Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3457009"
(→Contribution) |
(→Contribution) |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K3457009 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K3457009 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | <p>This biological is the CDS sequence of Cytosolic-abundant heat soluble protein 89226, also called CAHS 89226. It is a kind of Tardigrade intrinsically Disordered Protein (TDP). It is a heat soluble protein found from Tardigrade <i>Hypsibius dujardini</i> in 2017 <sup>[1]</sup>. Tardigrade, also called water bear, is a kind of tenacious organism. It can survive extreme environment, such as desiccation, freeze and vacuum. The super capacity of Tardigrade partially owes to TDPs. CAHS 89226 has been proven to protect the activity of purified proteins <sup>[1]</sup>. Here we found that expressing this protein can help bacteria survive the freeze-drying process and then the resultant dry bacteria powder can be stored for a long time at room temperature. </p> | + | <p> This biological part is the CDS sequence of Cytosolic-abundant heat soluble protein 89226, also called CAHS 89226. It is a kind of Tardigrade intrinsically Disordered Protein (TDP). It is a heat soluble protein found from Tardigrade <i>Hypsibius dujardini</i> in 2017 <sup>[1]</sup>. Tardigrade, also called water bear, is a kind of tenacious organism. It can survive extreme environment, such as desiccation, freeze and vacuum. The super capacity of Tardigrade partially owes to TDPs. CAHS 89226 has been proven to protect the activity of purified proteins <sup>[1]</sup>. Here we found that expressing this protein can help bacteria survive the freeze-drying process and then the resultant dry bacteria powder can be stored for a long time at room temperature. </p> |
===Contribution=== | ===Contribution=== | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
<h3><b>Author: Yixian Yang</b></h3> | <h3><b>Author: Yixian Yang</b></h3> | ||
<h3><b>Design</b></h3> | <h3><b>Design</b></h3> | ||
| − | [[File:T--QHFZ-China-- | + | [[File:T--QHFZ-China--89226 basic design.png|400px|thumb|left|Figure 1. The Schematic cartoon of the DNA construct of BBa_K3457009.]] |
