkaline adjusting system and a stable pH neutralizing ability.</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Experiment 2: OD changes=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:compare_od_glsa_phs_ph5.png|400px|thumb|center|Figure 1. The OD change of genetic pH shooting system_pET11a and Pasr-glsA_pET11a with pET11a (control) in the pH 5 initial environment]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:PHS-OD-6.png|400px|thumb|center|Figure 2. The OD change of genetic pH shooting system_pET11a in the pH 6 initial environment]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:compare_od_glsa_phs_ph7.png|400px|thumb|center|Figure 3. The OD change of genetic pH shooting system_pET11a and Pasr-glsA with pET11a (control) in the pH 7 initial environment]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:PHS-OD-8.png|400px|thumb|center|Figure 4. The OD change of genetic pH shooting system_pET11a in the pH 8 initial environment]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:compare_od_glsa_phs_ph9.png|400px|thumb|center|Figure 5. The OD change of genetic pH shooting system_pET11a and Pasr-glsA with pET11a (control) in the pH 9 initial environment]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>Overall, the OD of the genetic pH shooting system is higher than the Pasr-glsA. This demonstrated that the genetic pH shooting system worked to survive better in an acidic and alkaline environment. Particularly, the OD curve of the pH shooting system is significantly higher than the Pasr-glsA in a pH 9 environment, indicating that the base circuit facilitated the E.coli growth in an alkaline environment. | ||
| + | For the OD change of the genetic pH shooting system, The highest OD value is in the pH 7 environment, followed by pH 8, and pH 9. The OD value of pH 9 is lower than the other pH groups (pH 7, 8, and 9 of the genetic pH shooting system), which shows that the transformed E.coli might not grow as well as E.coli with an empty pET11a vector since it has to produce alkaline.</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Experiment 2: Western blot=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:PHS westernblot.png|600px|thumb|center|Figure 6. Our western blot result shows the protein expression in different pH environments. (glsA for Pasr-glsA, pHS for genetic pH shooting system)]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>The western blot was able to validate the quality of protein expression of glsA and the pH shooting system. In the experiment, there is a clear band of both the pH shooting system and glsA in 20ul samples at 30 kDa. There is a relatively more blended band of the 10ul samples. As predicted, it is clear that the glsA in the pH5 environment expresses the best.</p> | ||
| + | <!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 13:51, 12 October 2022
glsA, glutaminase1
GlsA encodes an acid-activated glutaminase, which is sufficient for an acid resistance system, and it is able to catalyze a reaction converting glutamate to glutamine and releasing the free gaseous ammonia. The free gaseous ammonia will consume the proton and increase the intracellular pH (Fig.1). The robust glutaminase activity only exists at pH 6.0 or lower. The highest activity is obtained at pH 4.0, followed by pH 5.0 and 6.0. In contrast, GlsA is not activated at pH 7.0 and 8.0. The dependence on pH makes it an effective tool to respond when necessary.
Fig.1 The mechanism of GlsA
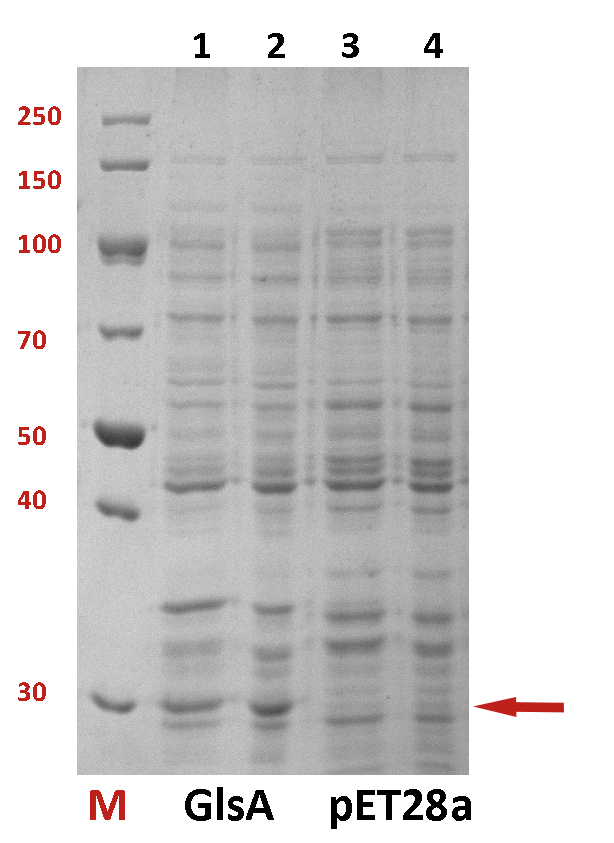
The difference between the testing group and the control group is not evident. We employed a strong promoter T7 to check whether the protein has been expressed. The functional gene GlsA was constructed on plasmid pET28a and the plasmid was transformed into BL21(DE3). 0.5% IPTG was added to induce the expression of the protein. The following is the picture of SDS-PAGE (Fig.2). It shows that our target protein has been expressed successfully.
