Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K4035008"
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| − | This protein is made of two copies of the yeast copper | + | This protein is made of two copies of the yeast copper metallothionein protein, CUP1 ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_M45090 BBa_M45090]), linked together by a semi-rigid linker made of the GGGGS(EAAAK)2GGGGS amino acid sequence. |
==Usage and Biology== | ==Usage and Biology== | ||
| − | Copper metallothionein CUP1 ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_M45090 BBa_M45090]) is a protein responsible for copper binding in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In order to increase the copper retrieval efficiency, two copies of CUP1 have been linked together by the GGGGS(EAAAK)2GGGGS aa sequence. This linker is composed of two flexible regions GGGGS separated by two rigid region EAAAK, making the linker rigid in the center with 2 flexible arms attached to the CUP1 proteins. This allows to maintain a net distance between the two proteins, avoiding their interaction and incorrect folding, and at the same time allowing several degrees of freedom and preserving the correct biological activity. This fusion protein was expressed on the outer membrane of S. cerevisiae by insertion of this part sequence into the | + | Copper metallothionein CUP1 ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_M45090 BBa_M45090]) is a protein responsible for copper binding in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In order to increase the copper retrieval efficiency, two copies of CUP1 have been linked together by the GGGGS(EAAAK)2GGGGS aa sequence. This linker is composed of two flexible regions GGGGS separated by two rigid region EAAAK, making the linker rigid in the center with 2 flexible arms attached to the CUP1 proteins. This allows to maintain a net distance between the two proteins, avoiding their interaction and incorrect folding, and at the same time allowing several degrees of freedom and preserving the correct biological activity. This fusion protein was expressed on the outer membrane of S. cerevisiae by insertion of this part sequence into the pCTcon2-V5 plasmid (1). The expression system ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K4035015 BBa_K4035015]) consists of fusing the dimer on a yeast surface display (1) under the control of the Gal1 promoter. This results in the production of a fusion protein Aga2-CUP1-GGGGS(EAAAK)2GGGGS-CUP1-V5. |
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
[[File:BBa_K4035008_WEB_image_1.jpg|400px|thumb|right|'''Figure 1''' : V5 tagged CUP1 dimer expression in the yeast S.cerevisiae]] | [[File:BBa_K4035008_WEB_image_1.jpg|400px|thumb|right|'''Figure 1''' : V5 tagged CUP1 dimer expression in the yeast S.cerevisiae]] | ||
| − | In order to characterize the protein expression, two experiments were performed, the first being a Western Blot analysis. After having transformed the EBY100 yeast with our newly formed plasmid | + | In order to characterize the protein expression, two experiments were performed, the first being a Western Blot analysis. After having transformed the EBY100 yeast with our newly formed plasmid pCTcon2-dimer-V5, we analyzed its protein expression. For control we also tested the wild type yeast (untransformed) as well as a transformed yeast with the plasmid backbone (without insert) in SGCAA, a medium containing galactose allowing for protein expression through the activation of the Gal1 promoter. As the plasmid contains a Gal1 promoter, the system can only be expressed in the presence of galactose. |
| − | '''Figure 1''' : The first lane (E2) is the yeast transformed with our plasmid containing the CUP1 dimer and the second and third lanes are, respectively, plasmid backbone and wild type yeast. EBY100 is the wild type yeast and serves as a negative control whereas | + | '''Figure 1''' : The first lane (E2) is the yeast transformed with our plasmid containing the CUP1 dimer and the second and third lanes are, respectively, plasmid backbone and wild type yeast. EBY100 is the wild type yeast and serves as a negative control whereas pCTcon2-V5 is the transformed yeast with only the plasmid backbone and serves as a positive control. |
Wild type yeast shows no presence of the V5 tag, as expected, while plasmid backbone has signal which proves that our system is expressed in the transformed yeast when induced with galactose. Our transformed yeast with the Aga2-CUP1-linker-CUP1-V5 protein also shows expression of the system. | Wild type yeast shows no presence of the V5 tag, as expected, while plasmid backbone has signal which proves that our system is expressed in the transformed yeast when induced with galactose. Our transformed yeast with the Aga2-CUP1-linker-CUP1-V5 protein also shows expression of the system. | ||
| Line 108: | Line 108: | ||
| − | === | + | ===Copper Absorption=== |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | To finally test our system we designed an experiment to measure how much copper our transformed yeast could absorb. We cultured different yeast strains in a medium containing a defined initial concentration of copper and collected samples at different time points to measure their copper concentration. The detailed protocol can be found [ here]. | |
| − | + | We compared the dimerized CUP1 (pCTcon2-CUP1-dimer7-V5) with the wild type yeast. | |
| − | + | Wild type yeasts (EBY100) absorbed copper well. However, we were not able to make our engineered yeast work ('''Figure 4'''). | |
| − | + | ||
| − | ''' | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | [[File:BBa_K4035004_CA_image_4.jpg|400px|thumb|left|'''Figure 4''' : Copper absorption by S.cerevisiae]] | ||
<!-- Uncomment this to enable Functional Parameter display | <!-- Uncomment this to enable Functional Parameter display | ||
===Functional Parameters=== | ===Functional Parameters=== | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K4035008 parameters</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K4035008 parameters</partinfo> | ||
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
Latest revision as of 01:03, 22 October 2021
Dimerization of the copper metallothionein 1 : CUP1-GGGGS(EAAAK)2GGGGS-CUP1
This protein is made of two copies of the yeast copper metallothionein protein, CUP1 (BBa_M45090), linked together by a semi-rigid linker made of the GGGGS(EAAAK)2GGGGS amino acid sequence.