| − | <p style="clear:left;">This part is the CDS of CAHS 89226. We obtained the sequence from the research paper in 2017 <sup>[1]</sup>. | + | <p style="clear:left;"> This biological part is the CDS sequence of Cytosolic-abundant heat soluble protein 89226, also called CAHS 89226. It is a kind of Tardigrade intrinsically Disordered Protein (TDP). It is a heat soluble protein found from Tardigrade <i>Hypsibius dujardini</i> in 2017 <sup>[1]</sup>. Tardigrade, also called water bear, is a kind of tenacious organism. It can survive extreme environments, such as desiccation, freeze, and vacuum. The super capacity of Tardigrade partially owes to TDPs. CAHS 89226 has been proven to protect the activity of purified proteins <sup>[1]</sup>. Here we found that expressing this protein can help bacteria survive the freeze-drying process, and then the resultant dry bacteria powder can be stored for a long time at room temperature. |
| + | This part is the CDS of CAHS 89226. We obtained the sequence from the research paper in 2017 <sup>[1]</sup>. With the help of a company, we optimized the sequence so that the part is suitable to work in <i>E. coli</i>, and there is no biobrick restriction enzyme cutting site in it. Moreover, we added a 6x His tag at the N-terminal of CAHS 89226, so it can be easily detected by Western Blot and be purified by Ni-chelating affinity chromatography (Fig.1). This year, the part is used in the composite part [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3457032 BBa_K3457032] | ||
| + | </p> | ||
<h3><b>Documentation:</b></h3> | <h3><b>Documentation:</b></h3> | ||
<h4><b>Introduction: </b></h4> | <h4><b>Introduction: </b></h4> | ||
| − | <p style="clear:left;">This year, we tried to introduce a new | + | <p style="clear:left;"> This year, we tried to introduce a new bio preservation method. We used freeze-drying to make the engineered into dry powder. Then the powder can be stored at room temperature for a long time. This method can store bacteria get rid of ultra-low temperature freezer to promote the practical application of engineered bacteria out of the laboratory. However, the stresses during freeze-drying and subsequent dry storage, including freeze, dry, and vacuum, are lethal to bacteria. We use TDPs, including CAHS 89226, to help bacteria survive the situation.</p> |
<h4><b>Protocol: </b></h4> | <h4><b>Protocol: </b></h4> | ||
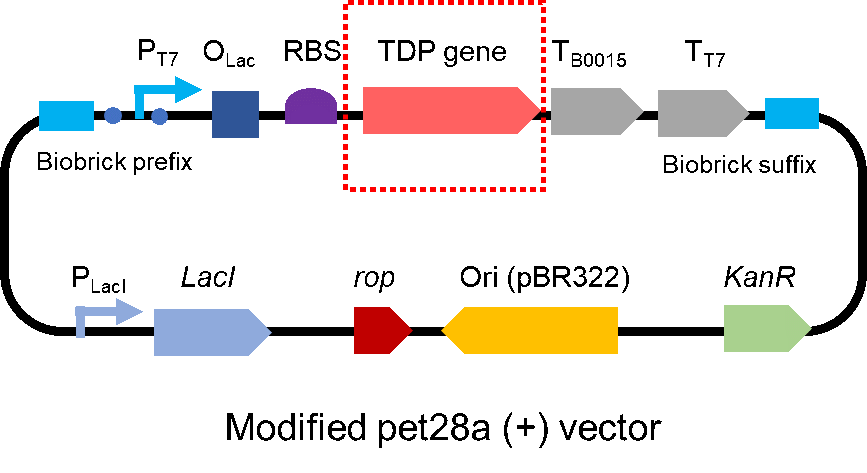
