Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K4365022"
Svetlana ia (Talk | contribs) (→Characterization of the pSB1KY in comparison to the p426 shuttle vector) |
Svetlana ia (Talk | contribs) (→Characterization of the pSB1KY in comparison to the p426 shuttle vector) |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
[[File:BBa_K4365022_plasmid_design.png|700px|center|thumb|Figure . '''A''' Plasmid map of the pSB1KY-URA3 shuttle plasmid. Its size after removal of the RFP device (BBa_J04550) is ~4.7 kb. '''B''' Plasmid map of the p426 shuttle plasmid. Its size is ~5.6 Kb. Created with Snapgene.]] | [[File:BBa_K4365022_plasmid_design.png|700px|center|thumb|Figure . '''A''' Plasmid map of the pSB1KY-URA3 shuttle plasmid. Its size after removal of the RFP device (BBa_J04550) is ~4.7 kb. '''B''' Plasmid map of the p426 shuttle plasmid. Its size is ~5.6 Kb. Created with Snapgene.]] | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | + | [[File:BBa_K4365022_growth_rate.png|300px|thumb|Figure 1: growth rates of yeast cells transformed with the new pSB1KY and the p426 shuttle plasmids.]] | |
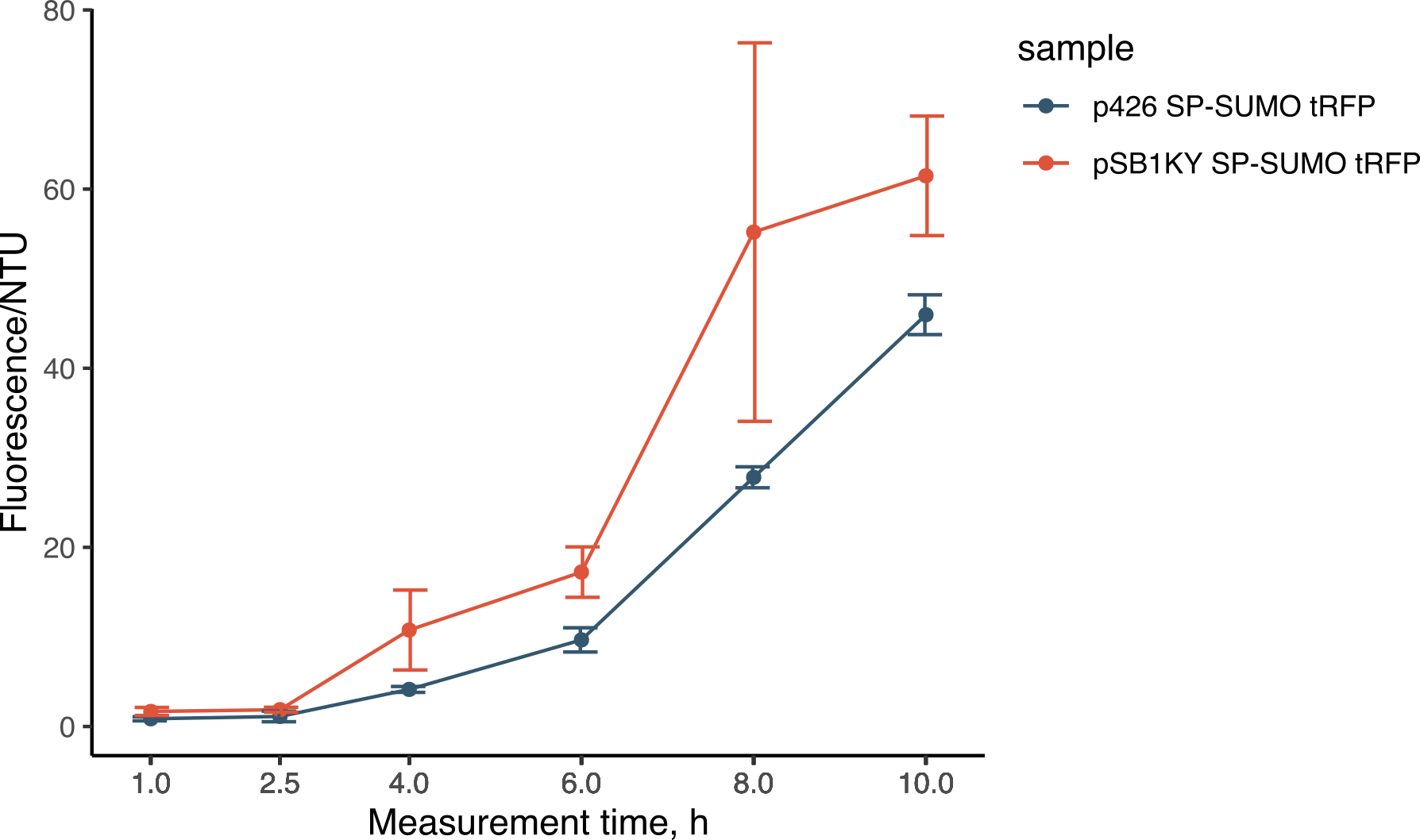
| + | [[File:BBa_K4365022_fluo.png|300px|thumb|Figure. fluorescence development normalized over nephelometric turbidity units of the expression and secretion of SP-SUMO from the p426 and the new pSB1KY.]] | ||
To understand whether the new functionalities introduced into the pSB1K were suitable for subsequent experiments, we compared the growth curves of the pSB1KY-transformed yeast cells and p426-transformed ones expressing turboRFP. Two main cultures were adjusted to 1 OD in 20 ml of MV medium in flasks and, after 12 hr, their growth rates were monitored using a spectrophotometer. | To understand whether the new functionalities introduced into the pSB1K were suitable for subsequent experiments, we compared the growth curves of the pSB1KY-transformed yeast cells and p426-transformed ones expressing turboRFP. Two main cultures were adjusted to 1 OD in 20 ml of MV medium in flasks and, after 12 hr, their growth rates were monitored using a spectrophotometer. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
From the plots of the growth rates (Figure 8) we were able to observe that the new pSB1KY performs just as well as the widely used p426 shuttle plasmid [1]. | From the plots of the growth rates (Figure 8) we were able to observe that the new pSB1KY performs just as well as the widely used p426 shuttle plasmid [1]. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
During the experiments for the creation of the SP-SUMO tag for protein production in yeast (read more about it here), we were once again able to compare the two plasmids. Both the p426 and the new pSB1KY were used to express the SP-SUMO device aminoterminally fused to the turboRFP fluorescent protein. This construct allowed the protein to be secreted in the medium and we were able to measure the development of fluorescence. The fluorescence intensity in the medium normalized over growth (expressed in nephelometric turbidity units) (Figure 9) showed that the pSB1KY is able to produce and secrete larger quantities of turboRFP. This was observed in two other experiments (data not shown) and seems to indicate that the pSB1KY allows for higher protein production. | During the experiments for the creation of the SP-SUMO tag for protein production in yeast (read more about it here), we were once again able to compare the two