Fig.2 The SDS-PAGE of GlsA and pET28a
Characterization from SCUT_China 2019:
GlsA is an acid tolerant factor also named ybaS which has a great influence on the acid resistance of the strain. SCUT_China 2019 have expressed this gene and tested their influence on the acid tolerance of E.coli MG1655-T7 RNAP (MGR). T7 RNA polymerase was integrated into the genome of E. coli MG1655(MG) by SCUT_China 2019 to test their VerProS system.
The functional gene ybaS was constructed on plasmid pET30a(+) and the plasmid was transformed into MGR. IPTG(0.2 mM) was added to induce the expression of the protein. Inoculated the MGR with pET30a(+)-ybaS in 10ML LB medium,37 ℃,250rpm for 12 hours,and then 1:100 transferred it to 12.5ml medium with IPTG (0.2 mM) for 18 hours. The following is the picture of SDS-PAGE (Fig.3) which shows that target protein has been expressed successfully.
Fig.3 The SDS-PAGE of gadB and ybaS
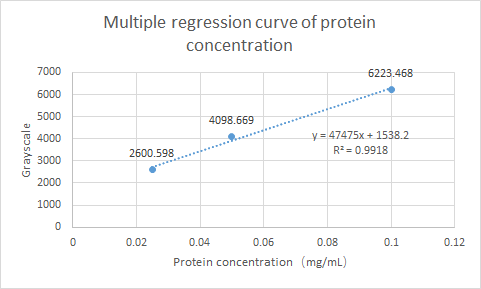
What’s more, SCUT_China 2019 have tested the Protein expression of ybaS. Using ImageJ for gray scale comparison, the multiple regression curve was drawn with the BSA of 0.0125m to 0.1m as the reference, as follow figure:
Fig.4 Multiple regression curve of protein concentration
Finally, the expression of ybaS was calculated as 0.0665 mg/ml.
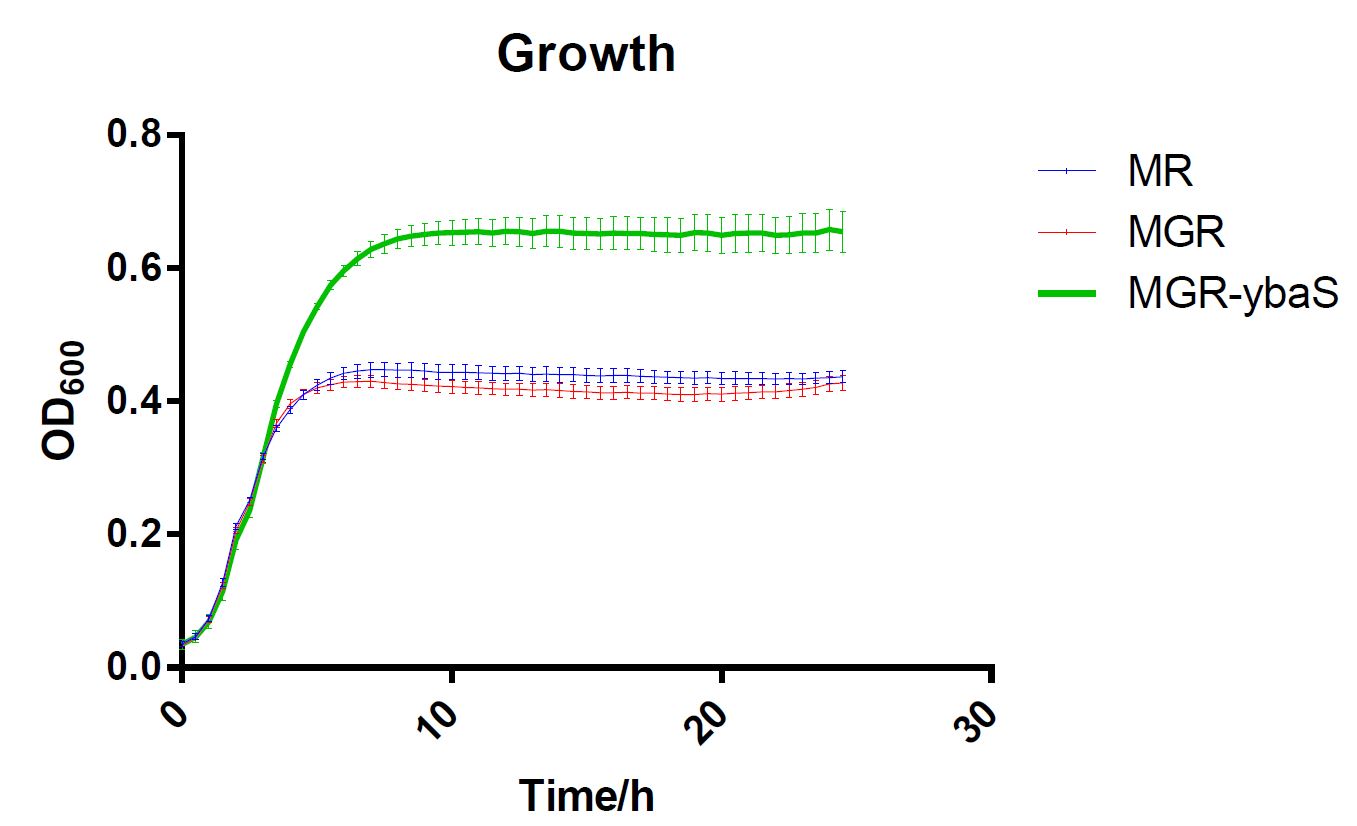
The last, SCUT_China 2019 have tested its influence on the acid tolerance of MGR. MG, MGR and MGR expressing ybaS were grown overnight (about 16 h) in LBG medium of pH 7.0 at 37 °C. The cultures were then diluted to initial OD600 0.05 in 300 μL LBG medium of pH 7.0, LBG medium acidified by HCl or succinic acid to pH 4.5. Then the cultures were incubated at 37 °C in 100-well Honeycomb microplates using an automated turbidimeter (Bioscreen C, Oy Growth Curves Ab Ltd., Helsinki, Finland) for online monitoring of OD600 for 24 h. A growth assay under moderate acid stress were performed to investigate the effect of overexpression ybaS or not on acid tolerance. Under moderate acid stress, the final OD600 value of strain MGR-ybaS(the strain overexpressing ybaS) was 53% higher than that of the wild type strain (MG) (Fig. 5).
Fig.5 Growth of strains MG,MGR and MGR-ybaS under acid stress.
PuiChing_Macau 2022
genetic pH shooting system (BBa_K4340609) and pET11a empty vector pH maintenance functional test
This year, PuiChing_Macau improved this part through design it with genetic pH shooting system. The system contains two circuits, an acid shooting circuit (ASC), which is the glsA part with Pasr promoter, and a base shooting circuit (BSC) including ldhA and P-atp2 alkaline promoter. This system improved the usage and efficiency of the original construct.