Usage and Biology
Copper metallothionein CUP1 (BBa_M45090) is a protein responsible for copper binding in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In order to increase the copper retrieval efficiency, two copies of CUP1 have been linked together by the GGGGS(EAAAK)2GGGGS aa sequence. This linker is composed of two flexible regions GGGGS separated by two rigid region EAAAK, making the linker rigid in the center with 2 flexible arms attached to the CUP1 proteins. This allows to maintain a net distance between the two proteins, avoiding their interaction and incorrect folding, and at the same time allowing several degrees of freedom and preserving the correct biological activity. This fusion protein was expressed on the outer membrane of S. cerevisiae by insertion of this part sequence into the pCTcon2-V5 plasmid (1). The expression system (BBa_K4035015) consists of fusing the dimer on a yeast surface display (1) under the control of the Gal1 promoter. This results in the production of a fusion protein Aga2-CUP1-GGGGS(EAAAK)2GGGGS-CUP1-V5.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 391
Characterization
Expression of the protein in S.cerevisiae
Western Blot Analysis
In order to characterize the protein expression, two experiments were performed, the first being a Western Blot analysis. After having transformed the EBY100 yeast with our newly formed plasmid pCTcon2-dimer-V5, we analyzed its protein expression. For control we also tested the wild type yeast (untransformed) as well as a transformed yeast with the plasmid backbone (without insert) in SGCAA, a medium containing galactose allowing for protein expression through the activation of the Gal1 promoter. As the plasmid contains a Gal1 promoter, the system can only be expressed in the presence of galactose.
Figure 1 : The first lane (E2) is the yeast transformed with our plasmid containing the CUP1 dimer and the second and third lanes are, respectively, plasmid backbone and wild type yeast. EBY100 is the wild type yeast and serves as a negative control whereas pCTcon2-V5 is the transformed yeast with only the plasmid backbone and serves as a positive control.
Wild type yeast shows no presence of the V5 tag, as expected, while plasmid backbone has signal which proves that our system is expressed in the transformed yeast when induced with galactose. Our transformed yeast with the Aga2-CUP1-linker-CUP1-V5 protein also shows expression of the system.
We can see that we have two bands on the gel, one is approximately 30 kDa which is the size of the fusion protein Aga2-CUP1-linker-CUP1-V5 and the other is slightly smaller. The smaller band could be a truncated version of the protein since we identified a second in-frame start codon in the DNA sequence.
The presence of our CUP1 dimer in our yeast transformants is thus shown.