plasmids. Both the p426 and the new pSB1KY were used to express the SP-SUMO device aminoterminally fused to the turboRFP fluorescent protein. This construct allowed the protein to be secreted in the medium and we were able to measure the development of fluorescence. The fluorescence intensity in the medium normalized over growth (expressed in nephelometric turbidity units) (Figure 9) showed that the pSB1KY is able to produce and secrete larger quantities of turboRFP. This was observed in two other experiments (data not shown) and seems to indicate that the pSB1KY allows for higher protein production. | ||
Revision as of 11:39, 11 October 2022
pSB1KY-URA3
backbone for shuttle vector. It is compatible with RFC1000 standart.
Sequence and Features
- 10INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]Plasmid lacks a prefix.
Plasmid lacks a suffix.
Illegal EcoRI site found at 4632
Illegal XbaI site found at 473
Illegal SpeI site found at 1481
Illegal PstI site found at 12 - 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Plasmid lacks a prefix.
Plasmid lacks a suffix.
Illegal EcoRI site found at 4632
Illegal SpeI site found at 1481
Illegal PstI site found at 12
Illegal NotI site found at 2554 - 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Plasmid lacks a prefix.
Plasmid lacks a suffix.
Illegal EcoRI site found at 4632
Illegal BamHI site found at 108
Illegal XhoI site found at 3482
Illegal XhoI site found at 4508 - 23INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]Plasmid lacks a prefix.
Plasmid lacks a suffix.
Illegal EcoRI site found at 4632
Illegal XbaI site found at 473
Illegal SpeI site found at 1481
Illegal PstI site found at 12 - 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Plasmid lacks a prefix.
Plasmid lacks a suffix.
Illegal EcoRI site found at 4632
Illegal XbaI site found at 473
Illegal SpeI site found at 1481
Illegal PstI site found at 12 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Plasmid lacks a prefix.
Plasmid lacks a suffix.
Illegal SapI site found at 4638
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 5
Usage and Biology
Characterization of the pSB1KY in comparison to the p426 shuttle vector
To understand whether the new functionalities introduced into the pSB1K were suitable for subsequent experiments, we compared the growth curves of the pSB1KY-transformed yeast cells and p426-transformed ones expressing turboRFP. Two main cultures were adjusted to 1 OD in 20 ml of MV medium in flasks and, after 12 hr, their growth rates were monitored using a spectrophotometer.
From the plots of the growth rates (Figure 8) we were able to observe that the new pSB1KY performs just as well as the widely used p426 shuttle plasmid [1].
During the experiments for the creation of the SP-SUMO tag for protein production in yeast (read more about it here), we were once again able to compare the two plasmids. Both the p426 and the new pSB1KY were used to express the SP-SUMO device aminoterminally fused to the turboRFP fluorescent protein. This construct allowed the protein to be secreted in the medium and we were able to measure the development of fluorescence. The fluorescence intensity in the medium normalized over growth (expressed in nephelometric turbidity units) (Figure 9) showed that the pSB1KY is able to produce and secrete larger quantities of turboRFP. This was observed in two other experiments (data not shown) and seems to indicate that the pSB1KY allows for higher protein production.