| − | <p style="clear:left;">To test the effect of CAHS 89226, we modified a frequently and widely used vector, pet28a+ and put this part into it (Fig. 2). Then we transformed the plasmid into <i>E. coli</i> BL21 strain. </p> | + | <p style="clear:left;"> To test the effect of CAHS 89226, we modified a frequently and widely used vector, pet28a+, and put this part into it (Fig. 2). Then we transformed the plasmid into <i>E. coli</i> BL21 strain. </p> |
| − | [[File:T--QHFZ-China-- | + | [[File:T--QHFZ-China--pet28am.png|400px|thumb|left|Figure 2. The Schematic cartoon of the vector.]] |
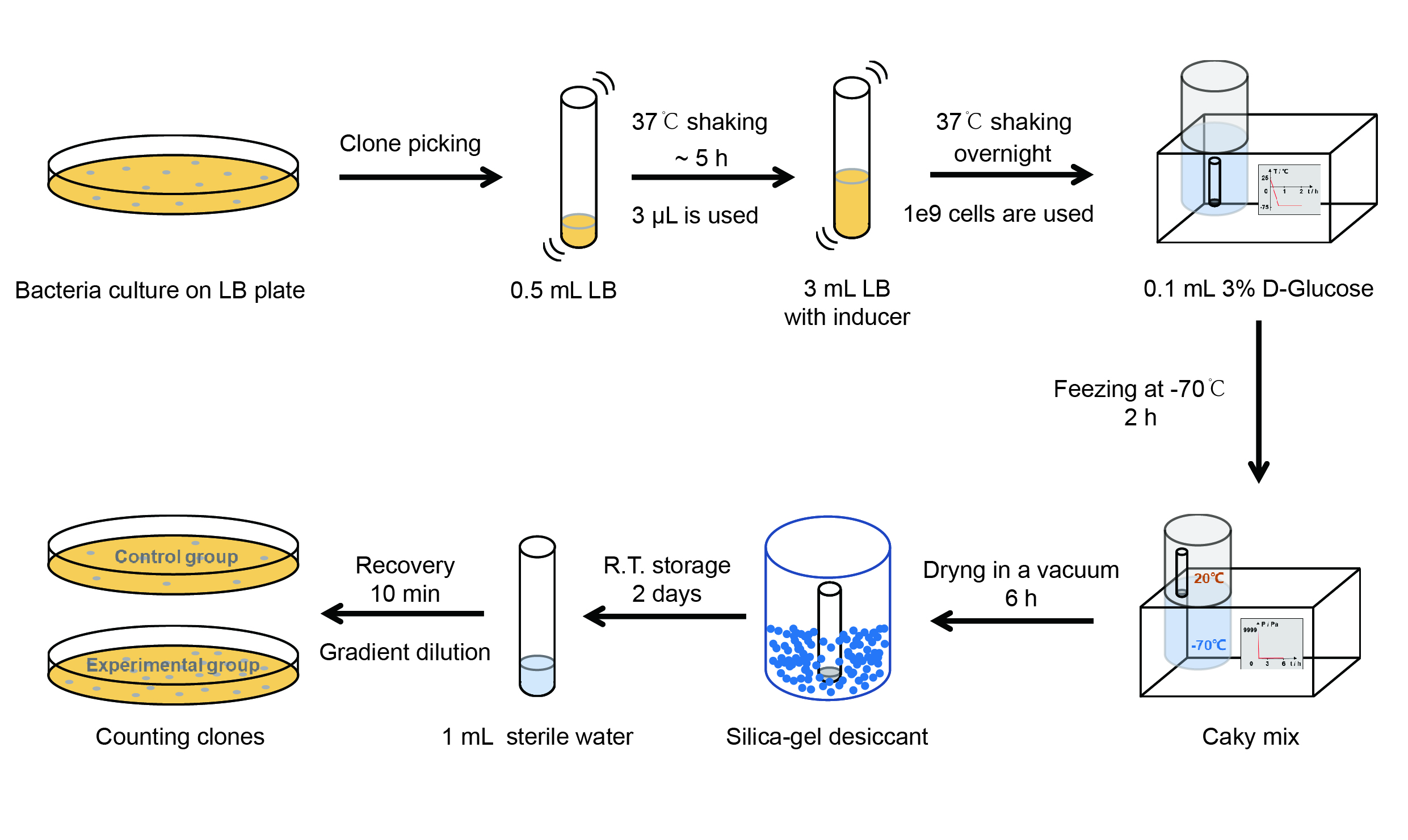
| − | <p style="clear:left;">Then we used the following protocols to verify its function (Fig. 3): </p> | + | <p style="clear:left;"> Then we used the following protocols to verify its function (Fig. 3): </p> |
| − | [[File:T--QHFZ-China-- | + | [[File:T--QHFZ-China--freeze-dry protocol.jpg|400px|thumb|left|Figure 3. Experiment protocol.]] |
<p style="clear:left;"> | <p style="clear:left;"> | ||
| − | 【Day 1】Induction culture | + | 【Day 1】Induction culture<br> |
| − | (1) Pick clones which are in good condition and put them into 500 μL LB medium | + | (1) Pick clones which are in good condition and put them into 500 μL LB medium containing antibiotics. Shake them to grow at 37℃ for 5~7 hours until the bacteria solution becomes turbid. <br> |
| − | (2) Add iPTG into | + | (2) Add 2 mM iPTG into 3 mL LB medium containing antibiotics. Add 3 μL of the bacteria solution mentioned in step 1 to dilute the bacteria by the ratio of 1:1000. Shake the solution to grow the bacteria at 37℃ overnight.<br> |
| − | 【Day 2】Freeze-dried | + | 【Day 2】Freeze-dried<br> |
| − | (1) If | + | (1) If fluorescence induced by the iPTG is detectable in the control group (GFP), continue conducting the experiment.<br> |
| − | (2) Use spectrophotometer to measure the | + | (2) Use spectrophotometer to measure the OD<sub>600</sub> of the bacteria solution, OD<sub>600</sub> = 1 equals to 10<sup>9</sup> cells. If the OD<sub>600</sub> value is between 0.1 and 1, There is a linear relationship between OD<sub>600</sub> and bacterial density. Calculate the volume of bacterial solution for 10<sup>9</sup> cells by using the formula V = 100 / (OD<sub>600</sub> × Dilution ratio).<br> |