Experiment 1: pH change
The pH change of the genetic pH shooting system is larger than the control group (pET11a) in the initial pH 5 environment in the first 5 hours, indicating that the genetic pH shooting system worked to converge the pH to neutral pH level. However, compared with Pasr-glsA, this system has less efficiency in acidic environment adjusting.(Figure 1)
In the initial pH 6 environment, the convergence of the genetic pH shooting system to neutral pH performed well in the 7th to 9th hours. In the following 15 hours, both the pH levels of the control and genetic pH shooting system group raised to pH 8 due to the possibility of the ammonia generated by the died E.coli. (Figure 2)
In the initial pH 7 environment, the pH curve of both groups are relatively similar, showing that the system does not function in a pH 7 environment, which conforms to the promoter design (Pasr for acidic environment and P-atp2 for alkaline environment) (Figure 3)
In both initial pH 8 and pH 9, the pH level of the genetic pH shooting system drops more than the control group (pET11a). This demonstrated that the base shooting circuit functioned to neutralize the alkaline environment. (Figure 4&5)
To sum up, the genetic pH shooting system worked and optimize the Pasr-glsA construct, with an alkaline adjusting system and a stable pH neutralizing ability.
Experiment 2: OD changes
Overall, the OD of the genetic pH shooting system is higher than the Pasr-glsA. This demonstrated that the genetic pH shooting system worked to survive better in an acidic and alkaline environment. Particularly, the OD curve of the pH shooting system is significantly higher than the Pasr-glsA in a pH 9 environment, indicating that the base circuit facilitated the E.coli growth in an alkaline environment. For the OD change of the genetic pH shooting system, The highest OD value is in the pH 7 environment, followed by pH 8, and pH 9. The OD value of pH 9 is lower than the other pH groups (pH 7, 8, and 9 of the genetic pH shooting system), which shows that the transformed E.coli might not grow as well as E.coli with an empty pET11a vector since it has to produce alkaline.
Experiment 2: Western blot
The western blot was able to validate the quality of protein expression of glsA and the pH shooting system. In the experiment, there is a clear band of both the pH shooting system and glsA in 20ul samples at 30 kDa. There is a relatively more blended band of the 10ul samples. As predicted, it is clear that the glsA in the pH5 environment expresses the best.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]