Immunocytochemistry Assay
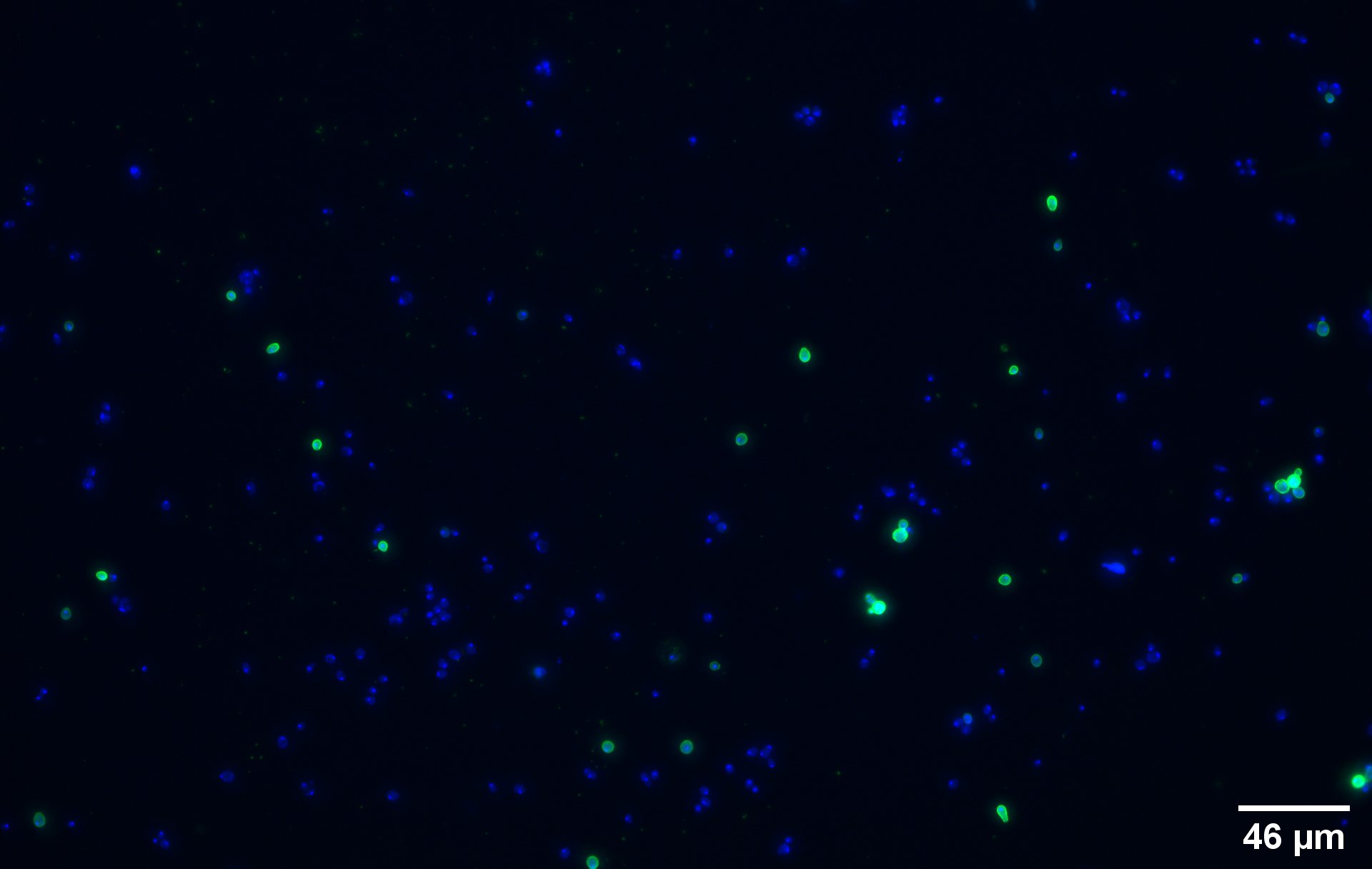
To show that the fusion protein is expressed at the membrane of the cell we performed an Immunocytochemistry assay. The cells were incubated with a primary mouse anti-V5 antibody as well as with a secondary goat anti-mouse couple with Alexa Fluor 488. The same strains for control have been used namely, plasmid backbone induced (Figure 2c) and wild type yeast (Figure 2d).
The nuclei have been stained with DAPI and are depicted in blue on the figures. The green disks are representing the transformed yeast cells expressing the CUP1 dimer at their surface (Figure 2a).
Due to the more intense circle we can clearly see that our system is expressed on the membrane of the protein (better seen on Figure 2b which is a higher magnification picture of yeast transformed with a single copy of CUP1, part BBa_K4035001).
We can also remark that not all the cells are expressing the system. This is because the expression is not 100% efficient, concordant to the published expression system (1).
On the negative control, the little green signal we see is background noise or nonspecific antibody binding.

Copper Absorption
To finally test our system we designed an experiment to measure how much copper our transformed yeast could absorb. We cultured different yeast strains in a medium containing a defined initial concentration of copper and collected samples at different time points to measure their copper concentration. The detailed protocol can be found [ here].
We compared the dimerized CUP1 (pCTcon2-CUP1-dimer7-V5) with the wild type yeast.
Wild type yeasts (EBY100) absorbed copper well. However, we were not able to make our engineered yeast work (Figure 4).