| − | (3) | + | (3) Take out a measured amount of 10<sup>9</sup> cells and centrifuge it at 8000 rpm for 3 min. Then pour out the supernatant.<br> |
| − | (4) | + | (4) Re-suspend the bacteria in a 15 mL tube with pre-refrigerated 100 μL 3% glucose solution.<br> |
| − | (5) Take off the cover and put the bacteria into | + | (5) Take off the cover of the tube and put the bacteria into the cold trap. Open the compressor of the lyophilization machine and freeze the shake tube for 2 h at -70℃.<br> |
| − | (6) | + | (6) Put the caky bacteria solution into the drying chamber of the lyophilization machine. Open the vacuum pump to dry it in vacuum for 6h at 1 Pa vacuum degree.<br> |
| − | (7) Turn off the vacuum pump | + | (7) Turn off the vacuum pump, place it at seal box filled with silica-gel desiccant a for 2 days at room temperature.<br> |
| − | 【Day 3】Room temperature storage | + | 【Day 3】Room temperature storage<br> |
| − | 【Day 4】Detect the survival rate | + | 【Day 4】Detect the survival rate<br> |
| − | (1) Add 1 | + | (1) Add 1 mL of sterile water to the tube, vortex for 15 s, placed it at room temperature for 10 min.<br> |
| − | (2) | + | (2) Adjust the density of the bacteria solution by gradient dilution, then spread 100 μL of the bacteria solution on the LB plate.<br> |
| − | (3) If the density above | + | (3) If the density above is not suitable, take 100μL of the solution and spread it on the LB plate after several gradient dilutions.<br> |
| − | (4) | + | (4) Culture the bacteria overnight at 37℃.<br> |
| − | 【Day 5】Cell Count | + | 【Day 5】Cell Count<br> |
| − | (1) Take out the LB plate and take photos to record | + | (1) Take out the LB plate and take photos to record experimental results.<br> |
| − | (2) Use the automatic cell counting function of Image J to count the | + | (2) Use the automatic cell counting function of Image J to count the clone number on the LB plate, then compare the results between each group. |
</p> | </p> | ||
<h4><b>Results:</b></h4> | <h4><b>Results:</b></h4> | ||
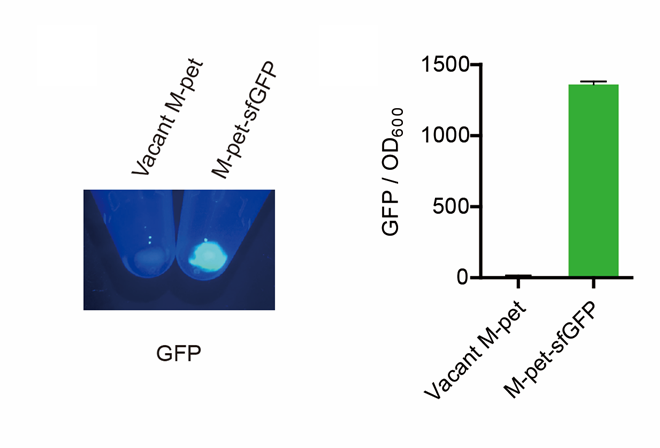
| − | <p style="clear:left;">First, | + | <p style="clear:left;"> First, through a reporter, we confirmed that the plasmid sfGFP can normally express exogenous proteins in the <i>E. coli</i> BL21 strain. Via SDS-PAGE, we observed the band of CAHS 89226 and further verified the successful expression.(Fig.5) </p> |
| − | [[File:T--QHFZ-China-- | + | [[File:T--QHFZ-China--pet28am sfGFP.png|400px|thumb|left|Figure 4. Via a reporter, sfGFP, the expression function of the modified pet28a vector was verified.]] |
| − | [[File:T--QHFZ-China-- | + | [[File:T--QHFZ-China--TDP SDS.png|400px|thumb|left|Figure 5. CAHS 89226 was expressed as expected.]] |
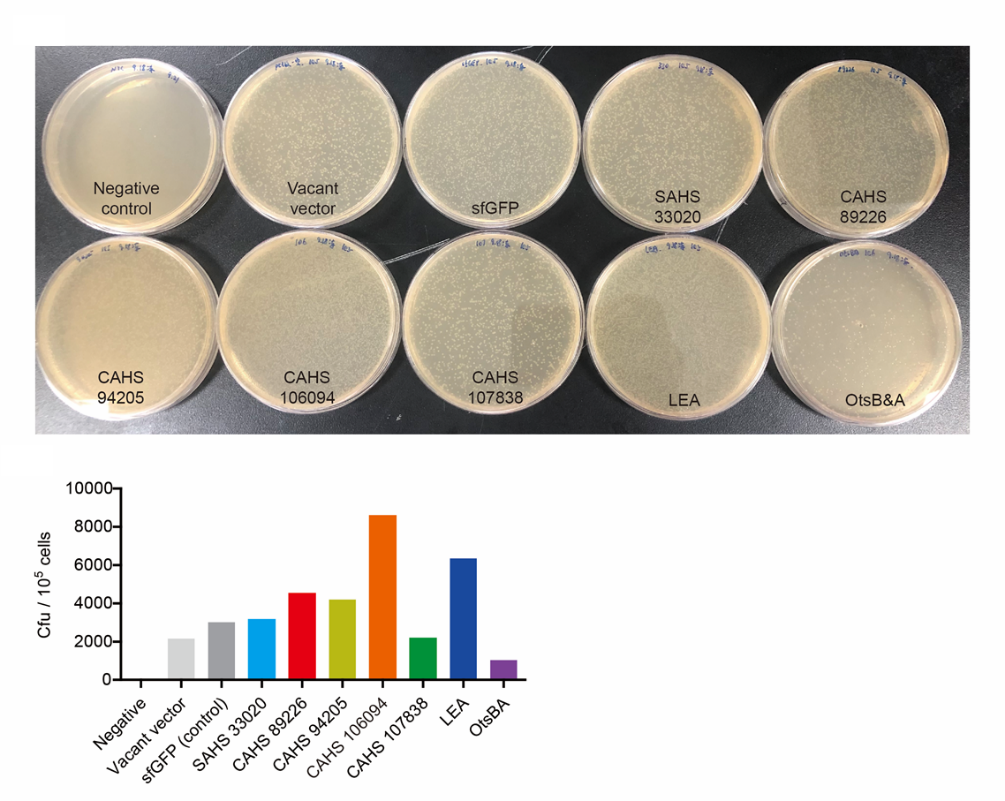
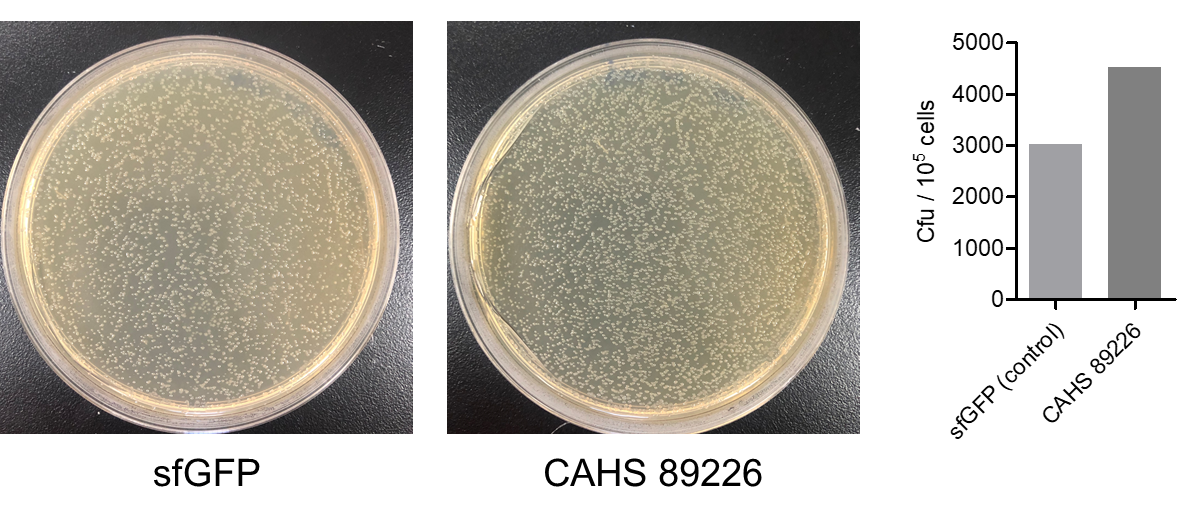
| − | <p style="clear:left;">Then, by freeze-drying and recover experiment, we found that compared with the control group (sfGFP), the bacteria expressing CAHS 89226 had a better survival rate (Fig. 6). We placed an enlarged picture as well (Fig. 7). </p> | + | <p style="clear:left;"> Then, by freeze-drying and recover experiment, we found that compared with the control group (sfGFP), the bacteria expressing CAHS 89226 had a better survival rate (Fig. 6). We placed an enlarged picture as well (Fig. 7). </p> |
| − | [[File:T--QHFZ-China-- | + | [[File:T--QHFZ-China--TDP freeze-dry.png|400px|thumb|left|Figure 6. CAHS 89226 protected bacteria during freeze-drying and subsequent dry storage.]] |
| − | [[File:T--QHFZ-China-- | + | [[File:T--QHFZ-China--89226.png|400px|thumb|left|Figure 7. An enlarged picture of fig. 6.]] |
<h4 style="clear:left;"><b>Summary: </b></h4> | <h4 style="clear:left;"><b>Summary: </b></h4> | ||
| − | <p style="clear:left;">CAHS 89226 helps the bacteria survive freeze-drying and subsequent dry storage. To achieve that, you need only to transform the sequence into your bacteria. You can | + | <p style="clear:left;"> CAHS 89226 helps the bacteria survive freeze-drying and subsequent dry storage. To achieve that, you need only to transform the sequence into your bacteria. You can also use the part to express and purify CAHS 89226 through Ni-chelating affinity chromatography. The purified CAHS 89226 can be used to protect protein products. </p> |
<h4><b>Reference: </b></h4> | <h4><b>Reference: </b></h4> | ||
Latest revision as of 17:50, 27 October 2020
CAHS 89226 with a 6X His tag
This biological part is the CDS sequence of Cytosolic-abundant heat soluble protein 89226, also called CAHS 89226. It is a kind of Tardigrade intrinsically Disordered Protein (TDP). It is a heat soluble protein found from Tardigrade Hypsibius dujardini in 2017 [1]. Tardigrade, also called water bear, is a kind of tenacious organism. It can survive extreme environment, such as desiccation, freeze and vacuum. The super capacity of Tardigrade partially owes to TDPs. CAHS 89226 has been proven to protect the activity of purified proteins [1]. Here we found that expressing this protein can help bacteria survive the freeze-drying process and then the resultant dry bacteria powder can be stored for a long time at room temperature.
Contribution
Group: QHFZ-China iGEM 2020
Author: Yixian Yang
Design
This biological part is the CDS sequence of Cytosolic-abundant heat soluble protein 89226, also called CAHS 89226. It is a kind of Tardigrade intrinsically Disordered Protein (TDP). It is a heat soluble protein found from Tardigrade Hypsibius dujardini in 2017 [1]. Tardigrade, also called water bear, is a kind of tenacious organism. It can survive extreme environments, such as desiccation, freeze, and vacuum. The super capacity of Tardigrade partially owes to TDPs. CAHS 89226 has been proven to protect the activity of purified proteins [1]. Here we found that expressing this protein can help bacteria survive the freeze-drying process, and then the resultant dry bacteria powder can be stored for a long time at room temperature. This part is the CDS of CAHS 89226. We obtained the sequence from the research paper in 2017 [1]. With the help of a company, we optimized the sequence so that the part is suitable to work in E. coli, and there is no biobrick restriction enzyme cutting site in it. Moreover, we added a 6x His tag at the N-terminal of CAHS 89226, so it can be easily detected by Western Blot and be purified by Ni-chelating affinity chromatography (Fig.1). This year, the part is used in the composite part BBa_K3457032
Documentation:
Introduction:
This year, we tried to introduce a new bio preservation method. We used freeze-drying to make the engineered into dry powder. Then the powder can be stored at room temperature for a long time. This method can store bacteria get rid of ultra-low temperature freezer to promote the practical application of engineered bacteria out of the laboratory. However, the stresses during freeze-drying and subsequent dry storage, including freeze, dry, and vacuum, are lethal to bacteria. We use TDPs, including CAHS 89226, to help bacteria survive the situation.
Protocol:
To test the effect of CAHS 89226, we modified a frequently and widely used vector, pet28a+, and put this part into it (Fig. 2). Then we transformed the plasmid into E. coli BL21 strain.
Then we used the following protocols to verify its function (Fig. 3):
【Day 1】Induction culture
(1) Pick clones which are in good condition and put them into 500 μL LB medium containing antibiotics. Shake them to grow at 37℃ for 5~7 hours until the bacteria solution becomes turbid.
(2) Add 2 mM iPTG into 3 mL LB medium containing antibiotics. Add 3 μL of the bacteria solution mentioned in step 1 to dilute the bacteria by the ratio of 1:1000. Shake the solution to grow the bacteria at 37℃ overnight.
【Day 2】Freeze-dried
(1) If fluorescence induced by the iPTG is detectable in the control group (GFP), continue conducting the experiment.
(2) Use spectrophotometer to measure the OD600 of the bacteria solution, OD600 = 1 equals to 109 cells. If the OD600 value is between 0.1 and 1, There is a linear relationship between OD600 and bacterial density. Calculate the volume of bacterial solution for 109 cells by using the formula V = 100 / (OD600 × Dilution ratio).
(3) Take out a measured amount of 109 cells and centrifuge it at 8000 rpm for 3 min. Then pour out the supernatant.
(4) Re-suspend the bacteria in a 15 mL tube with pre-refrigerated 100 μL 3% glucose solution.
(5) Take off the cover of the tube and put the bacteria into the cold trap. Open the compressor of the lyophilization machine and freeze the shake tube for 2 h at -70℃.
(6) Put the caky bacteria solution into the drying chamber of the lyophilization machine. Open the vacuum pump to dry it in vacuum for 6h at 1 Pa vacuum degree.
(7) Turn off the vacuum pump, place it at seal box filled with silica-gel desiccant a for 2 days at room temperature.
【Day 3】Room temperature storage
【Day 4】Detect the survival rate
(1) Add 1 mL of sterile water to the tube, vortex for 15 s, placed it at room temperature for 10 min.
(2) Adjust the density of the bacteria solution by gradient dilution, then spread 100 μL of the bacteria solution on the LB plate.
(3) If the density above is not suitable, take 100μL of the solution and spread it on the LB plate after several gradient dilutions.
(4) Culture the bacteria overnight at 37℃.
【Day 5】Cell Count
(1) Take out the LB plate and take photos to record experimental results.
(2) Use the automatic cell counting function of Image J to count the clone number on the LB plate, then compare the results between each group.
Results:
First, through a reporter, we confirmed that the plasmid sfGFP can normally express exogenous proteins in the E. coli BL21 strain. Via SDS-PAGE, we observed the band of CAHS 89226 and further verified the successful expression.(Fig.5)
Then, by freeze-drying and recover experiment, we found that compared with the control group (sfGFP), the bacteria expressing CAHS 89226 had a better survival rate (Fig. 6). We placed an enlarged picture as well (Fig. 7).
Summary:
CAHS 89226 helps the bacteria survive freeze-drying and subsequent dry storage. To achieve that, you need only to transform the sequence into your bacteria. You can also use the part to express and purify CAHS 89226 through Ni-chelating affinity chromatography. The purified CAHS 89226 can be used to protect protein products.
Reference:
[1] Boothby, T.C., Tapia, H., Brozena, A.H., Piszkiewicz, S., Smith, A.E., Giovannini, I., Rebecchi, L., Pielak, G.J., Koshland, D., and Goldstein, B. (2017). Tardigrades Use Intrinsically Disordered Proteins to Survive Desiccation. Mol Cell 65, 975-984 e975.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]